(Ph. Eur. monograph 1020)
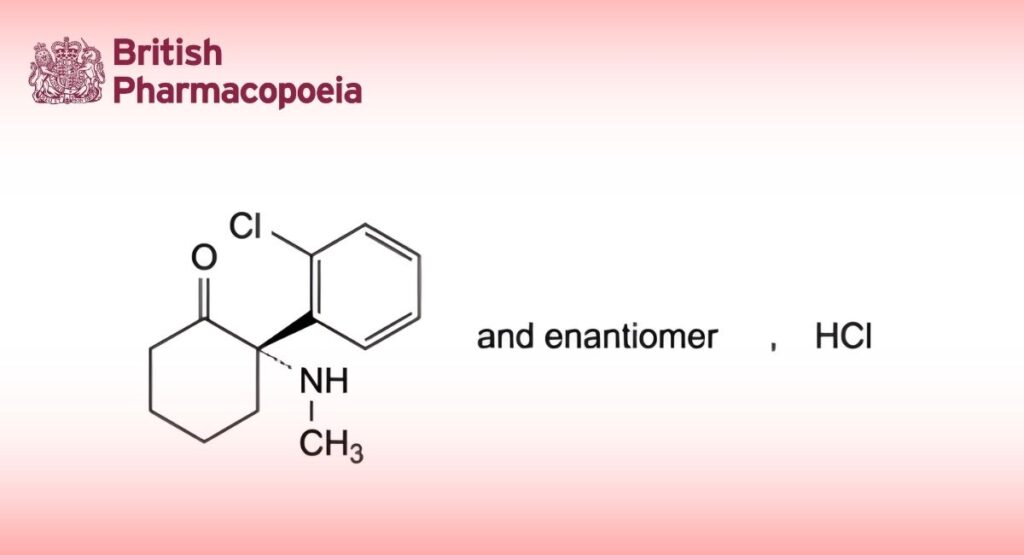
C13H17Cl2NO 274.2 1867-66-9
Action and use
Intravenous general anaesthetic
Preparations
Ketamine Injection
Ketamine Nasal Spray
Ketamine Oral Solution
DEFINITION
(2RS)-2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone hydrochloride.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in methanol, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
mp
About 260 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: ketamine hydrochloride CRS.
C. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
3.5 to 4.1.
Dilute 10 mL of solution S to 20 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.2° to + 0.2°.
Dilute 2.5 mL of solution S to 25.0 mL with water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5 mg of ketamine impurity A CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase (using ultrasound if necessary). To 1.0 mL of the solution, add 0.5 mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Dissolve 0.95 g of sodium hexanesulfonate R in 1 L of a mixture of 25 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 75 volumes of water R and add 4 mL of acetic acid R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 10 times the retention time of ketamine.
Relative retention: With reference to ketamine (retention time = about 3 min): impurity A = about 1.6; impurity B = about 3.3; impurity C = about 4.6.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to ketamine and impurity A.
Limits:
— impurities A, B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 50 mL of methanol R and add 1.0 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid. Carry out a potentiometric titration (2.2.20), using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Read the volume added between the 2 points of inflexion.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 27.42 mg of C13H17Cl2NO.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
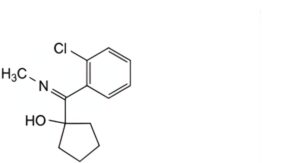
A. 1-(2-chloro-N-methylbenzimidoyl)cyclopentanol,
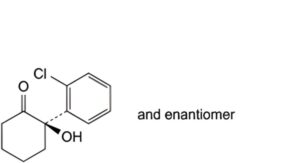
B. (2RS)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxycyclohexanone,
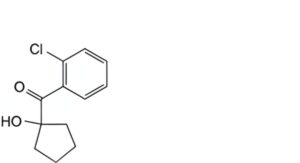
C. (2-chlorophenyl)(1-hydroxycyclopentyl)methanone.