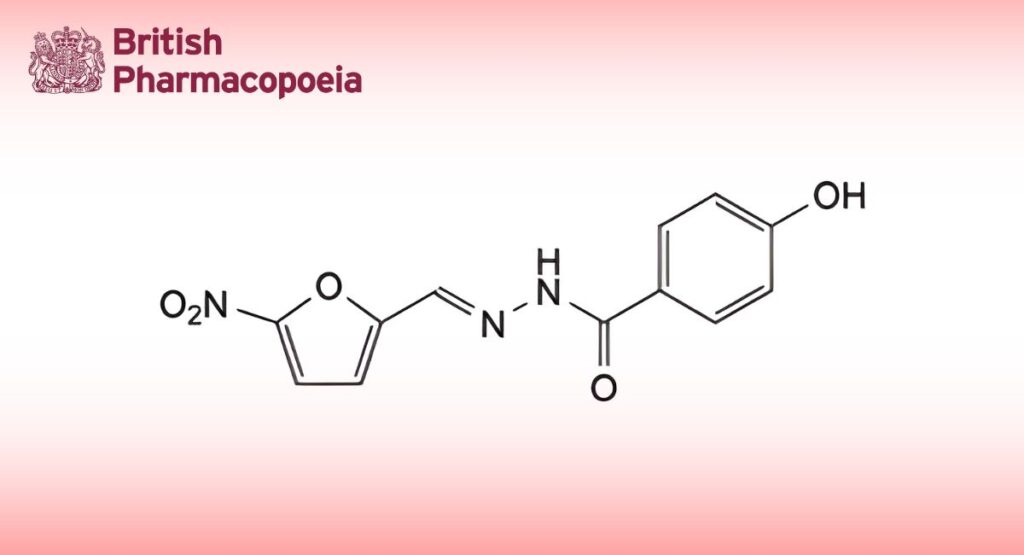
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1999)
C12H9N3O5 275.2 965-52-6
Action and use
Antibacterial.
DEFINITION
(E)-4-Hydroxy-N′-[(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]benzohydrazide.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Bright yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: nifuroxazide CRS.
TESTS
Specific absorbance (2.2.25)
940 to 1000 at the absorption maximum at 367 nm.
Protected from light, dissolve 10.0 mg in 10 mL of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether R and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with methanol R.
Impurity A
Maximum 0.05 per cent.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 1.0 g of the substance to be examined in dimethyl sulfoxide R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): To 5.5 mL of test solution (a) add 50.0 mL of water R while stirring. Allow to stand for 15 min and filter.
Reference solution: To 0.5 mL of test solution (a) add 5.0 mL of a 50 mg/L solution of 4- hydroxybenzohydrazide R (impurity A) in dimethyl sulfoxide R. Add 50.0 mL of water R while stirring. Allow to stand for 15 min and filter.
Add 0.5 mL of phosphomolybdotungstic reagent R and 10.0 mL of sodium carbonate solution R separately to 10.0 mL of test solution (b) and to 10.0 mL of the reference solution. Allow to stand for 1 h. Examine the 2 solutions at 750 nm. The absorbance (2.2.25) of the solution obtained with test solution (b) is not greater
than that obtained with the reference solution.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use amber volumetric flasks, unless otherwise specified.ư
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, water R (40:60 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture, using sonication for not more than 5 min, and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): In order to prepare impurity E in situ, dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture in a colourless volumetric flask, using sonication for 5 min, and dilute to 50 mL with the solvent mixture. Allow to stand in ambient light for 1 h.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5.0 mg of methyl parahydroxybenzoate CRS (impurity B) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.\
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: spherical octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 10 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: tetrahydrofuran R, water R (5:95 V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 10 | 67 | 33 |
| 10 – 30 | 67 → 43 | 33 → 57 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection: 50 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to nifuroxazide (retention time = about 8 min): impurity A (keto-enol tautomers) = about 0.36 and 0.39; impurity E = about 0.9; impurity B = about 1.2; impurity C = about 2.6; impurity D = about 3.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity E and nifuroxazide.
Limits:
— impurity E: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
— impurities B, C, D: for each impurity, not more than 0.6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.3 per cent), and not more than 1 such peak has an area greater than 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than E: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.05 per cent); disregard the peaks due to impurity A.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g, with heating if necessary, in 30 mL of dimethylformamide R and add 20 mL of water R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 27.52 mg of C12H9N3O5.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
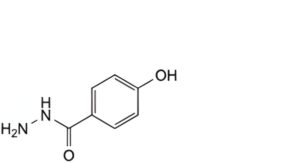
A. 4-hydroxybenzohydrazide (p-hydroxybenzohydrazide),
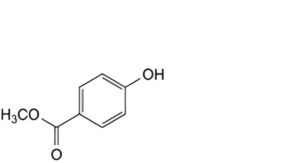
B. methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate (methyl parahydroxybenzoate),
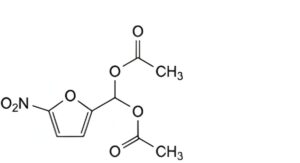
C. (5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene diacetate,
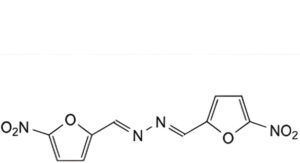
D. (E,E)-N,N′-bis[(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]hydrazine (5-nitrofurfural azine),
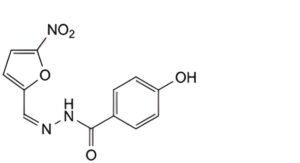
E. (Z)-4-hydroxy-N′-[(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]benzohydrazide.