Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Aminoglycoside antibacterial.
Preparations
Dexamethasone and Neomycin Ear Spray Hydrocortisone and Neomycin Cream Hydrocortisone Acetate and Neomycin Ear Drops Hydrocortisone Acetate and
Neomycin Eye Drops Hydrocortisone Acetate and Neomycin Eye Ointment Neomycin Eye Drops
Neomycin Eye Ointment Neomycin Tablets
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
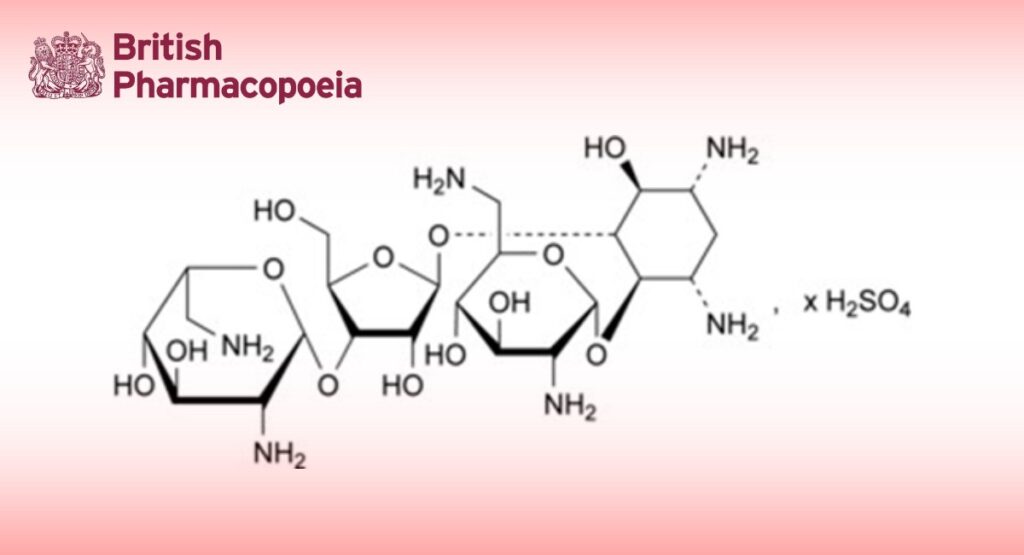
Mixture of sulfates of substances produced by the growth of certain selected strains of Streptomyces fradiae, the main component being the sulfate of 2-deoxy-4-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D- glucopyranosyl)-5-O-[3-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-β-L-idopyranosyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]-D-streptamine (neomycin B).
Content
Minimum of 680 IU/mg (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results:
— the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is approximately the same as that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e);
— it complies with the limits given for impurity C.
B. It gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 7.5.
Dissolve 0.1 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 53.5 to + 59.0 (dried substance).
Dissolve 1.00 g in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 25.0 mg of framycetin sulfate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve the contents of a vial of neamine CRS (corresponding to 0.5 mg) in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (e) Dissolve 10 mg of neomycin sulfate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 20.0 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R, 6.0 mL of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution R and 500 mL of water R, allow to equilibrate, dilute to 1000 mL with water R and degas.
Flow rate 0.7 mL/min.
Post-column solution carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution R diluted 1 in 25 previously degassed, which is added pulse-less to the column effluent using a 375 µL polymeric mixing coil.
Flow rate 0.5 mL/min.
Detection Pulsed amperometric detector with a gold indicator electrode, a silver-silver chloride reference electrode and a stainless steel auxiliary electrode which is the cell body, held at respectively 0.00 V detection, + 0.80 V oxidation and -0.60 V reduction potentials, with pulse durations according to the instrument used.
Injection 10 µL; inject the test solution and the reference solutions (b), (c), (d) and (e).
Run time 1.5 times the retention time of neomycin B.
Relative retention With reference to neomycin B (retention time = about 10 min): impurity A = about 0.65; impurity C = about 0.9; impurity G = about 1.1.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum of 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity C and to neomycin B in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e); if necessary, adjust the volume of the carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution in the mobile phase;
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 10 for the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (2.0 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (15.0 per cent) and not less than 0.6 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (3.0 per cent);
— any other impurity: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (5.0 per cent);
— total of other impurities: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (15.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (1.0 per cent).
Sulfate
27.0 per cent to 31.0 per cent (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in 100 mL of water R and adjust the solution to pH 11 using concentrated ammonia R. Add 10.0 mL of 0.1 M barium chloride and about 0.5 mg of phthalein purple R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium edetate adding 50 mL of alcohol R when the colour of the solution begins to change, continuing the titration until the violet-blue colour disappears.
1 mL of 0.1 M barium chloride is equivalent to 9.606 mg of SO4.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 8.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Carry out the microbiological assay of antibiotics (2.7.2). Use neomycin sulfate for microbiological assay CRS as the chemical reference substance.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
A. 2-deoxy-4-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-streptamine (neamine or neomycin A-LP),
B. 3-N-acetyl-2-deoxy-4-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-streptamine (3-acetylneamine),
C. 2-deoxy-4-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-5-O-[3-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-α-D- glucopyranosyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]-D-streptamine (neomycin C),
D. 4-O-(2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-D-streptamine (paromamine or neomycin D),
E. 4-O-(2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-2-deoxy-5-O-[3-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-β-L- idopyranosyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]-D-streptamine (paromomycin I or neomycin E),