(Ph. Eur. monograph 1792)
96055-45-7
Action and use
Aid to smoking cessation.
Preparation
Nicotine Resinate Medicated Chewing Gum
DEFINITION
Complex of nicotine (3-[(2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]pyridine) with a weak cationic exchange resin.
Content
95.0 per cent to 115.0 per cent of the declared content of nicotine (C10H14N2) stated on the label (dried substance).
It may contain glycerol.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or slightly yellowish powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Shake a quantity of the substance to be examined equivalent to 100 mg of nicotine with a mixture of 10 mL of dilute ammonia R2, 10 mL of water R, 5 mL of strong sodium hydroxide solution R and 20 mL of hexane R for 5 min. Transfer the upper layer to a beaker and evaporate to produce an oily residue.
Record the spectrum of the oily residue as a thin film between sodium chloride R plates.
Comparison: Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of nicotine.
B. Nicotine release (see Tests).
TESTS
Nicotine release
Minimum 70 per cent of the content determined under Assay in 10 min.
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of the substance to be examined, equivalent to about 4 mg of nicotine, to a glass-stoppered test-tube, add 10.0 mL of a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R previously heated to 37 °C and shake vigorously for 10 min. Immediately filter the liquid through a dry filter paper discarding the 1st millilitre of filtrate. Transfer 1.0 mL of the filtrate to a 20 mL volumetric flask, dilute to 20 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and mix. Determine the absorbance (2.2.25) at the minima at about 236 nm and 282 nm and at the maximum at 259 nm using 1.0 mL of a 9 g/L solution of sodium chloride R diluted to
20 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid as compensation liquid.
Calculate the percentage of nicotine release using the following expression:

323 = specific absorbance of nicotine at 259 nm;
C = percentage of nicotine in the substance to be examined determined in the assay;
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in milligrams;
A236, A259, A282 = absorbances of the solution at the wavelength indicated by the subscript.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Weigh a quantity of the substance to be examined, equivalent to 30.0 mg of nicotine, into a glass-stoppered test-tube, add 10.0 mL of dilute ammonia R2 and shake vigorously for 10 min. Centrifuge for 20 min at about 3000 r/min. To 5.0 mL of the clear solution, add 5 mL of a 60 g/L solution of acetic acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of nicotine for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, D, E, F and G) in 1.0 mL of water R.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 10.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 46.0 mg of nicotine ditartrate CRS in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped polar-embedded octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: to 900 mL of water R, add 25 mL of a 60 g/L solution of acetic acid R, then add 6 mL of concentrated ammonia R1; adjust to pH 10.0 with dilute ammonia R2 or dilute acetic acid R and dilute to 1 L with water R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 3 | 100 | 0 |
| 3 – 3.01 | 100 → 95 | 0 → 5 |
| 3.01 – 28 | 95 → 74 | 5 → 26 |
| 28 – 32 | 74 → 60 | 26 → 40 |
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with nicotine for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D, E, F and G.
Relative retention: With reference to nicotine (retention time = about 18 min): impurity E = about 0.3; impurity C = about 0.55; impurity F = about 0.7; impurity A = about 0.8; impurity D = about 0.86; impurity G = about 0.9; impurity B = about 1.6.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurity G and nicotine.
Limits:
— impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G: for each impurity, not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 8 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.8 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 7.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of nicotine (C10H14N2) taking into account the assigned content of C10H14N2 in nicotine ditartrate CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
LABELLING
The label states the content of nicotine.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G.
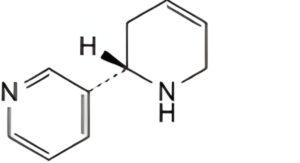
A. (2S)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,3′-bipyridine (anatabine),
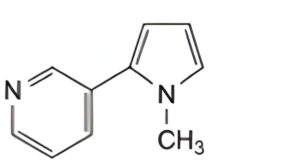
B. 3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)pyridine (β-nicotyrine),
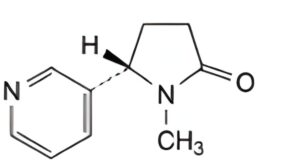
C. (5S)-1-methyl-5-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidin-2-one (cotinine),






