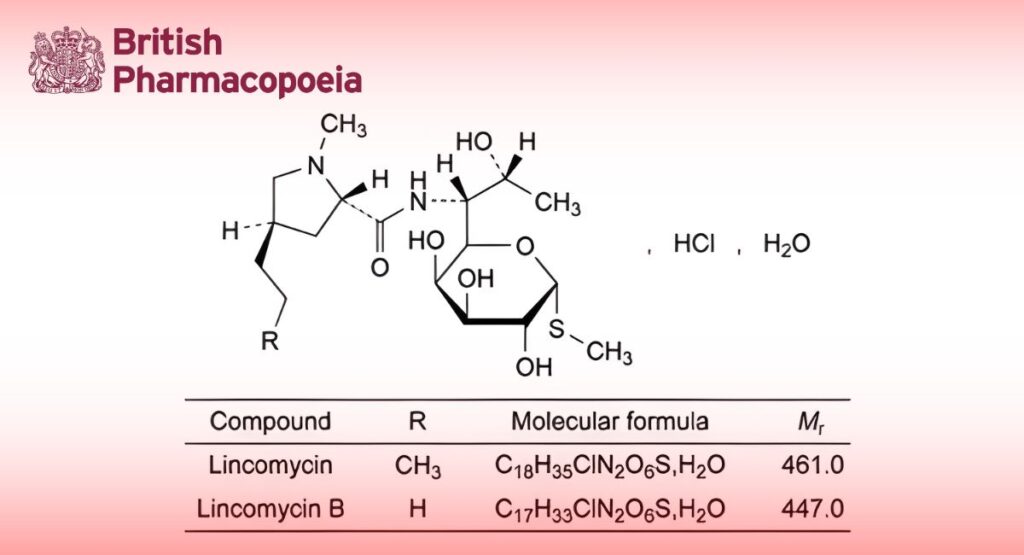
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0583)
Lincomycin hydrochloride monohydrate 7179-49-9
Action and use
Antibacterial.
Preparations
Lincomycin Capsules
Lincomycin Injection
DEFINITION
Mixture of antibiotics produced by Streptomyces lincolnensis var. lincolnensis or obtained by any other means, the main component being methyl 6,8-dideoxy-6-[[[(2S,4R)-1-methyl-4-propylpyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-D-erythro-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside (lincomycin) hydrochloride monohydrate.
Content
— sum of the contents of lincomycin hydrochloride and lincomycin B hydrochloride: 96.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance);
— lincomycin B hydrochloride: maximum 5.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: lincomycin hydrochloride CRS.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
3.5 to 5.5 for solution S.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 135 to + 150 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 1.000 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 25.0 mg of lincomycin hydrochloride CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of lincomycin hydrochloride for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B and C) in 2 mL of the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Buffer solution pH 6.1: Dissolve 34 g of phosphoric acid R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, adjust to pH 6.1 with concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Mobile phase: methanol R, acetonitrile R1, buffer solution pH 6.1 (8:17:75 V/V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection: 20 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c) and (d).
Run time: 5.5 times the retention time of lincomycin.
Relative retention: With reference to lincomycin (retention time = about 10 min): impurity C = about 0.4; lincomycin B = about 0.5; impurity A = about 0.7; impurity B = about 1.2 and 1.3.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 1.8 between the peak due to lincomycin and the 1 peak due to impurity B.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.5 per cent);
— sum of the areas of the peaks due to impurity B: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (2.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.05 per cent).
Water (2.5.12)
3.1 per cent to 4.6 per cent, determined on 0.500 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.50 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection: Test solution and reference solutions (a) and (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C18H35ClN2O6S (lincomycin) and C17H33ClN2O6S (lincomycin B) taking into account the assigned content of C18H35ClN2O6S in lincomycin hydrochloride CRS. Determine the content of lincomycin by comparing with the area of the peak due to lincomycin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a). Determine the content of lincomycin B by comparing with the area of the peak due to lincomycin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c).
STORAGE
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-evident container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) D, E, F.
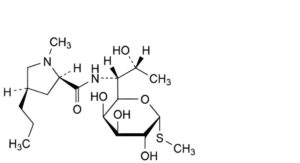
A. methyl 6,8-dideoxy-6-[[[(2R,4R)-1-methyl-4-propylpyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-D-erythro-α-D- galacto-octopyranoside (α-amide epimer),
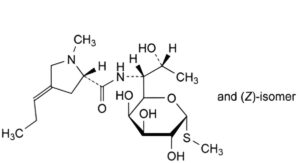
B. methyl 6,8-dideoxy-6-[[[(2S,4EZ)-1-methyl-4-propylidenepyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-D-erythro-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside (propylidene analogues),
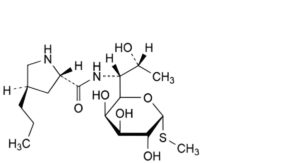
C. methyl 6,8-dideoxy-6-[[[(2S,4R)-4-propylpyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-D-erythro-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside (N-desmethyl lincomycin),
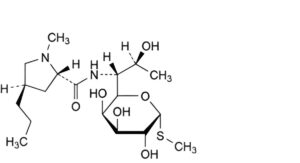
D. methyl 6,8-dideoxy-6-[[[(2S,4R)-1-methyl-4-propylpyrrolidin-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-L-threo-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside (7-epi-lincomycin),
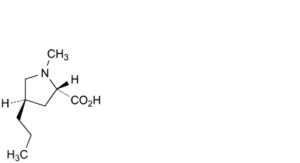
E. (2S,4R)-1-methyl-4-propylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (4-propyl hygric acid),
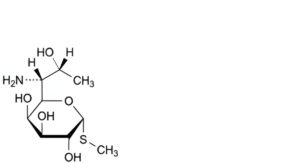
F. methyl 6-amino-6,8-dideoxy-1-thio-D-erythro-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside (methyl-1-thiolincosaminide).