(Liquid Lactulose, Ph. Eur. monograph 0924)
Action and use
Osmotic laxative.
DEFINITION
Aqueous solution of 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-arabino-hex-2-ulofuranose normally prepared by alkaline isomerisation of lactose. It may contain other sugars including lactose, epilactose, galactose, tagatose and fructose.
Content
Minimum 620 g/L of lactulose (C12H22O11; Mr 342.3) and 95.0 per cent to 105.0 per cent of the content of lactulose stated on the label.
It may contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, viscous liquid, colourless or pale brownish-yellow.
Solubility
Miscible with water. It may be a supersaturated solution or may contain crystals that disappear on heating.
A 10 per cent V/V solution is laevorotatory.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, C, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dilute 0.50 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 60.0 mg of lactulose CRS in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, 50 g/L solution of boric acid R, methanol R, ethyl acetate R (10:15:20:55 V/V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: At 100-105 °C for 5 min and allow to cool.
Detection: Spray with a 1.0 g/L solution of 1,3-dihydroxynaphthalene R in a mixture of 10 volumes of sulfuric acid R and 90 volumes of methanol R; heat at 110 °C for 5 min.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
C. To 0.1 g add 10 mL of water R and 3 mL of cupri-tartaric solution R and heat. A red precipitate is formed.
D. To 0.25 g add 5 mL of water R and 5 mL of ammonia R. Heat in a water-bath at 80 °C for 10 min. A red colour develops.
TESTS
Solution S
Mix 10 g with carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY5 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
3.0 to 7.0.
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of a saturated solution of potassium chloride R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Mix 4.00 g of the substance to be examined and 20 mL of water R. Add 25.0 mL of acetonitrile R with gentle heating and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): To 5.0 mL of the test solution add 47.5 mL of acetonitrile R with gentle heating and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2.00 g of lactulose CRS in 20 mL of water R. Add 25.0 mL of acetonitrile R with gentle heating and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 65 mg of fructose CRS (impurity D) in a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve 1 g of lactulose for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, E, F, G and H) in reference solution (c) and dilute to 25 mL with reference solution (c).
Reference solution (e): Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R.
Column 1:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: aminopropylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 38 ± 1 °C.
Column 2:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: aminopropylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 38 ± 1 °C.
Columns 1 and 2 are coupled in series.
Mobile phase: Dissolve 0.253 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 200 mL of water for chromatography R and dilute to 1000 mL with acetonitrile R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Differential refractometer maintained at a constant temperature (e.g. 35 °C).
Injection: 20 μL of the test solution and of reference solutions (a), (d) and (e).
Run time: Twice the retention time of lactulose.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with lactulose for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H.
Relative retention: With reference to lactulose (retention time = about 18 min): impurity F = about 0.2; impurity E = about 0.38; impurity D = about 0.42; impurity B = about 0.6; impurity G = about 0.8; impurity A = about 0.9; impurity C = about 1.2; impurity H = about 1.5.
System suitability Reference solution (d):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 5.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to lactulose.
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than 3 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (15.0 per cent);
— impurities A, C: for each impurity, not more than twice the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (10.0 per cent);
— impurities E, F: for each impurity, not more than 0.8 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (4.0 per cent);
— impurities G, H: for each impurity, not more than 0.3 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.5 per cent);
— impurity D: not more than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— sum of impurities eluting after impurity H: not more than 0.26 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.3 per cent);
— total (excluding impurities B and C): not more than 2.4 times the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (12.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: not more than the area of the peak due to lactulose in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e) (0.25 per cent).
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
Methanol
Head-space gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard solution: Mix 0.5 mL of propanol R and 100.0 mL of water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: To 0.13 g of the substance to be examined in a 20 mL vial add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution and 5 μL of a 0.1 per cent V/V solution of methanol R.
Reference solution: To 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution in a 20 mL vial add 5 μL of a 0.1 per cent V/V solution of methanol R.
Column:
— size: l = 2 m, Ø = 2 mm;
— stationary phase: ethylvinylbenzene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (180 μm).
Carrier gas: helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 30 mL/min.
Static head-space conditions that may be used:
— equilibration temperature: 60 °C;
— equilibration time: 1 h;
— pressurisation time: 1 min.
Temperature:
— column: 140 °C;
— injection port: 200 °C;
— detector: 220 °C.
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 mL of the gaseous phase.
Calculate the content of methanol, taking its density (2.2.5) at 20 °C to be 0.79 g/mL.
Limit:
— methanol: calculate the ratio (R) of the area of the peak due to methanol to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution; calculate the ratio of the area of the peak due to methanol to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution: this ratio is not greater than 2R (30 ppm).
Sulfites
Maximum 30 ppm.
Mix 5.0 g with 40 mL of water R, add 2.0 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 100 mL with water R.
To 10.0 mL of this solution, add 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid R1, 2.0 mL of decolorised fuchsin solution R1 and 2.0 mL of a 0.5 per cent V/V solution of formaldehyde R. Allow to stand for 30 min and measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at 583 nm using as the compensation liquid a solution prepared at the same time and in the same manner with 10.0 mL of water R instead of the solution of the substance to be examined. The absorbance is not greater than that of a reference solution prepared at the same time and in the same manner using 10.0 mL of sulfite standard solution (1.5 ppm SO2) R instead of the solution of the substance to be examined.
Boron
Maximum 5 ppm.
Avoid where possible the use of glassware.
Reference solution Dissolve 56.0 mg of boric acid R in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Keep in a well-closed polyethylene container.
In 4 polyethylene 25 mL flasks, place separately:
— 1.00 g of the substance to be examined and 1 mL of water R (solution A);
— 1.00 g of the substance to be examined and 1 mL of the reference solution (solution B);
— 1 mL of the reference solution and 1 mL of water R (solution C);
— 2 mL of water R (solution D).
To each flask, add 4.0 mL of acetate-edetate buffer solution pH 5.5 R. Mix and add 4.0 mL of freshly prepared azomethine H solution R. Mix and allow to stand for 1 h.
Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of solutions A, B and C at 420 nm, using solution D as the compensation liquid. The test is not valid unless the absorbance of solution C is at least 0.25. The absorbance of solution B is not less than twice that of solution A.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.5 g and calculated with reference to the declared content of lactulose.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 102 CFU/g (2.6.12).
TYMC: acceptance criterion 101 CFU/g (2.6.12).
Absence of Escherichia coli (2.6.13).
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (b).
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— symmetry factor: 0.6 to 2.0 for the principal peak.
Calculate the percentage content of C12H22O11 taking into account the assigned content of lactulose CRS.
LABELLING
The label states the declared content of lactulose.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H.
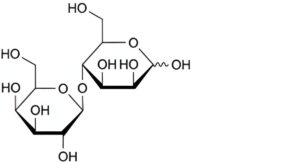
A. 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-mannopyranose (epilactose),
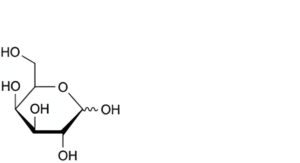
B. D-galactopyranose (galactose),
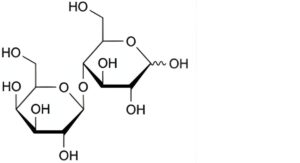
C. 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucopyranose (lactose),
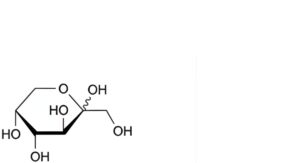
D. D-arabino-hex-2-ulopyranose (fructose),
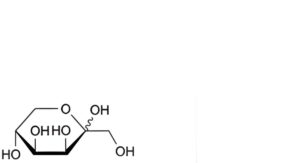
E. D-lyxo-hex-2-ulopyranose (tagatose),
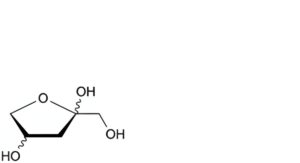
F. (2Ξ,4Ξ)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-2,4-diol,
G. unknown structure,
H. unknown structure.






