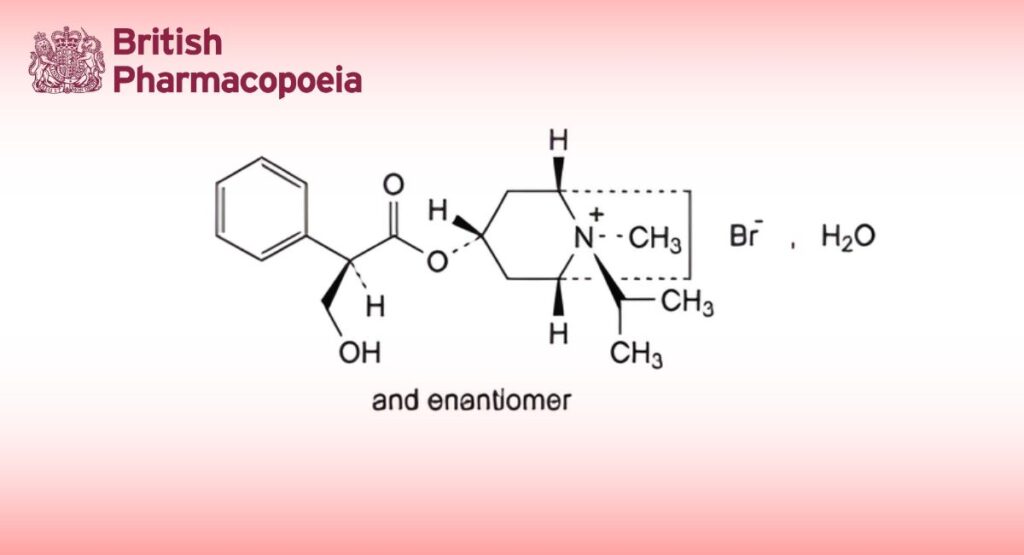
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0919)
C20H30BrNO3,H2O 430.4 66985-17-9
Action and use
Anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) bronchodilator.
Preparations
Ipratropium Nebuliser Solution
Ipratropium Pressurised Inhalation
DEFINITION
(1R,3r,5S,8r)-3-[[(2RS)-3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane bromide monohydrate.
Content
99.0 per cent to 100.5 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent)
mp
About 230 °C, with decomposition.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, E.
Second identification: B, C, D, E.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison ipratropium bromide CRS.
B. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for impurity A.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. To 5 mL of solution S (see Tests), add 2 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. No precipitate is formed.
D. To about 1 mg add 0.2 mL of nitric acid R and evaporate to dryness on a water-bath. Dissolve the residue in 2 mL of acetone R and add 0.1 mL of a 30 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R in methanol R. A violet colour develops.
E. It gives reaction (a) of bromides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.50 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY7(2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
5.0 to 7.5 for solution S.
Impurity A
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 1.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 20 mg of ipratropium bromide CRS in methanol R and dilute to 1.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 20 mg of methylatropine bromide CRS in 1.0 mL of reference solution (a).
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 5 mg of ipratropium impurity A CRS in 100.0 mL of methanol R. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 5.0 mL with methanol R.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 μm).
Mobile phase anhydrous formic acid R, water R, ethanol (96 per cent) R, methylene chloride R (1:3:18:18 V/V/V/V).
Application 1 μL.
Development Over a path of 6 cm.
Drying At 60 °C for 15 min.
Detection Spray with potassium iodobismuthate solution R5, allow the plate to dry in air, spray with a 50 g/L solution of sodium nitrite R and protect immediately with a sheet of glass.
System suitability The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 2 clearly separated principal spots.
Limit:
— impurity A: any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.1 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 10.0 mg of ipratropium bromide CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of ipratropium bromide CRS and 5 mg of ipratropium impurity B CRS in 1 mL of methanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.9 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase Dissolve 12.4 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and 1.7 g of tetrapropylammonium chloride R in 870 mL of water for chromatography R; adjust to pH 5.5 with a 180 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate R and add 130 mL of methanol R1.
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection 5 μL.
Run time 6 times the retention time of ipratropium.
Relative retention With reference to ipratropium (retention time = about 4.9 min): impurity C = about 0.7; impurity B = about 1.2; impurity D = about 1.8; impurity E = about 2.3; impurity F = about 5.1.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to impurity B and ipratropium;
— symmetry factor: maximum 2.5 for the principal peak.
Limits:
— correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity C = 0.3; impurity D = 0.2; impurity F = 0.5;
— impurity D: not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent);
— impurities B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent);
— disregard limit: one-third of the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.03 per cent); disregard the peak due to the bromide ion.
Water (2.5.12)
3.9 per cent to 4.4 per cent, determined on 0.50 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.350 g in 50 mL of water R and add 3 mL of dilute nitric acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M silver nitrate, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 41.24 mg of C20H30BrNO3.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by
the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) E, F.
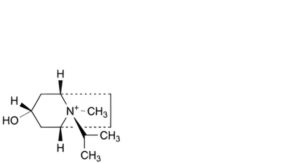
A. (1R,3r,5S,8r)-3-hydroxy-8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane,
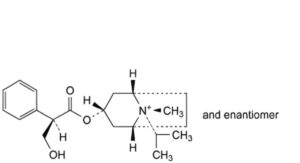
B. (1R,3r,5S,8s)-3-[[(2RS)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane,
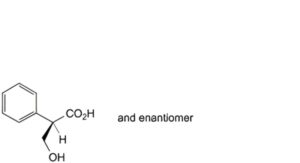
C. (2RS)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoic acid (DL-tropic acid),
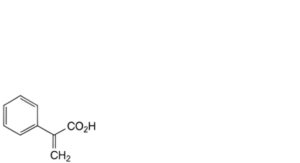
D. 2-phenylpropenoic acid (atropic acid),
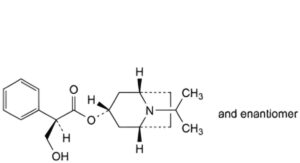
E. (1R,3r,5S)-8-(1-methylethyl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl (2RS)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate,
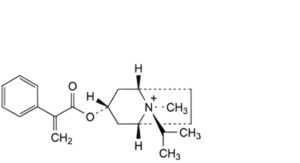
F. (1R,3r,5S,8r)-8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)-3-[(2-phenylpropenoyl)oxy]-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane.