(Ph. Eur. monograph 1332)
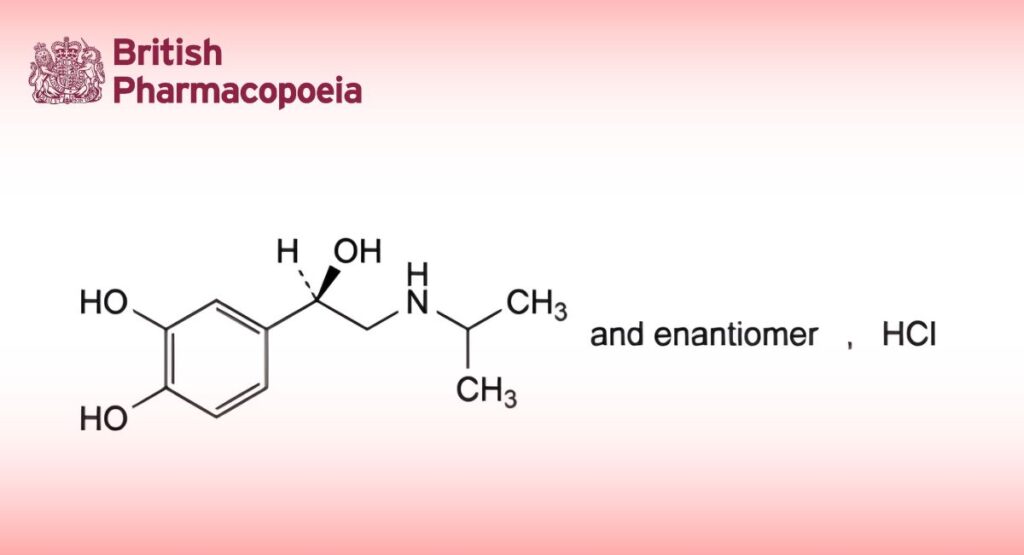
C11H18ClNO3 247.7 51-30-9
Action and use
Adrenoceptor agonist.
Preparation
Isoprenaline Injection
DEFINITION
(1RS)-1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethanol hydrochloride.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, C, E.
Second identification: A, C, D, E.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 165 °C to 170 °C, with decomposition.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: isoprenaline hydrochloride CRS.
C. Optical rotation (see Tests).
D. To 0.1 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 0.05 mL of ferric chloride solution R1 and 0.9 mL of water R. A green colour is produced. Add dropwise sodium hydrogen carbonate solution R. The colour becomes blue and then red.
E. To 0.5 mL of solution S add 1.5 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solution S
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B7 or BY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
4.3 to 5.5.
Mix 5 mL of solution S and 5 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.10° to + 0.10°, determined on solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 2.5 mg of orciprenaline sulfate CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): To 5 mL of reference solution (a) add 5 mL of reference solution (b).
Reference solution (d): Dissolve 6.0 mg of isoprenaline impurity A CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: methanol R, 11.5 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R (5:95 V/V).
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 7 times the retention time of isoprenaline.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peak due to impurity A; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to orciprenaline.
Relative retention: With reference to isoprenaline (retention time = about 4 min): orciprenaline = about 1.5; impurity A = about 1.8. If necessary, adjust the concentration of methanol in the mobile phase.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to isoprenaline and orciprenaline.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.5 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 15-25 °C for 4 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
In order to avoid overheating in the reaction medium, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.150 g in 10 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and add 50 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 24.77 mg of C11H18ClNO3.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
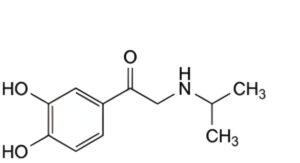
A. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethanone.