BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
General Notices
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1619)
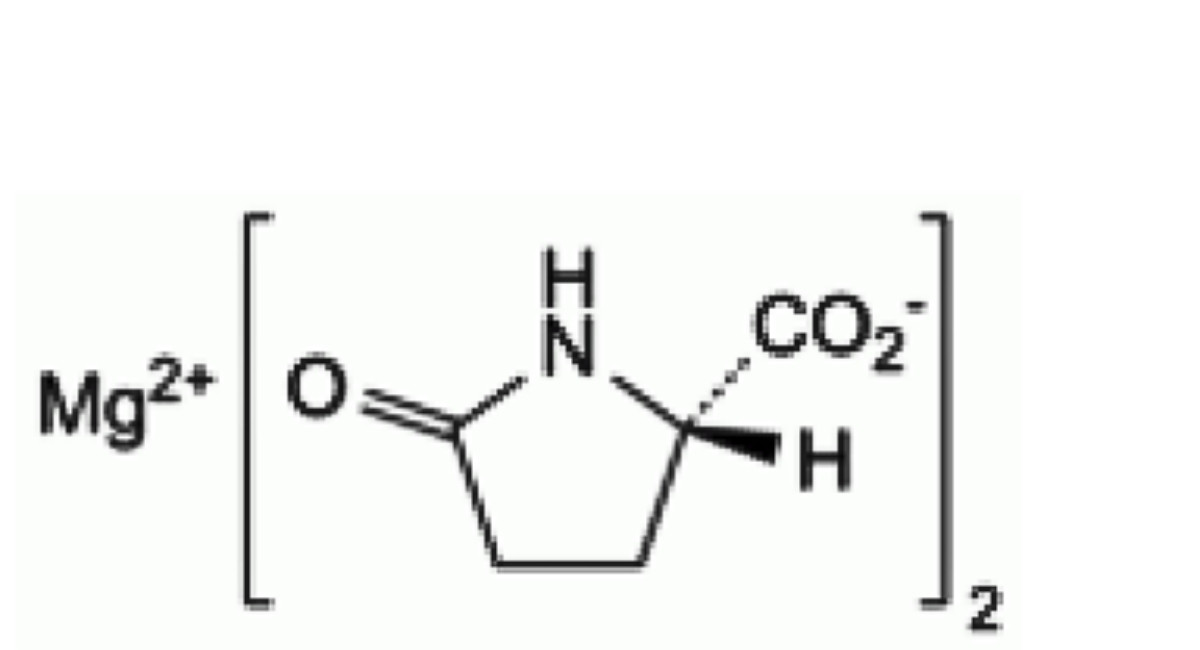 C10H12MgN2O6 280.5 62003-27-4
C10H12MgN2O6 280.5 62003-27-4
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
Magnesium bis[(2S)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylate].
Content
8.49 per cent to 8.84 per cent of Mg (Ar = 24.31) (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Amorphous, white or almost white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 60 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of water R and dilute to 10 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution Dissolve 55 mg of pidolic acid CRS in 2 mL of water R and dilute to 10 mL with methanol R.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase methanol R, glacial acetic acid R, methylene chloride R (15:20:65 V/V/V).
Application 1 μL.
Development Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying At 100-105 °C for 15 min.
Detection Spray with strong sodium hypochlorite solution R. Allow to stand for 10 min and spray abundantly with glacial acetic acid R. Allow to stand again for 10 min and dry at 100-105 °C for 2 min. Spray with potassium iodide and starch solution R until spots appear.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution. The chromatogram obtained with the test solution may show 2 faint secondary spots.
B. To 0.15 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 1.8 mL of water R. The solution gives the reaction of magnesium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.00 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B8 (2.2.2, Method I).
pH (2.2.3)
5.5 to 7.0 for solution S.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-26.5 to -23.3 (anhydrous substance), determined on solution S.
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in 4 mL of water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 60.0 mg of glutamic acid R in 50 mL of water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with methanol R.
Related substances
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.10 per cent);
— total of other impurities: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit:5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.05 per cent); disregard any peak due to the nitrate ion (NO3–).
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 500 ppm.
Dilute 1.0 mL of solution S to 15.0 mL with water R.
Nitrates
Examine the chromatogram obtained with the test solution in the test for related substances.
Limit:
— nitrates: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (200 ppm).
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 0.1 per cent.
Dilute 1.5 mL of solution S to 15.0 mL with distilled water R.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 0.5 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 8.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.300 g in 50 mL of waterR. Carry out the complexometric titration of magnesium (2.5.11).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 2.431 mg of Mg.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
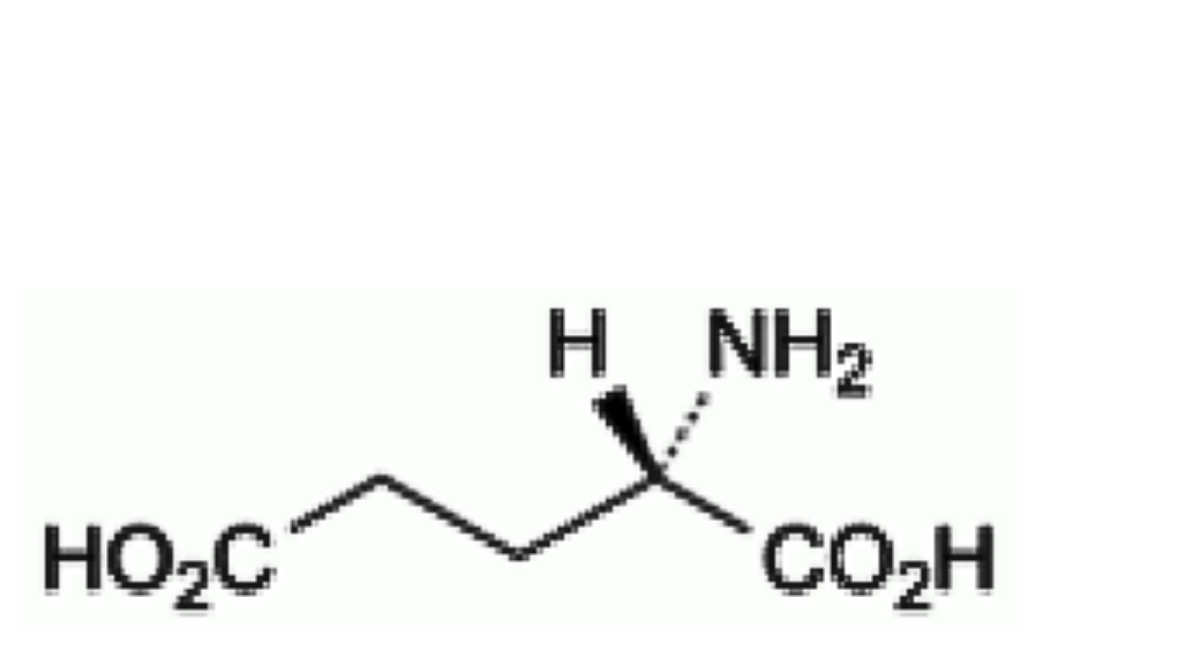
A. (2S)-2-aminopentanedioic acid (glutamic acid),
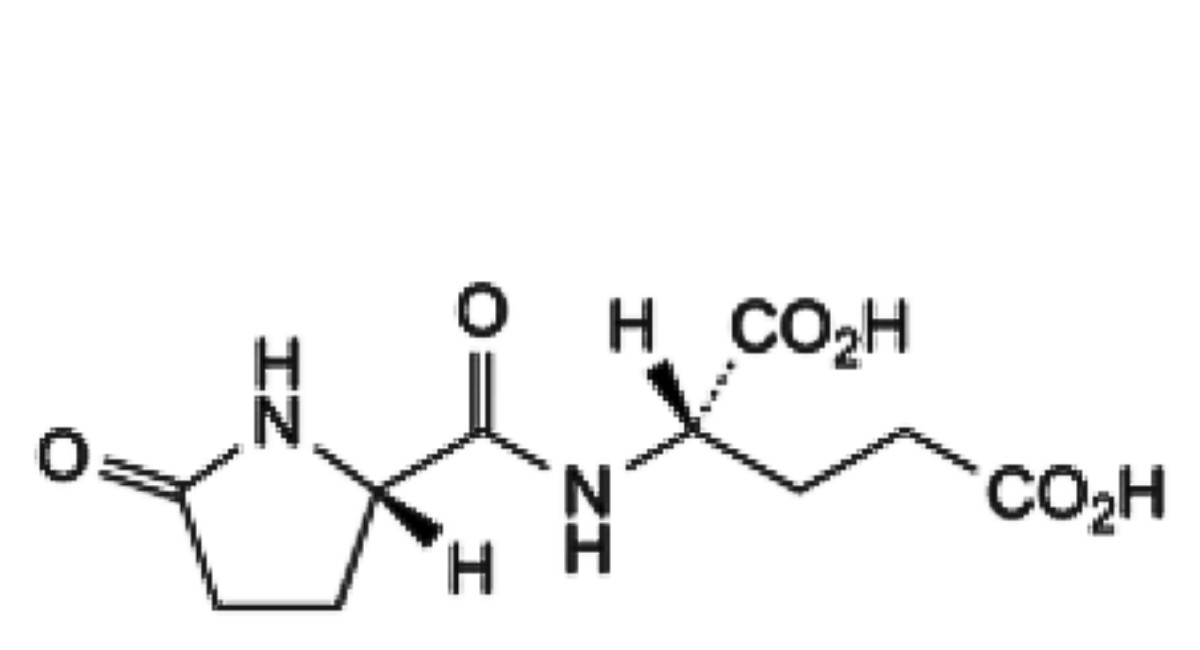
B. (2S)-2-[(2S)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamido]pentanedioic acid.
Ph Eur






