Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
General Notices (Magnesium Aspartate Dihydrate, Ph. Eur monograph 1445)
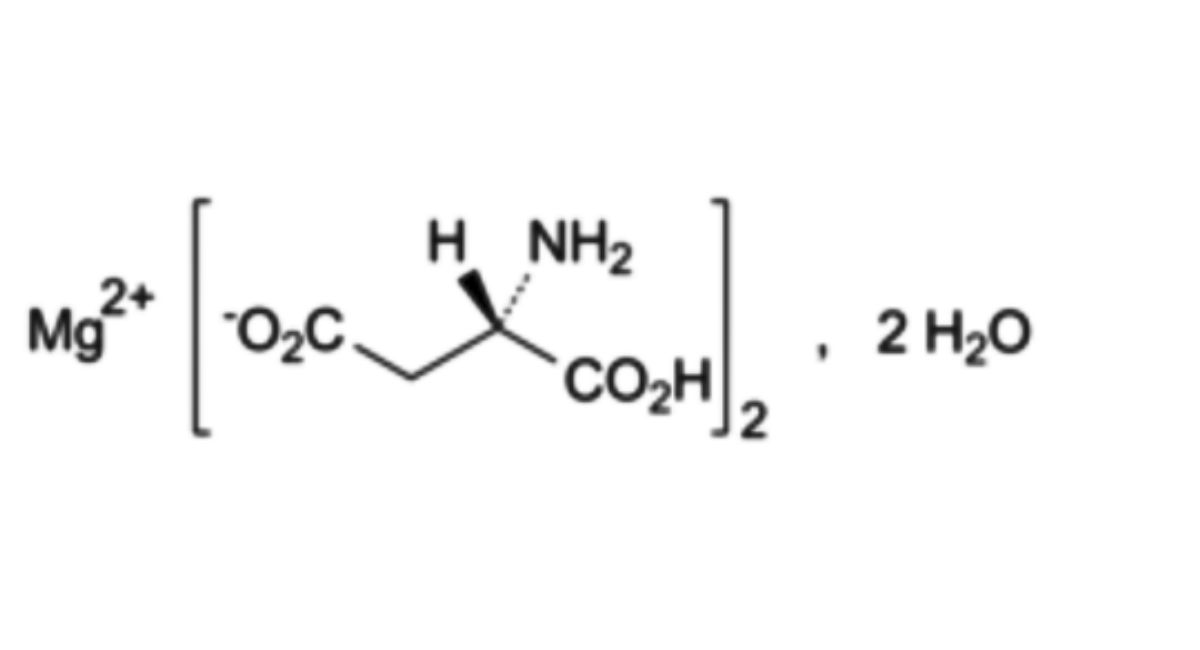
C8H12MgN2O8,2H2O 324.5 215533-00-9
DEFINITION
Magnesium bis[(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropanoate] dihydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water.
IDENTIFICATION
Carry out either tests A, C, D, E or tests B, C, D, E.
A. Specific optical rotation (2.2.7): + 22.0 to + 24.0 (anhydrous substance). Dissolve 0.50 g in a 515 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same acid.
B. Enantiomeric purity (see Tests).
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 10 mg of magnesium aspartate dihydrate CRS in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase glacial acetic acid R, water R, butanol R (20:20:60 V/V/V).
Application 5 pL.
Development Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In air.
Detection Spray with ninhydrin solution R and heat at 105 °C for 15 min.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. Ignite about 15 mg until a white residue is obtained. Dissolve the residue in 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R, neutralise to red litmus paper R by adding dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and filter if necessary. The solution gives the reaction of magnesium (2.3.1).
E. Water (see Tests).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
6.0 to 8.0 for solution S.
Enantiomeric purity
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.120 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 0.100 g of D-aspartic acid R (impurity A) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 0.120 g of the substance to be examined in 90 mL of water R, add 0.3 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 100 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 0.3 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, 0 = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: L-penicillamine coated silica gel for chiral separations R (5 pm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase 2-propanol R, 0.5 g/L solution of copper sulfate pentahydrate R (5:95 V/V).
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection 20 pL.
Relative retention With reference to magnesium aspartate (retention time = about 12 min): impurity A = about 0.85.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
– resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and magnesium aspartate.
Calculation of percentage content:
– for impurity A, use the concentration of impurity A in reference solution (c).
Limit:
– impurity A: maximum 0.3 per cent.
Other dicarboxylic acids
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.600 g of the substance to be examined in 2.0 mL of a 618 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 20.0 mg of malic acid R (impurity B) in water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10.0 mg of maleic acid R (impurity I) in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 1 mL of reference solution (b) to 10 mL with reference solution (a).
Reference solution (d) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (e) Dissolve 10 mg of fumaric acid R (impurity C) in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1 mL of the solution to 100 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.30 m, 0 = 7.8 mm;
— stationary phase: cation-exchange resin R (9 pm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase 0.39 g/L solution of sulfuric acid R.
Flow rate 0.6 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Injection 10 pL.
Run time 4 times the retention time of impurity I.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities B and I; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e) to identify the peak due to impurity C.
Relative retention With reference to impurity I (retention time = about 7.5 min): impurity B = about 1.2; impurity C = about 2.0.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities I and B.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurities C and I, use the concentration of impurity I in reference solution (b).
— for impurities other than C and I, use the concentration of impurity B in reference solution (d).
Limits:
— impurity C: maximum 0.10 per cent;
— impurity I: maximum 0.10 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Ninhydrin-positive substances
Amino acid analysis (2.2.56). For analysis, use Method 1.
The concentrations of the test and reference solutions may be adapted according to the sensitivity of the equipment used. The concentrations of all solutions are adjusted so that the system suitability requirements described in general chapter 2.2.46 are fulfilled, keeping the ratios of concentrations between all solutions as described.
Solution A dilute hydrochloric acid R1 or a sample preparation buffer suitable for the apparatus used.
Test solution Dissolve 35.0 mg of the substance to be examined in solution A and dilute to 50.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 30.0 mg of proline R in solution A and dilute to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 250.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 6.0 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R to 50.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 30 mg of isoleucine R and 30 mg of leucine R in solution A and dilute to 50 mL with solution A. Dilute 1 mL of the solution to 200 mL with solution A.
Blank solution Solution A.
Inject suitable, equal amounts of the test solution, blank solution and reference solutions (a), (b) and (d) into the amino acid analyser. Run a program suitable for the determination of physiological amino acids.
System suitability Reference solution (d):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to isoleucine and leucine.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for any ninhydrin-positive substance detected at 570 nm, use the concentration of magnesium aspartate dihydrate in reference solution (a);
— for any ninhydrin-positive substance detected at 440 nm, use the concentration of proline in reference solution (b); if a peak is above the reporting threshold at both wavelengths, use the result obtained at 570 nm for quantification.
Limits:
— any ninhydrin-positive substance: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm.
Dilute 12 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R. Carry out the evaluation of the test after 30 min.
Ammonium
Amino acid analysis (2.2.56) as described in the test for ninhydrin-positive substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution, reference solution (c) and blank solution.
Limit:
— ammonium at 570 nm: not more than twice the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.04 per cent), taking into account the peak due to ammonium in the chromatogram obtained with the blank solution.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 50 ppm.
In a separating funnel, dissolve 0.20 g in 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methyl isobutyl ketone R1, shaking for 3 min each time. To the combined organic layers add 10 mL of water R and shake for 3 min. Use the aqueous layer.
Water (2.5.12)
10.0 per cent to 16.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
Dissolve the substance to be examined in a mixture of 2 mL of anhydrous methanol R and 10 mL of formamide R1 at 50 °C protected from moisture. Allow to cool. Carry out a blank determination.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.260 g in 10 mL of water R and carry out the complexometric titration of magnesium (2.5.11).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 28.85 mg of C8H12MgN2O8.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, C, I.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, D, E, F G, H.
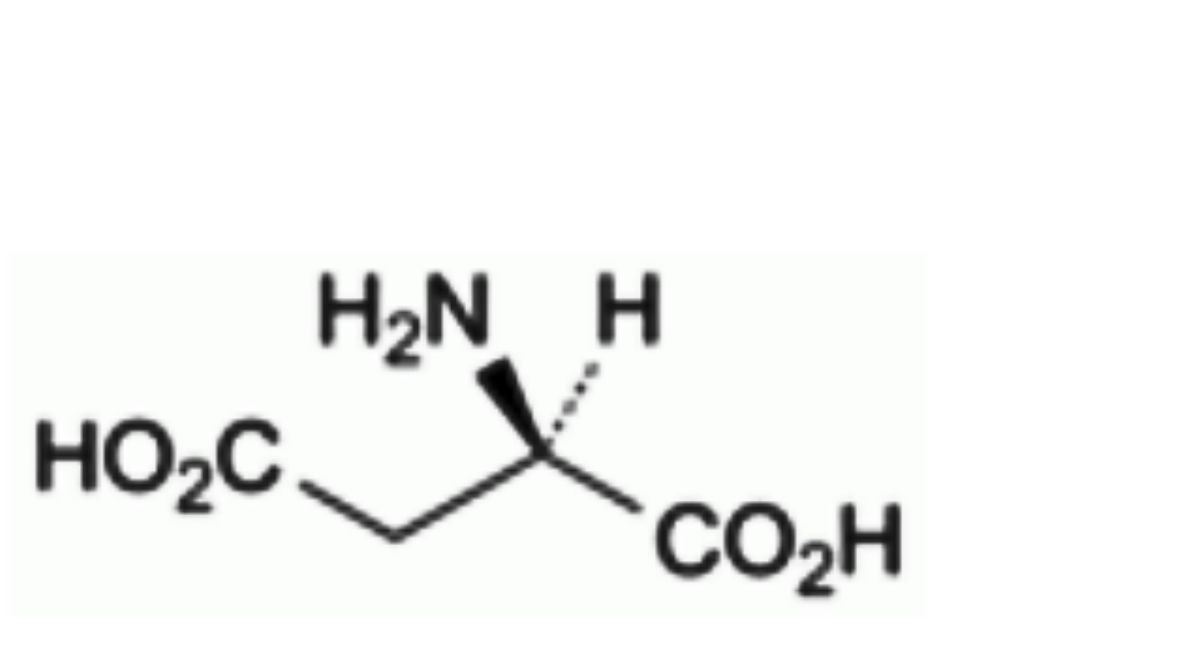
A. (2R)-2-aminobutanedioic acid (D-aspartic acid),
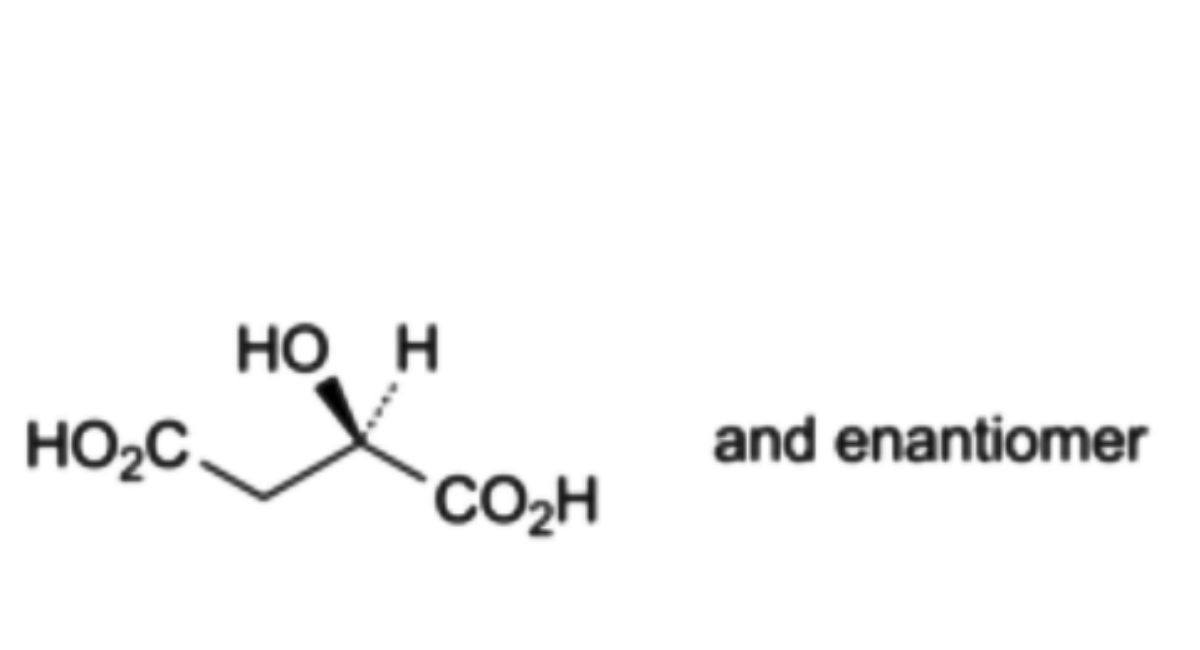
B. (2RS)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid (malic acid),
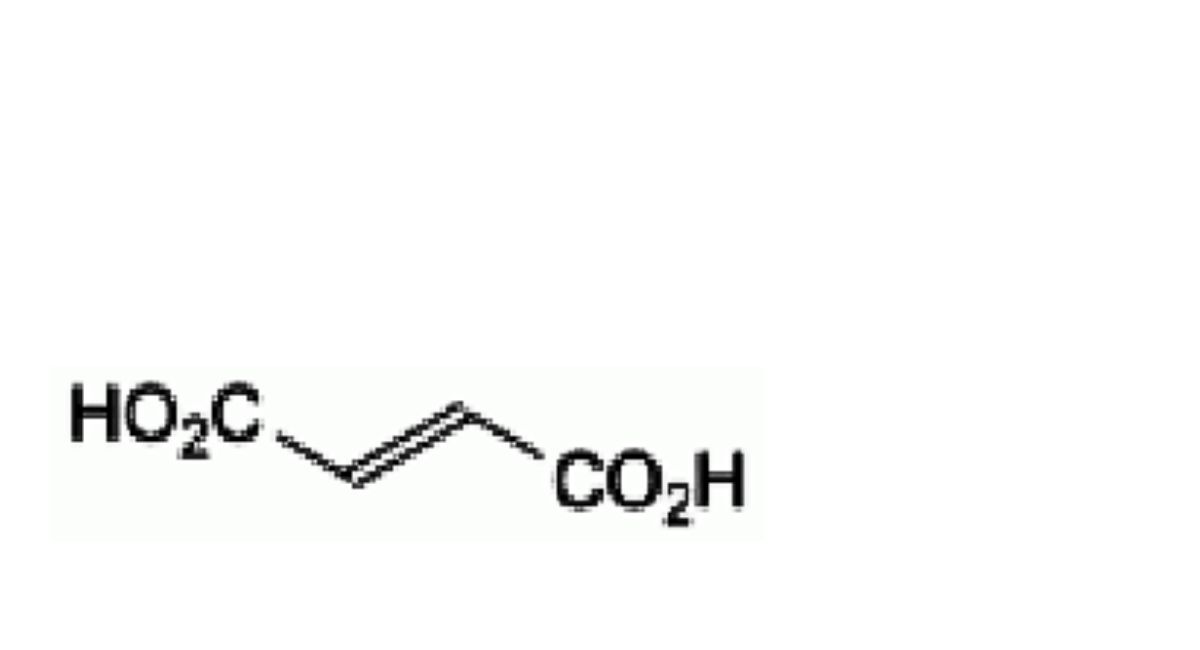
C. (2E)-but-2-enedioic acid (fumaric acid),
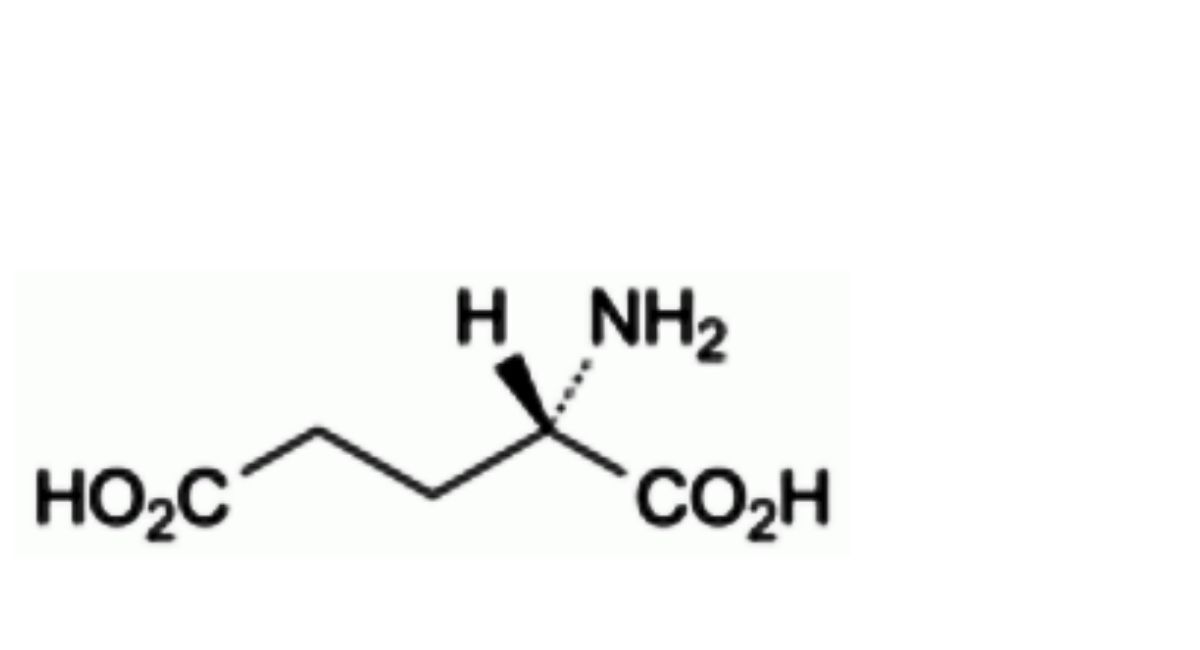
D. (2S)-2-aminopentanedioic acid (glutamic acid),
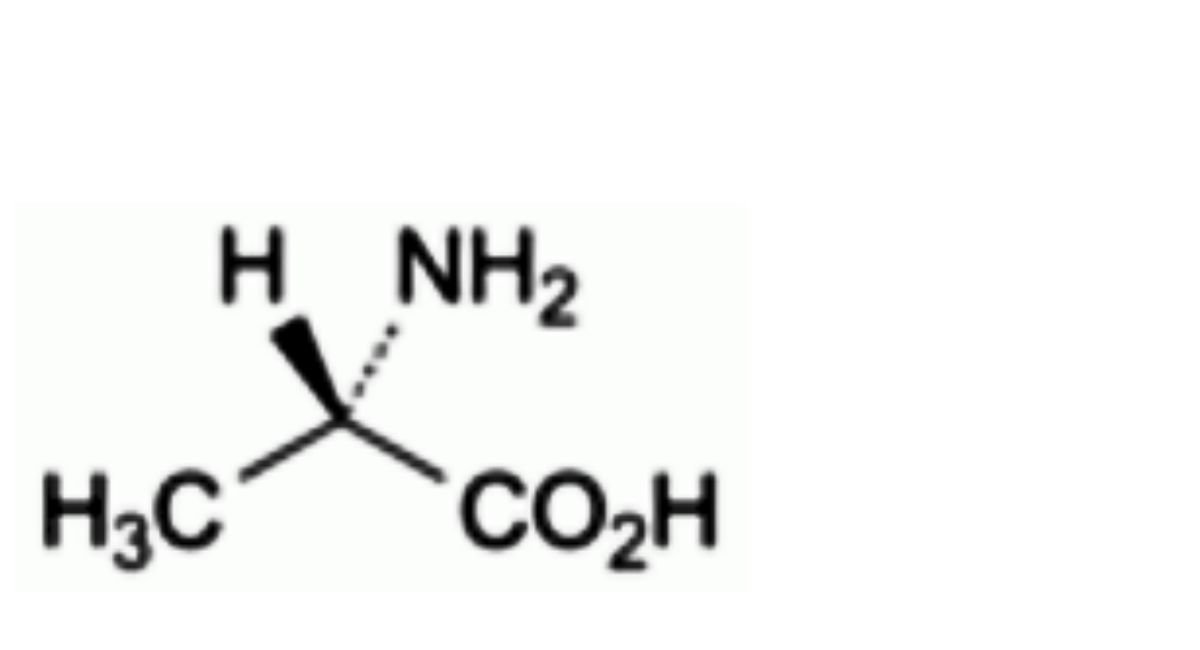
E. (2S)-2-aminopropanoic acid (alanine),
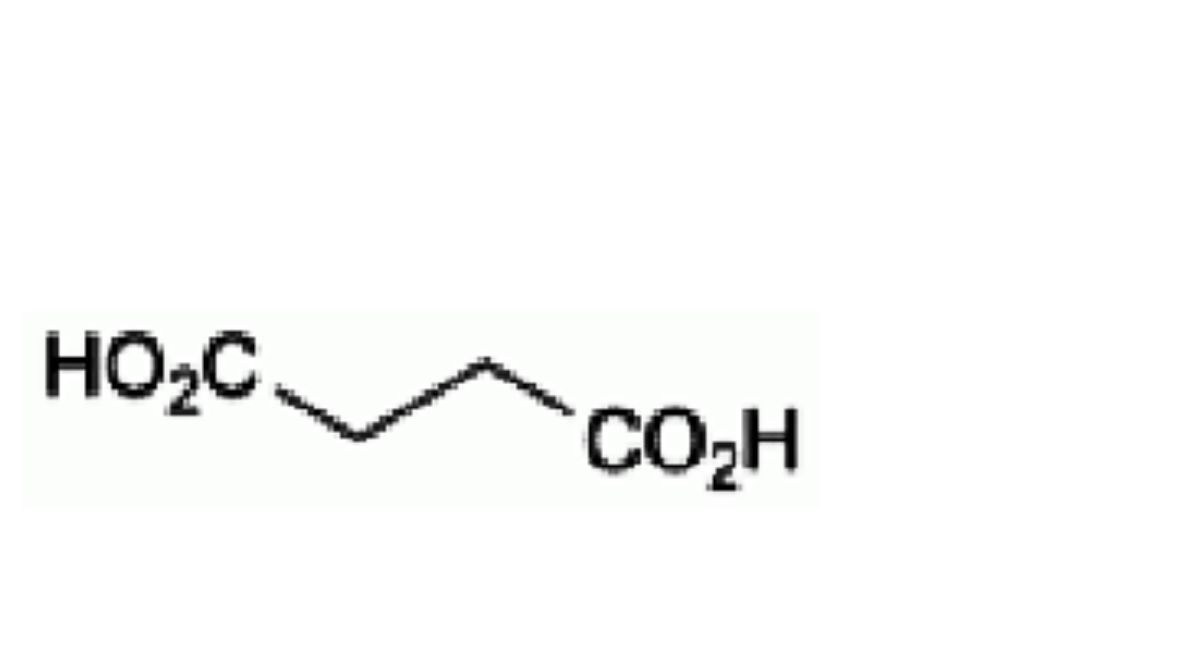
F. butanedioic acid (succinic acid),
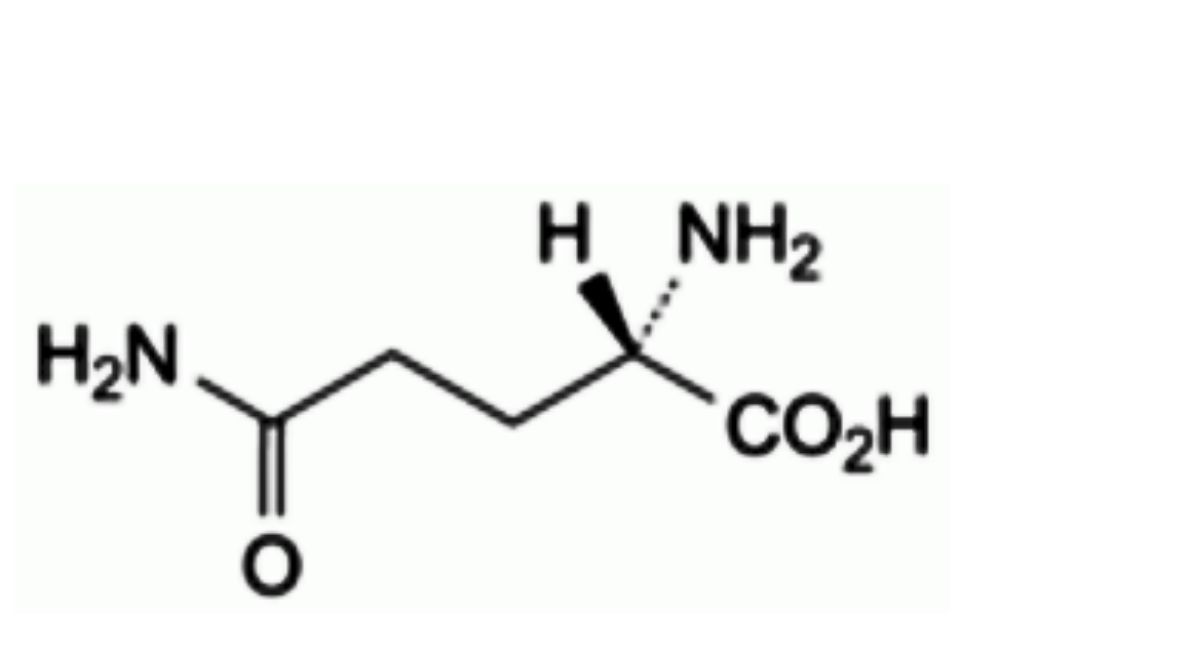
G. (2S)-2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid (L-glutamine),
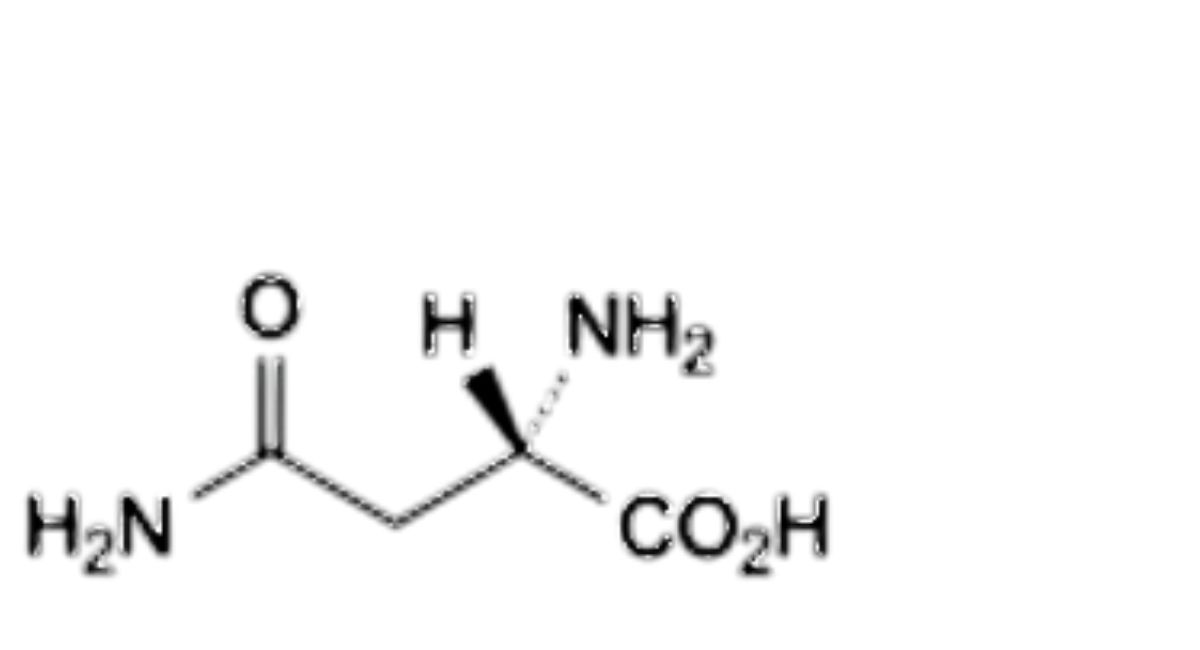
H. (2S)-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid (asparagine),
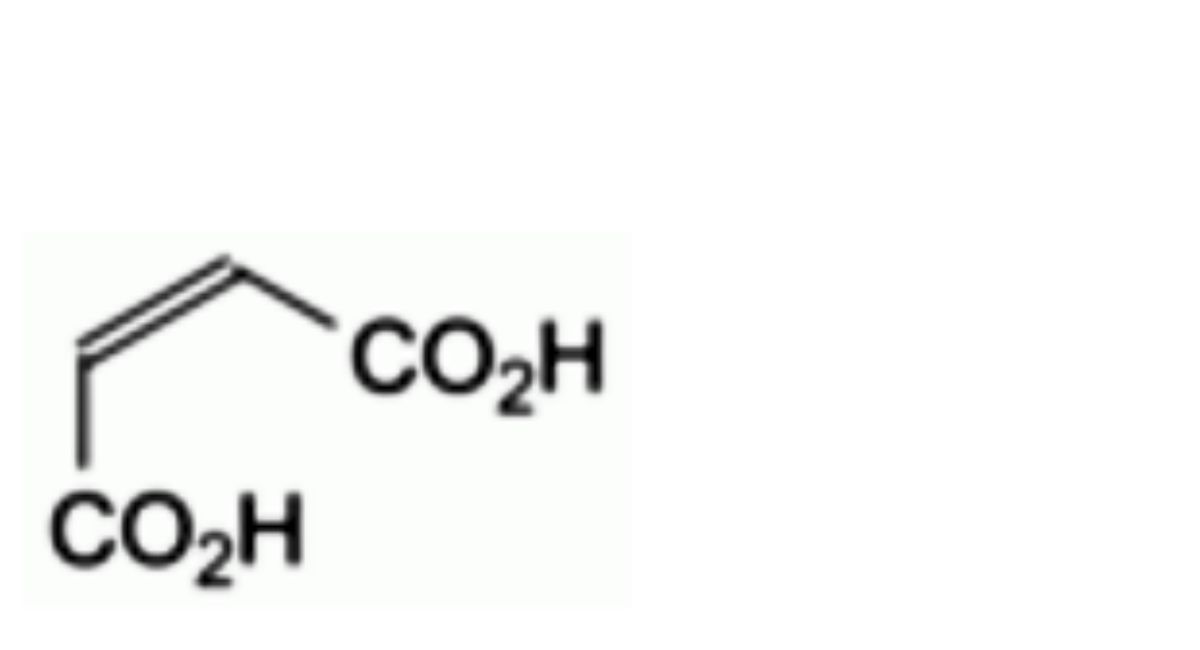
I. (2Z)-but-2-enedioic acid (maleic acid).






