Action and use
Central nervous system stimulant; nicotine replacement therapy.
DEFINITION
Nicotine Resinate Medicated Chewing Gum contains Nicotine Resinate in a suitable gum basis.
The medicated chewing gum complies with the requirements stated under Medicated Chewing Gums and with the following requirements.
Content of nicotine C10H14N2
90.0 to 113.5% of the stated amount.
Carry out all of the following procedures protected from light.
IDENTIFICATION
Cut a quantity of gum containing the equivalent of 20 mg of nicotine into small pieces, place in a centrifuge tube and add 10 mL of chloroform. Place in an ultrasonic bath for 30 minutes and centrifuge for 10 minutes. Cool the mixture to 15°, add two 3-mL quantities of 0.5M hydrochloric acid and mix. Centrifuge the mixture for 10 minutes. Transfer 5 mL of the aqueous layer to a separating funnel and add sufficient 0.5M sodium hydroxide to obtain a pH of 10.5, add 3 mL of chloroform, shake and retain the chloroform layer. The infrared absorption spectrum of the solution, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of nicotine (RS 452).
TEST
Dissolution
Carry out the test for drug release from medicated chewing gum, Appendix XII B4, using the following conditions.
(1) Use a dissolution medium volume of 20.0 mL prepared from equal volumes of phosphate buffer solution, pH 7.4 and 0.2% w/v sodium dodecyl sulfate at a temperature of 37°, as the medium.
(2) Use a chewing frequency of 60 cycles per minute.
(3) Take samples at 30 minutes.
Insert a whole gum into the chewing chamber and start the chewing process. At the appropriate sampling time withdraw 3 mL of the dissolution medium through a 5-mL syringe. Filter through a 0.4-μm PTFE filter, discard the first 2 mL and use the remaining 1 mL for analysis.
PROCEDURE
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Use the filtered solution from the chewing chamber.
(2) Dissolve a quantity of nicotine ditartrate dihydrate BPCRS in the dissolution medium to produce a solution equivalent to the concentration of the final solution expected for solution (1).
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (5 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped polar-embedded octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer (3.5 μm) (Waters XBridge is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution using the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 35°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 260 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
150 volumes of acetonitrile, 425 volumes of 1M ammonium hydroxide and 425 volumes of 0.1M ammonium phosphate.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the total content of nicotine, C10H14N2, in the medium using the declared content of C10H14N2 in nicotine ditartrate dihydrate BPCRS.
LIMITS
The amount of nicotine, C10H14N2, released is not less than 70% (Q) of the stated amount.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in 0.2M potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate adjusted to pH 2.0 with orthophosphoric acid (solvent A).
(1) Transfer a quantity of gum containing the equivalent of 20 mg of nicotine into a separating funnel, add 50 mL of solvent A, 100 mL of hexane and shake for at least 45 minutes or until all of the gum has dissolved. Remove the lower aqueous layer and filter through a 0.4-μm PTFE filter.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 100 volumes.
(3) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 10 volumes.
(4) 0.04% w/v of nicotine impurity standard BPCRS.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped polar-embedded octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer column (3.5 μm) (Waters XBridge is suitable) fitted with a guard column (3 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with the same material.
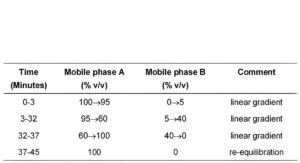
(b) Use gradient elution using the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A: Add 25 volumes of 1M acetic acid to 1000 volumes with water, add 6.2 volumes of 18M ammonia and adjust the pH to 10 with 18M ammonia.
Mobile phase B: acetonitrile.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (4):
identify the peaks due to cotinine, myosmine, cis-nicotine-1′-oxide and trans-nicotine-1′-oxide.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
identify any peak in the chromatogram corresponding to cis-nicotine-1′-oxide and multiply the area of this peak by a correction factor of 1.5;
identify any peak in the chromatogram corresponding to trans-nicotine-1′-oxide and multiply the area of this peak by a correction factor of 1.5.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4), the resolution between trans-nicotine-1′-oxide and cotinine is at least 2.0.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to cotinine is not greater than 0.6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.6%);
the area of any peak corresponding to myosmine is not greater than 0.6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.6%);
the area of any peak corresponding to cis-nicotine-1′-oxide is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (3.0%);
the area of any peak corresponding to trans-nicotine-1′-oxide is not greater than 4.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (4.5%);
the sum of the areas of any other secondary peaks is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%);
the sum of the areas of all secondary peaks is not greater than 7.7 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (7.7%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.1%).
ASSAY
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in 0.2M potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate the pH of which is adjusted to 2.0 with orthophosphoric acid (solvent A).
(1) Transfer a quantity of gum containing the equivalent of 20 mg of nicotine into a 500 mL separating flask, add 50 mL of solvent A and 100 mL of hexane and shake for at least 45 minutes or until all of the gum has dissolved. Remove the lower aqueous layer and filter through a 0.4-μm filter. Dilute 1 volume of the resulting solution to 10 volumes.
(2) 0.0124% w/v of nicotine ditartrate dihydrate BPCRS.
(3) 0.04% w/v of nicotine impurity standard BPCRS.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
The chromatographic conditions described under Related substances may be used.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between trans-nicotine-1′-oxide and cotinine at least 2.0.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the total content of nicotine, C10H14N2, in the gum using the declared content of C10H14N2 in nicotine ditartrate dihydrate BPCRS.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed under Nicotine Resinate.






