Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Aminoglycoside antibacterial. Ph Eur
DEFINITION
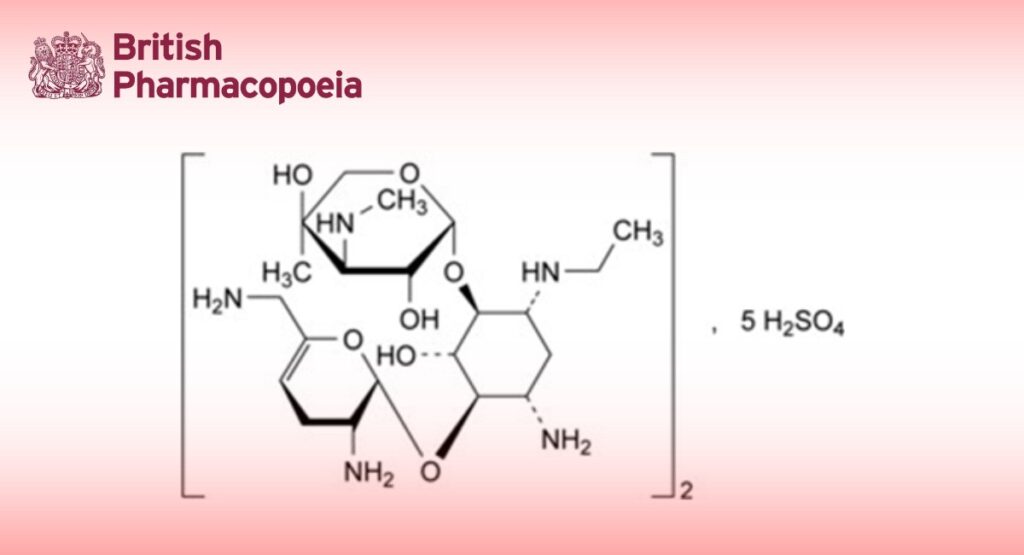
Bis[2-deoxy-6-O-[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-β-L-arabinopyranosyl]-4-O-(2,6-diamino-2,3,4,6- tetradeoxy-α-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl)-1-N-ethyl-D-streptamine] pentasulfate.
Substance obtained by synthesis from sisomicin.
Semi-synthetic product derived from a fermentation product.
Content
95.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white, very hygroscopic powder.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. It gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.80 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and its absorbance (2.2.25) at 400 nm is not greater than 0.08.
pH (2.2.3)
3.5 to 5.5 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Perform weighing steps as quickly as possible and immediately after opening the sample container.
Test solution Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve the contents of a vial of netilmicin sulfate for LC assay CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 25.0 mg of sisomicin sulfate CRS (impurity A) in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 25.0 mg of 1-N-ethylgaramine sulfate CRS (impurity B) in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d) Dilute 0.6 mL of reference solution (a), 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) and 1.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (e) Dissolve 5.0 mg of netilmicin for peak identification CRS (containing impurities E and F) in the mobile phase and dilute to 2.5 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase Solution in carbon dioxide-free water R containing 0.3 g/L of sodium octanesulfonate R, 20 g/L of anhydrous sodium sulfate R1, 20 mL/L of tetrahydrofuran R and 50 mL/L of 0.2 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R, adjusted to pH 3.0 with a 22.5 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R; degas.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Post-column solution Mixture of 1 volume of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution R and 24 volumes of previously degassed carbon dioxide-free water R, which is added pulse-free to the column effluent using a 375 µL polymeric mixing coil.
Flow rate of post-column solution 0.3 mL/min.
Detection Pulsed amperometric detector or equivalent with a gold indicator electrode, a silver-silver chloride reference electrode and a stainless steel auxiliary electrode which is the cell body, held at respectively + 0.05 V detection, + 0.75 V oxidation and – 0.15 V reduction potentials, with pulse durations according to the instrument used.
Injection 20 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (d) and (e).
Run time 3 times the retention time of netilmicin.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and B; use the chromatogram supplied with netilmicin for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e) to identify the peaks due to impurities E and F.
Relative retention With reference to netilmicin (retention time = about 16 min): impurity B = about 0.4; impurity A = about 0.7; impurity E = about 1.9; impurity F = about 2.1.
System suitability Reference solution (d):
— resolution: minimum 10.0 between the peaks due to impurities B and A; minimum 6.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and netilmicin; if necessary, adjust the concentration of sodium octanesulfonate in the mobile phase.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurities A and B, use the concentration of each impurity in reference solution (d);
— for impurities other than A and B, use the concentration of netilmicin sulfate in reference solution (d).
Limits:
— impurities A, B, E, F: for each impurity, maximum 1.0 per cent;
— any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.3 per cent;
— total: maximum 3.0 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.1 per cent.
Sulfate
31.5 per cent to 35.0 per cent (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.12 g in 100 mL of water R and adjust the solution to pH 11 using concentrated ammonia R. Add 30.0 mL of 0.1 M barium chloride and about 0.5 mg of phthalein purple R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium edetate adding 50 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R when the colour of the solution begins to change and continue the titration until the violet-blue colour disappears.
1 mL of 0.1 M barium chloride is equivalent to 9.606 mg of SO4.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 15.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying at 110 °C under high vacuum for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 0.5 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Perform weighing steps as quickly as possible and immediately after opening the sample container.
Test solution Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution Dissolve the contents of a vial of netilmicin sulfate for LC assay CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase Solution in carbon dioxide-free water R containing 0.15 g/L of sodium octanesulfonate R, 20 g/L of anhydrous sodium sulfate R1, 20 mL/L of 2-methyl-2-propanol R and 50 mL/L of 0.2 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate R, adjusted to pH 3.0 with dilute phosphoric acid R; degas.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 205 nm.
Injection 10 µL.
Run time 1.3 times the retention time of netilmicin.
Retention time Netilmicin = about 4 min.
Calculate the percentage content of C42H92N10O34S5 taking into account the assigned content of netilmicin sulfate for LC assay CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light. If the substance is sterile, the container is also sterile and tamper-evident.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, E, F.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) C, D.
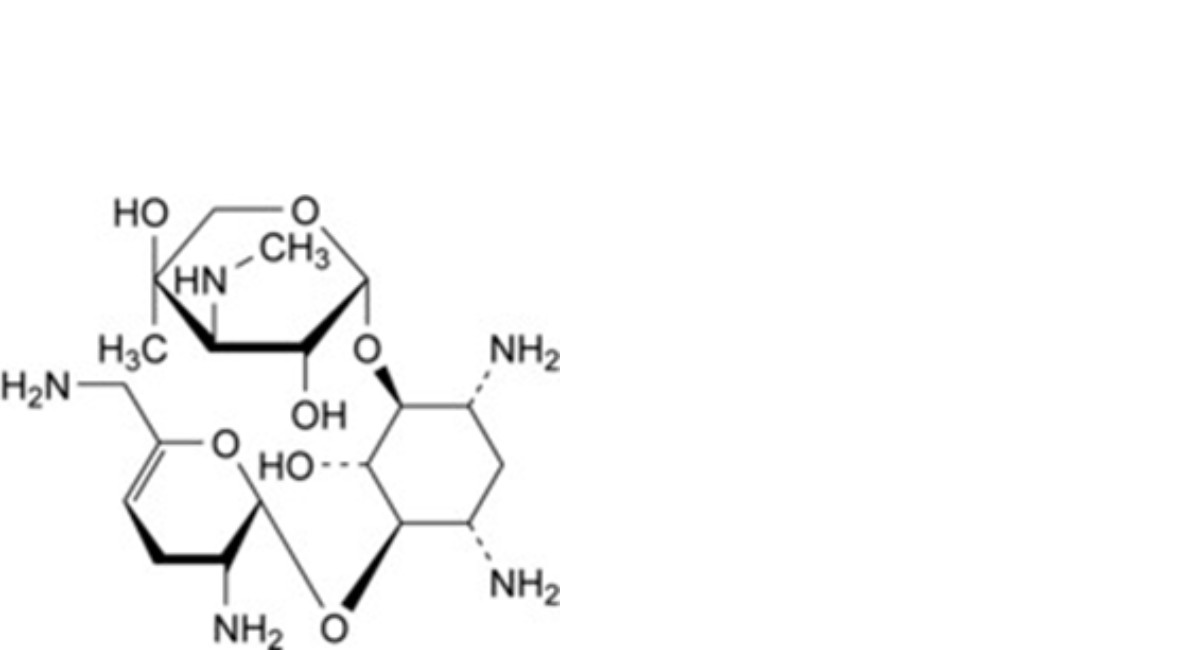
A. 2-deoxy-4-O-[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-β-L-arabinopyranosyl]-6-O-(2,6-diamino-2,3,4,6- tetradeoxy-α-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl)-L-streptamine (sisomicin),
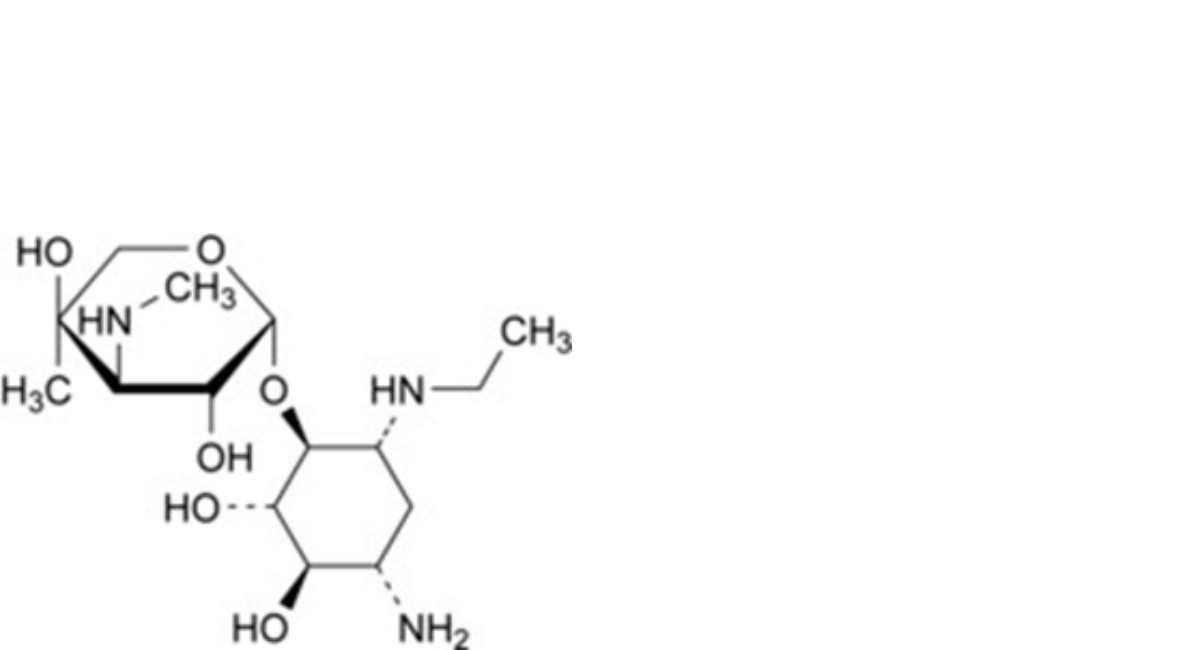
B. 2-deoxy-6-O-[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-β-L-arabinopyranosyl]-1-N-ethyl-D-streptamine (1-N- ethylgaramine),
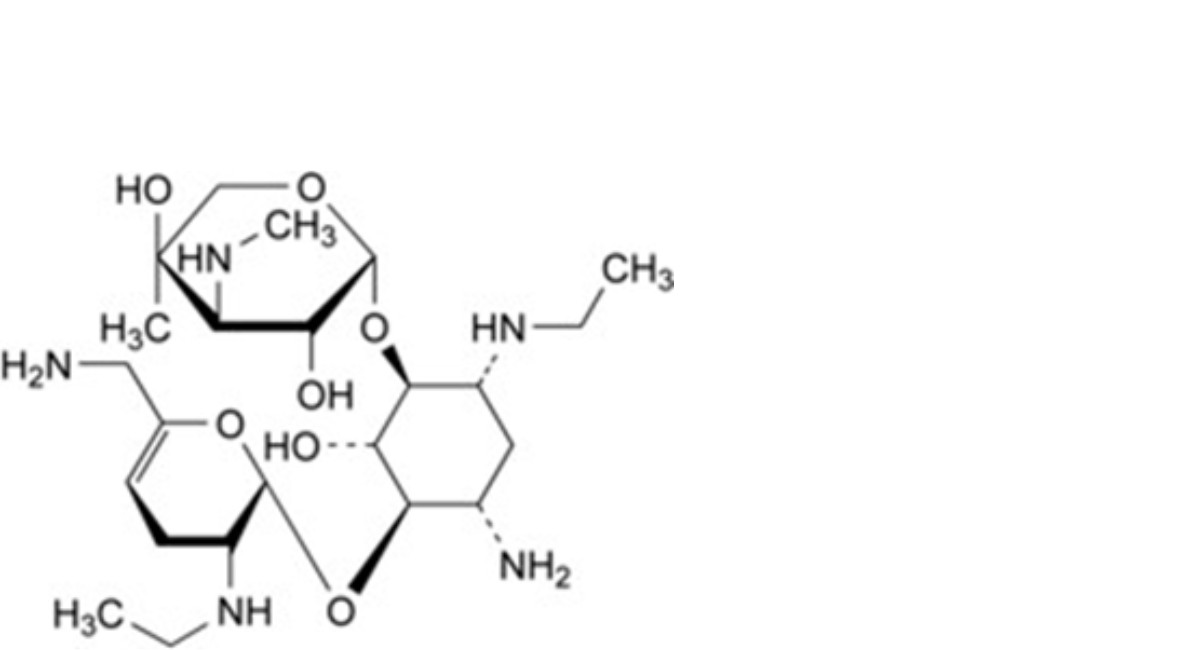
C. 4-O-[6-amino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-2-(ethylamino)-α-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl]-2-deoxy-6-O-[3- deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-β-L-arabinopyranosyl]-1-N-ethyl-D-streptamine (2′-N-ethylnetilmicin),
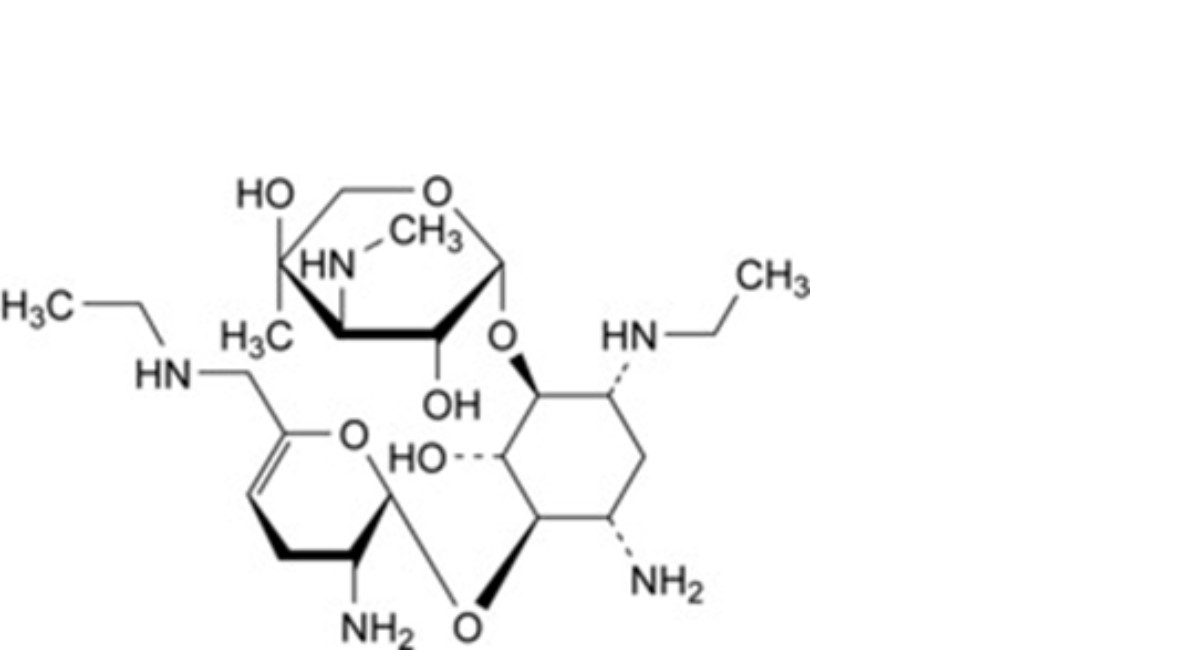
D. 4-O-[2-amino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-6-(ethylamino)-α-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl]-2-deoxy-6-O-[3- deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-β-L-arabinopyranosyl]-1-N-ethyl-D-streptamine (6′-N-ethylnetilmicin),
E. unknown structure,
F. unknown structure.
Ph Eur