Mesalazine Rectal Foam
Action and use
Aminosalicylate; treatment of ulcerative colitis.
DEFINITION
Mesalazine Foam Enema is a rectal foam containing Mesalazine in a suitable vehicle.
The foam enema complies with the requirements stated under Rectal
Preparations and with the following requirements.
Content of mesalazine, C7H7NO3
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Filter a quantity of the foam enema containing 1.0 g of Mesalazine and discard the filtrate. Dry the residue at 110°. The infrared absorption spectrum of the residue, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of mesalazine (RS 454).
B. In the Assay, the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar to that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
TESTS
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions prepared immediately before use.
(1) Mix for 10 minutes with the aid of ultrasound, a quantity of the foam enema containing 1 g of Mesalazine in 600 mL of 0.01M hydrochloric acid, add sufficient 0.01M hydrochloric acid to produce 1 L, mix using a vortex mixer and filter through a 0.45-μm membrane filter.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 100 volumes with 0.01M hydrochloric acid. Dilute 1 volume of the resulting solution to 10 volumes with 0.01M hydrochloric acid.
(3) 0.1% w/v of mesalazine for system suitability EPCRS in 0.01M hydrochloric acid.
(4) 0.0001% w/v each of 4-aminosalicylic acid (impurity E), 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (impurity G), 2-chlorobenzoic acid (impurity L), 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (impurity M), 5-nitrosalicylic acid (impurity N), sulfanilic acid (impurity O), 3- nitrosalicylic acid (impurity R) and 0.0003% w/v of salicylic acid (impurity H) in 0.01M hydrochloric acid.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer (5 μm) (XTerra MS C18 is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 40°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 240 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A: A 0.69% w/v solution of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate monohydrate, adjusted to pH 6.2 with dilute sodium hydroxide.
Mobile phase B: 40 volumes of acetonitrile and 60 volumes of mobile phase A.
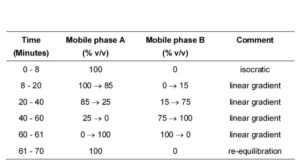
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the relative retentions with reference to mesalazine (retention time about 6 minutes) are: impurity O, about 0.55; impurity J, about 0.6; impurity E, about 0.8; impurity F, about 1.36; impurity G, about 1.4; impurity P, about 1.5; impurity L, about 2.0; impurity M, about 3.3; impurity H, about 3.5; impurity R, about 5.1 and impurity N, about 5.5.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the peak-to-valley ratio is at least 3.0, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity F and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to mesalazine.
LIMITS
Use the chromatogram supplied with mesalazine for system suitability EPCRS and the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) to identify any peaks due to impurities F, J and P and the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) to identify any peaks due to impurities E, G, H, L, M, N, O and R in the chromatogram obtained in solution (1). Multiply the area of these peaks by the corresponding correction factors: impurity E, 1.3; impurity G, 1.4; impurity H, 1.4; impurity J, 2.0; impurity L, 4.5; impurity M, 1.7; impurity O, 0.6; impurity P, 0.6; impurity R, 1.3.
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity H is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.3%);
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity E, F, G, J, L, M, P or R is not greater than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15% of each);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.1%);
the sum of the areas of any secondary peaks is not greater than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Impurity C
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions and freshly prepared mobile phase.
(1) To a weighed quantity of the enema containing 1 g of Mesalazine, add 400 mL of mobile phase A and mix for 10 minutes with the aid of ultrasound with occasional shaking. Add sufficient mobile phase A to produce 1 L, mix and filter through a 0.45-μm membrane filter.
(2) 0.00002% w/v of 2-aminophenol (impurity C) in mobile phase A.
(3) To 1 volume of solution (1) add sufficient of mobile phase A to produce 200 volumes, mix 1 volume of this solution with 1 volume of 0.0005% w/v of 2-aminophenol in mobile phase A.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with spherical end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (3 μm) (Nucleosil C18 is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 220 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Mobile phase A: 0.22% w/v of perchloric acid and 0.1% w/v of orthophosphoric acid in water.
Mobile phase B: 0.17% w/v of perchloric acid and 0.1% w/v of orthophosphoric acid in acetonitrile R1.
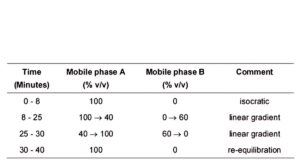
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the relative retentions with reference to mesalazine (retention time about 9 minutes) are: impurity A, about 0.5 and impurity C, about 0.9.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the two principal peaks is at least 3.0.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity C is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (200 ppm).
Impurity K
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Add 2 mL of 1M sodium hydroxide to a quantity of the foam enema containing 1 g of Mesalazine, add 300 mL of the mobile phase, mix for 20 minutes with the aid of ultrasound, add sufficient of the mobile phase to produce 500 mL and filter through a 0.45-μm membrane filter.
(2) 0.00000278% w/v of aniline hydrochloride in the mobile phase.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer (5 μm) (XTerra MS C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 40°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 205 nm.
(f) Inject 50 μL of each solution.
(g) Allow the chromatography to proceed for three times the retention time of aniline (impurity K).
MOBILE PHASE
15 volumes of methanol and 85 volumes of a solution containing 0.141% w/v of potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate and 0.047% w/v of disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate previously adjusted to pH 8.0 with 4.2% w/v of sodium hydroxide.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the retention time of aniline is about 15 minutes.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to aniline (impurity K) is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (10 ppm).
ASSAY
Prepare a mixture of 2 volumes of methanol and 5 volumes of water (solvent A).
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Shake and invert the container. Dissolve a weighed quantity of the foam containing 1 g of Mesalazine in 250 mL of 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid and mix with the aid of ultrasound. Add sufficient 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid to produce 500 mL and filter (Whatman GF/A is suitable). Dilute 1 volume of this solution to 10 volumes with solvent A.
(2) Dissolve 20 mg of mesalazine BPCRS in 10 mL of 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid and mix with the aid of ultrasound. Dilute with a sufficient quantity of solvent A to produce a solution containing 0.02% w/v of Mesalazine.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Spherisorb C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 220 nm.
(f) Inject 50 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
5 volumes of methanol and 95 volumes of a 0.007% w/v solution of ammonium carbamate previously adjusted to pH 3.68 with 2M hydrochloric acid.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Determine the weight per mL of the foam enema, Appendix V G, and calculate the content of C7H7NO3 using the declared content of C7H7NO3 in mesalazine BPCRS.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include impurities B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, O, P,
Q, R and S listed under Mesalazine.






