(Ph. Eur. Monograph 0401)
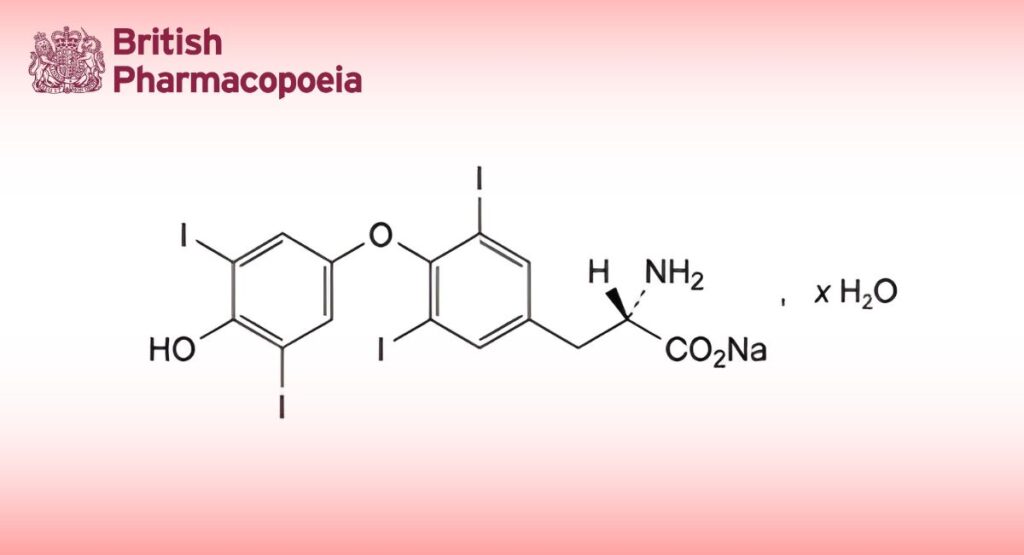
C15H10I4NNaO4,xH2O (x ≈ 5) 799 (anhydrous substance) 25416-65-3
Action and use
Thyroid hormone replacement.
Preparations
Levothyroxine Oral Solution
Levothyroxine Tablets
DEFINITION
Sodium (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoate.
Content
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Almost white or slightly brownish-yellow, fine, slightly hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: levothyroxine sodium CRS.
B. To 200 mg add 2 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Heat on a water-bath and then carefully over a naked flame, increasing the temperature gradually up to 600 ± 50 °C. Continue the ignition until most of the black particles have disappeared.
Dissolve the residue in 2 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.500 g in 23 mL of a gently boiling mixture of 1 volume of 1 M hydrochloric acid and 4 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R. Cool and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Appearance of solution
Freshly prepared solution S is not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY3 (2.2.2, Method II).
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 16 to + 20 (anhydrous substance), determined on freshly prepared solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Solvent mixture: Mobile phase A, ethanol (96 per cent) R (1:2 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 2.5 mg of levothyroxine sodium CRS and 2.5 mg of liothyronine sodium CRS (impurity A) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 25.0 mg of levothyroxine sodium CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve 2.0 mg of levothyroxine for peak identification CRS (containing impurities F and G) in 10.0 mL of the solvent mixture and sonicate for 10 min.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 1.97 g of phosphoric acid R in water R and dilute to 2 L with the same solvent;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 1.97 g of phosphoric acid R in acetonitrile R1 and dilute to 2 L with the same solvent;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 10 | 70 | 30 |
| 10 – 40 | 70 → 20 | 30 → 80 |
| 40 – 50 | 20 | 80 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 225 nm.
Injection: 25 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a), (b) and (d).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with levothyroxine for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities F and G.
Relative retention: With reference to levothyroxine (retention time = about 11 min): impurity A = about 0.5; impurity F = about 2.0; impurity G = about 2.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and levothyroxine.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with
reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
— impurity F: not more than 5 times the area of the peak due to levothyroxine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— impurity G: not more than 3 times the area of the peak due to levothyroxine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the peak due to levothyroxine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
— total: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the peak due to levothyroxine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
Water (2.5.32)
6.0 per cent to 12.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C15H10I4NNaO4 taking into account the assigned content of levothyroxine sodium CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light, at a temperature of 2 °C to 8 °C.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, F, G.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, D, E, H, I, J, K.
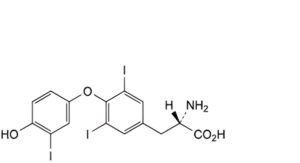
A. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid (liothyronine),
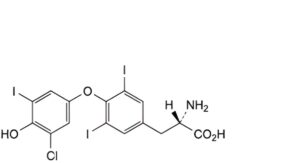
B. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(3-chloro-4-hydroxy-5-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid,
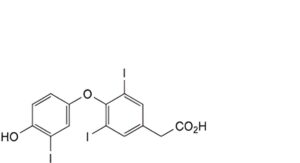
C. [4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]acetic acid (triiodothyroacetic acid),
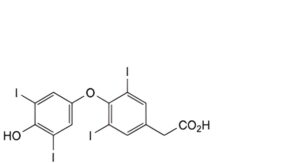
D. [4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]acetic acid (tetraiodothyroacetic acid),
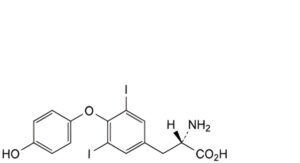
E. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid (diiodothyronine),
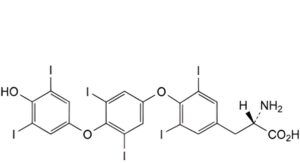
F. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenoxy]-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid,
G. unknown structure,
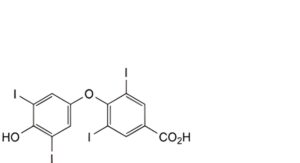
H. 4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodobenzoic acid,
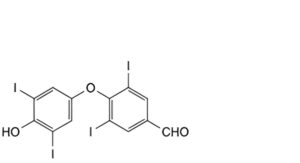
I. 4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodobenzaldehyde,
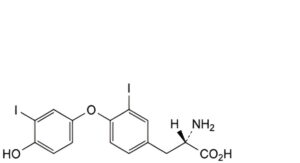
J. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3-iodophenyl]propanoic acid,
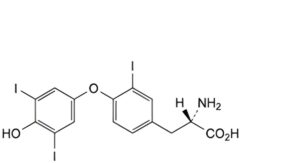
K. (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3-iodophenyl]propanoic acid.