Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
DEFINITION
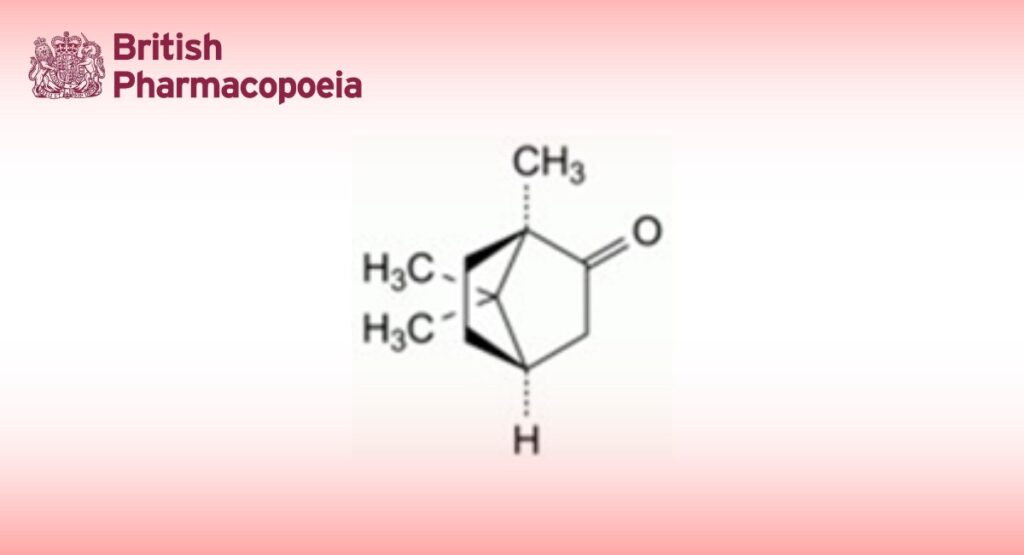
(1R,4R)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or friable, crystalline masses. Highly volatile even at room temperature.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, very soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in light petroleum, freely soluble in fatty oils, very slightly soluble in glycerol.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, C.
Second identification: A, B, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Melting point (2.2.14): 175 °C to 179 °C.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison racemic camphor CRS.
D. Dissolve 1.0 g in 30 mL of methanol R. Add 1.0 g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride R and 1.0 g of anhydrous sodium acetate R. Boil under a reflux condenser for 2h. Allow to cool and add 100 mL of water R. Filter, wash the precipitate obtained with 10 mL of water R and recrystallise from 10 mL of a mixture of 4 volumes of alcohol R and 6 volumes of water R. The crystals, dried in vacuo, melt (2.2.14) at 118 °C to 121 °C.
TESTS
Carry out the weighings and dissolution rapidly.
Solution S
Dissolve 2.50 g in 10 mL of alcohol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1. The solution is colourless. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 41.0 to + 44.0, determined on solution S.
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Test solution Dissolve 2.50 g of the substance to be examined in heptane R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with heptane R. Reference solution (b) Dilute 10.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with heptane R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 0.50 g of borneol R in heptane R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with heptane R.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 50 mg of linalol R and 50 mg of bornyl acetate R in heptane R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Column:
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.25 mm,
— stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 R (0.25 µm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R. Split ratio 1:70.
Flow rate 45 cm/s.
Temperature:
| Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | |
| Column | 0 – 10 | 50 |
| 10 – 35 | 50 → 100 | |
| 35 – 45 | 100 → 200 | |
| 45 – 55 | 200 | |
| Injection port | 220 | |
| Detector | 250 | |
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 µL.
System suitability Reference solution (d).
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to bornyl acetate and to linalol.
Limits:
— borneol: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (2.0 per cent),
— any other impurity: not more than half of the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent),
— total of other impurities: not more than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (4.0 per cent),
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Halogens
Maximum 100 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of 2-propanol R in a distillation flask. Add 1.5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and 50 mg of nickel-aluminium alloy R. Heat on a water-bath until the 2-propanol R has evaporated. Allow to cool and add 5 mL of water R. Mix and filter through a wet filter previously washed with water R until free from chlorides. Dilute the filtrate to 10.0 mL with water R. To 5.0 mL of the solution, add nitric acid R dropwise until the precipitate which forms is redissolved and dilute to 15 mL with water R. The solution complies with the limit test for chlorides (2.4.4).
Residue on evaporation (2.8.9) Maximum 0.05 per cent.
Evaporate 2.0 g on a water-bath and dry in an oven at 100-105 °C for 1 h. The residue weighs a maximum of 1 mg.
Water
Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of light petroleum R. The solution is clear (2.2.1).
IMPURITIES
A. 2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene (α-pinene),
B. 2,2-dimethyl-3-methylenebicyclo[2.2.1]heptane (camphene),
C. 6,6-dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane (β-pinene),
D. 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (cineole),
E. 1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one (fenchone),
F. exo-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol (fenchol),
G. exo-2,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol (camphene hydrate),