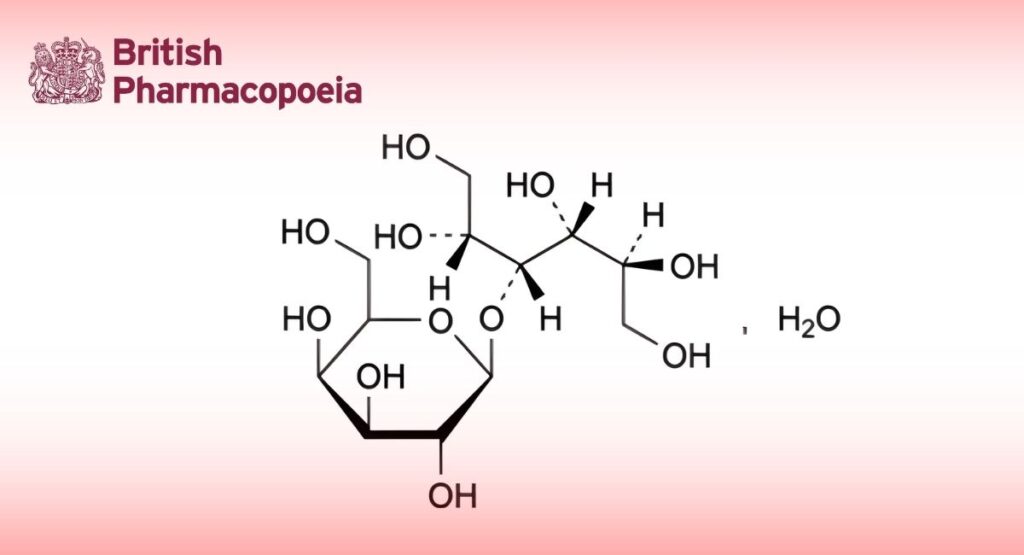
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1337)
C12H24O11,H2O 362.3 81025-04-9
Action and use
Osmotic laxative.
DEFINITION
4-O-β-D-Galactopyranosyl-D-glucitol monohydrate.
Content
96.5 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble to very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: lactitol monohydrate CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5 mg of lactitol monohydrate CRS in methanol R and dilute to 2 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2.5 mg of sorbitol CRS (impurity E) in 1 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 10 mL with methanol R.
Plate: TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase: water R, acetonitrile R (25:75 V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Spray with 4-aminobenzoic acid solution R and dry in a current of cold air until the acetone is removed; heat at 100 °C for 15 min and allow to cool; spray with a 2 g/L solution of sodium periodate R and dry in a current of cold air; heat at 100 °C for 15 min.
System suitability: The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.000 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. To 10 mL of this solution add 0.05 mL of phenolphthalein solution R. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to pink. To a further 10 mL of the solution add 0.05 mL of methyl red solution R. Not more than 0.3 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator to red.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 13.5 to + 15.5 (anhydrous substance), determined on solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 2.0 mL of test solution (a) to 50.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5.0 mg of lactitol monohydrate CRS and 5 mg of glycerol R in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dilute 2.5 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.30 m, Ø = 7.8 mm;
— stationary phase: strong cation-exchange resin (calcium form) R;
— temperature: 60 °C.
Mobile phase: water for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 0.6 mL/min.
Detection: Differential refractometer maintained at a constant temperature (e.g. 35 °C).
Injection: 100 μL; inject test solution (a) and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of lactitol.
Relative retention: With reference to lactitol (retention time = about 13 min): impurity A = about 0.7; impurity B = about 0.8; glycerol = about 1.3; impurity C = about 1.5; impurity D = about 1.8;
impurity E = about 1.9.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to lactitol and glycerol.
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than the area of the peak due to lactitol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (1.0 per cent);
— total of other impurities: not more than the area of the peak due to lactitol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (1.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Reducing sugars
Maximum 0.2 per cent.
Dissolve 5.0 g in 3 mL of water R with gentle heating. Cool and add 20 mL of cupri-citric solution R and a few glass beads. Heat so that boiling begins after 4 min and maintain boiling for 3 min. Cool rapidly and add 100 mL of a 2.4 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R and 20.0 mL of 0.025 M iodine. With continuous shaking, add 25 mL of a mixture of 6 volumes of hydrochloric acid R and 94 volumes of water R.
When the precipitate has dissolved, titrate the excess of iodine with 0.05 M sodium thiosulfate using 1 mL of starch solution R added towards the end of the titration, as indicator. Not less than 12.8 mL of
0.05 M sodium thiosulfate is required.
Water (2.5.12)
4.5 per cent to 5.5 per cent, determined on 0.300 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
TYMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
Absence of Escherichia coli (2.6.13).
Absence of Salmonella (2.6.13).
Absence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (2.6.13).
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C12H24O11 taking into account the assigned content of lactitol monohydrate CRS.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
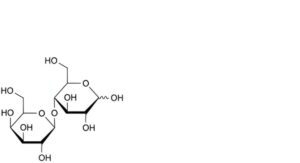
A. 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucopyranose (lactose),
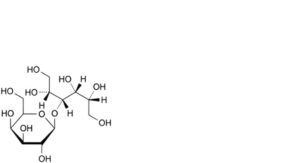
B. 3-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-mannitol (lactulitol),
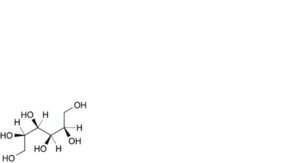
C. D-mannitol,
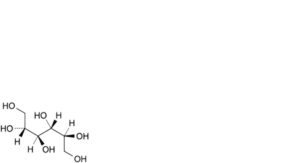
D. galactitol (dulcitol),
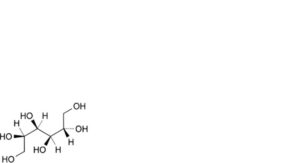
E. D-glucitol (D-sorbitol).