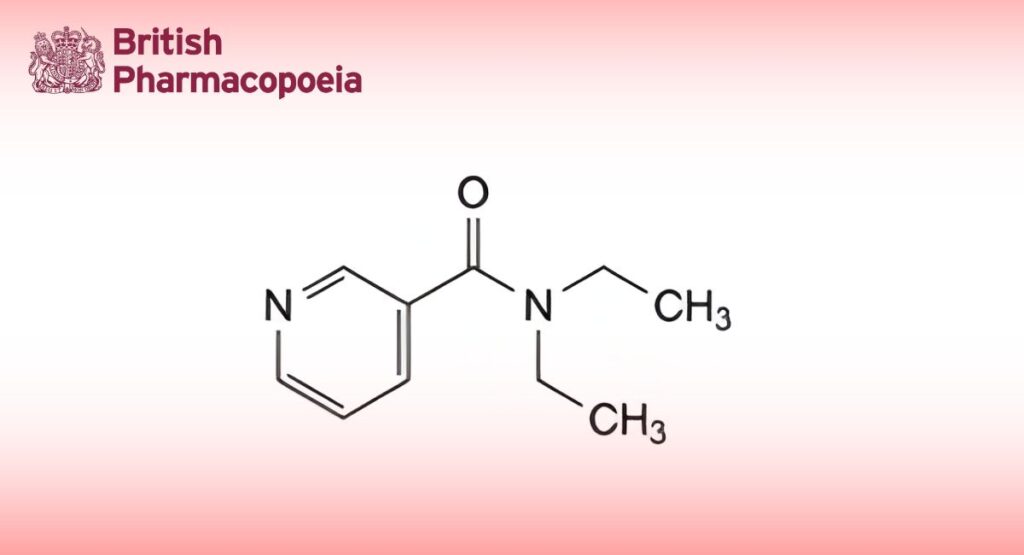
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0233)
C10H14N2O 178.2 59-26-7
Action and use
Central nervous system stimulant.
DEFINITION
Nikethamide contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of N,N- diethylpyridine-3-carboxamide, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
CHARACTERS
An oily liquid or a crystalline mass, colourless or slightly yellowish, miscible with water and with ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Dissolve 0.15 g in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same acid. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Examined between 230 nm and 350 nm (2.2.25) in a 2 cm cell, the solution shows a single absorption maximum, at 263 nm. The specific absorbance at the maximum is about 285.
B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with nikethamide CRS.
C. Heat 0.1 g with 1 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. Diethylamine is evolved progressively and is recognisable by its characteristic odour and by its turning red litmus paper R blue.
D. Dilute 1 mL of solution S (see Tests) to 250 mL with water R. To 2 mL of this solution add 2 mL of cyanogen bromide solution R. Add 3 mL of a 25 g/L solution of aniline R and shake. A yellow colour develops.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance
The substance to be examined, in liquid form or liquefied by slight heating, is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y5 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
The pH of solution S is 6.0 to 7.8.
Refractive index (2.2.6)
1.524 to 1.526.
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using silica gel GF254 R as the coating substance.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.4 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 40 mg of ethylnicotinamide CRS in methanol R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of reference solution (a) to 10 mL with methanol R.
Apply separately to the plate 10 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 25 volumes of propanol R and 75 volumes of chloroform R. Allow the plate to dry in air and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. In the chromatogram obtained with the test solution, any spot corresponding to ethylnicotinamide is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent) and any spot, apart from the principal spot and the spot corresponding to ethylnicotinamide, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
Not more than 0.3 per cent, determined on 2.00 g by the semi-micro determination of water.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in a mixture of 5 mL of acetic anhydride R and 20 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 17.82 mg of C10H14N2O.