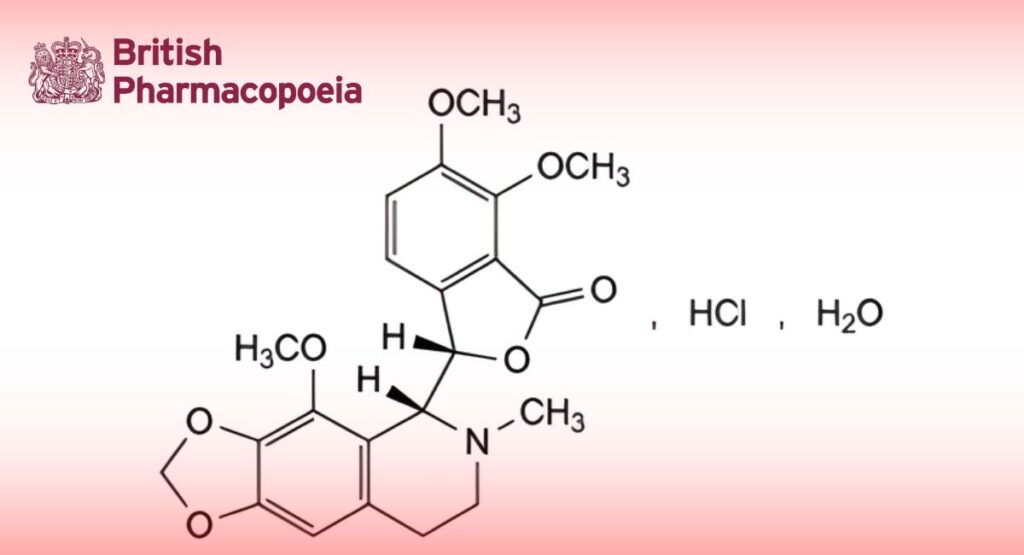
Noscapine Hydrochloride
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0515)
C22H24ClNO7,H2O 467.9
Action and use
Opioid receptor agonist; cough suppressant.
DEFINITION
(3S)-6,7-Dimethoxy-3-[(5R)-4-methoxy-6-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolin-5-yl]-2-benzofuran-1(3H)-one hydrochloride hydrate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent). Aqueous solutions are slightly acid; the base may be precipitated when the solutions are allowed to stand.
mp
About 200 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: C, E.
Second identification: A, B, D, E.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Melting point (2.2.14) of the precipitate obtained in identification test E: 174 °C to 177 °C.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Examine the precipitate obtained in identification test E.
Comparison: noscapine CRS.
D. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 22 mg of noscapine CRS in acetone R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, ethanol (96 per cent) R, acetone R, toluene R (1:3:20:20 V/V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with dilute potassium iodobismuthate solution R.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
E. Dissolve about 40 mg in a mixture of 2 mL of water R and 3 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R and add 1 mL of dilute ammonia R2. Heat until dissolution is complete. Allow to cool, scratching the wall of the tube with a glass rod. Filter. The filtrate gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1). Wash the precipitate with water R, dry at 100-105 °C and reserve for identification tests B and C.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 or BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.5 g in water R, add 0.3 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25 mL with water R.
pH (2.2.3)
Minimum 3.0.
Dissolve 0.2 g in 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 38.5 to + 44.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.500 g in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R, with the aid of ultrasound, and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5.0 mg of papaverine hydrochloride CRS (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase (solution A). Dilute 1.0 mL of solution A to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 6.0 mL of solution A to 10.0 mL with the test solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: cyanosilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: methanol R, phosphate buffer solution pH 6.0 R1 (35:65 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of noscapine.
Relative retention: With reference to noscapine (retention time = about 10 min): impurity A = about 1.3.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 2 between the peaks due to noscapine and impurity A.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
2.5 per cent to 6.5 per cent, determined on 0.200 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
In order to avoid over heating in the reaction medium, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.400 g in a mixture of 3 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and 30 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 44.99 mg of C22H24ClNO7.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
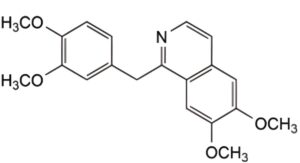
A. 1-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-6,7-dimethoxyisoquinoline (papaverine).