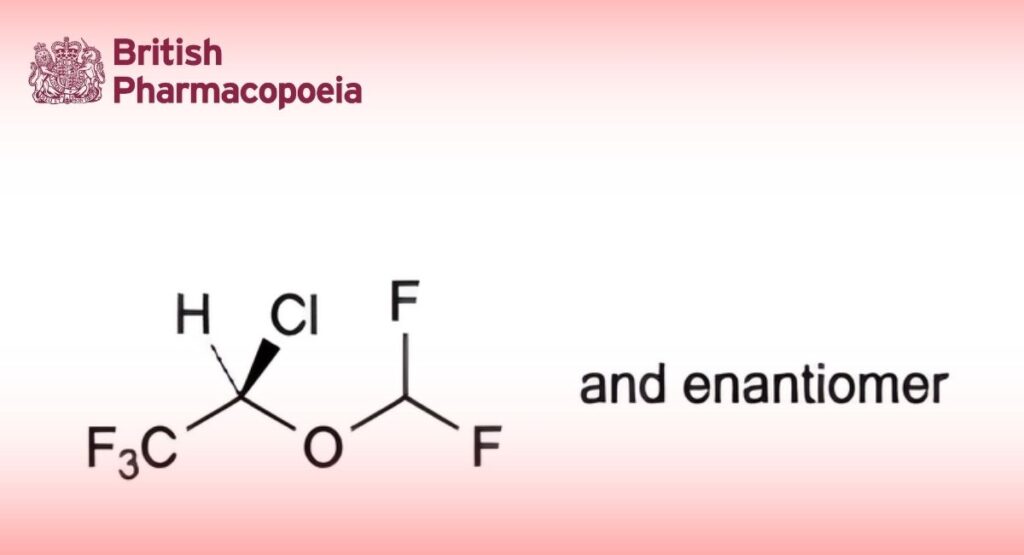
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1673)
C3H2ClF5O 184.5 26675-46-7
Action and use
General anaesthetic.
DEFINITION
(2RS)-2-Chloro-2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1-trifluoroethane.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, colourless, mobile, heavy liquid.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol.
bp
About 48 °C.
It is non-flammable.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Examine the substance in the gaseous state.
Comparison: Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of isoflurane.
TESTS
Acidity or alkalinity
To 20 mL add 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R, shake for 3 min and allow to stand. Collect the upper layer and add 0.2 mL of bromocresol purple solution R. Not more than 0.1 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide or 0.6 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Test solution: The substance to be examined.
Reference solution:To 80 mL of anhydrous ethanol R, add 1.0 mL of the substance to be examined and 1.0 mL of acetone R, avoiding loss by evaporation. Dilute to 100.0 mL with anhydrous ethanol R.
Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with anhydrous ethanol R.
Column:
— material: fused silica,
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.32 mm,
— stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness 0.25 μm).
Carrier: gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:25.
Temperature:
— column: 35 °C,
— injection port: 150 °C,
— detector: 250 °C.
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1.0 μL of each solution and 1.0 μL of anhydrous ethanol R as a blank.
Run time: Until elution of the ethanol peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
Relative retention: With reference to isoflurane (retention time = about 3.8 min): acetone = about 0.75.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum of 5 between the peaks due to acetone and to isoflurane,
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation 15.0 per cent for the peak due to isoflurane after 3 injections.
Limits:
— acetone: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.01 per cent),
— any other impurity: not more than the area of the peak due to isoflurane in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.01 per cent),
— total: not more than 3 times the area of the peak due to isoflurane in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.03 per cent),
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the peak due to isoflurane in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.001 per cent).
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 10 ppm.
To 10 mL add 10 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide and shake for 3 min. To 5 mL of the upper layer add 10 mL of water R.
Fluorides
Maximum 10 ppm.
Determine by potentiometry (2.2.36, Method I) using a fluoride-selective indicator-electrode and a silver-silver chloride reference electrode.
Test solution: To 10.0 mL in a separating funnel, add 10 mL of a mixture of 30.0 mL of dilute ammonia R2 and 70.0 mL of distilled water R. Shake for 1 min and collect the upper layer. Repeat this extraction procedure twice collecting the upper layer each time. Adjust the combined upper layers to pH 5.2 using dilute hydrochloric acid R. Add 5.0 mL of fluoride standard solution (1 ppm F) R and dilute to 50.0 mL with distilled water R. To 20.0 mL of the solution add 20.0 mL of total-ionic-strength-adjustment buffer R and dilute to 50.0 mL with distilled water R.
Reference solutions: To each of 5.0 mL, 4.0 mL, 3.0 mL, 2.0 mL and 1.0 mL of fluoride standard solution (10 ppm F) R add 20.0 mL of total-ionic-strength-adjustment buffer R and dilute to 50.0 mL with distilled water R.
Carry out the measurements on 20 mL of each solution. Calculate the concentration of fluorides using the calibration curve, taking into account the addition of fluoride to the test solution.
Non-volatile matter
Maximum 200 mg/L.
Evaporate 10.0 mL to dryness with the aid of a stream of cold air and dry the residue at 50 °C for 2 h. The residue weighs a maximum of 2.0 mg.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 1.0 mg/mL, determined on 10.0 mL.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
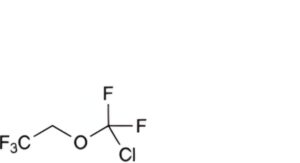
A. 2-(chlorodifluoromethoxy)-1,1,1-trifluoroethane,
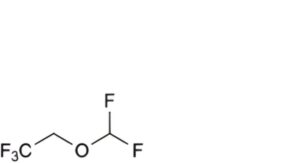
B. 2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1-trifluoroethane,
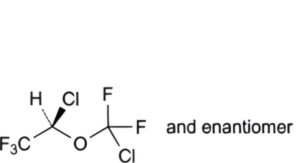
C. (2RS)-2-chloro-2-(chlorodifluoromethoxy)-1,1,1-trifluoroethane,
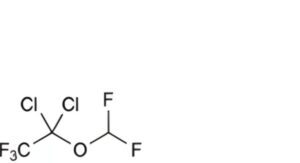
D. 1,1-dichloro-1-(difluoromethoxy)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane,
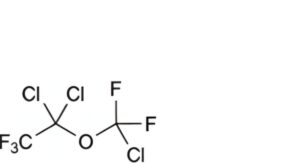
E. 1,1-dichloro-1-(chlorodifluoromethoxy)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane,
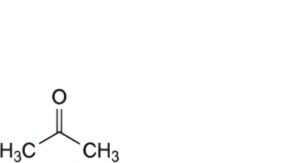
F. propanone (acetone).