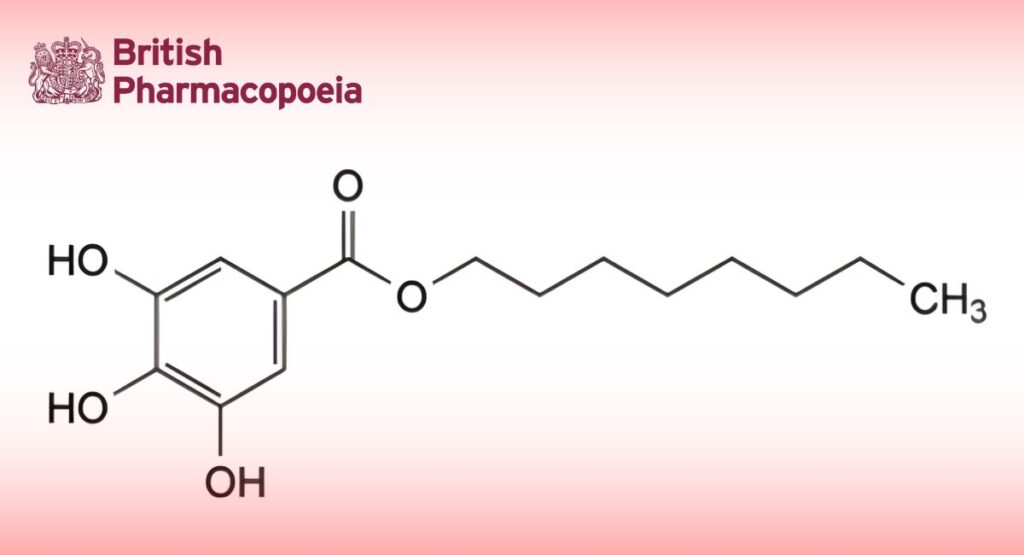
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2057)
C15H22O5 282.3 1034-01-1
Action and use
Used in treatment of alcohol dependence.
DEFINITION
Octyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate.
Content
97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Melting point (2.2.14).
Determine the melting point of the substance to be examined. Mix equal parts of the substance to be examined and octyl gallate CRS and determine the melting point of the mixture. The difference between the
melting points (which are about 101 °C) is not greater than 2 °C.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for impurity A.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.20 g of the substance to be examined in acetone R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 20 mL with acetone R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of octyl gallate CRS in acetone R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20 mg of gallic acid R in acetone R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) to 10 mL with acetone R.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) to 5 mL with test solution (a).
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous formic acid R, ethyl formate R, toluene R (10:40:50 V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL of test solutions (a) and (b) and reference solutions (a), (c) and (d).
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In air for 10 min.
Detection: Spray with a mixture of 1 volume of ferric chloride solution R1 and 9 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R.
System suitability: Reference solution (d):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated principal spots.
Limit: Test solution (a):
— impurity A: any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.5 per cent).
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 100 ppm.
To 1.65 g add 50 mL of water R. Shake for 5 min. Filter. 15 mL of the filtrate complies with the test.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 70 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.100 g in methanol R and dilute to 250.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 200.0 mL with methanol R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 275 nm.
Calculate the content of C15H22O5 taking the specific absorbance to be 387.
STORAGE
In a non-metallic container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
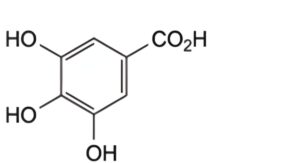
A. 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (gallic acid).