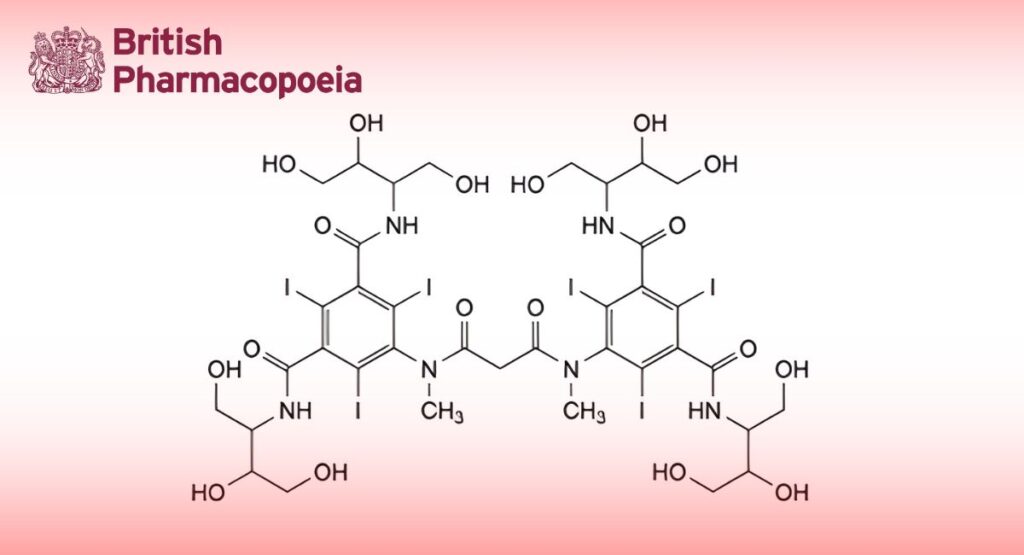
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1754)
C37H48I6N6O18 1626 79770-24-4
Action and use
Iodinated contrast medium.
DEFINITION
Mixture of stereoisomers of 5,5′-[propanedioylbis(methylimino)]bis[N,N′-bis[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]2,4,6- triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide].
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish-white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: iotrolan CRS.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 18.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Conductivity (2.2.38)
Maximum 25 μS·cm .
Dissolve 1.000 g in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Primary aromatic amines
Protect the solutions from light throughout the test. All given times are critical for the test results. The test solution, the reference solution and the blank solution must be processed in parallel.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.500 g of the substance to be examined in 20.0 mL of water R in a 25 mL volumetric flask.
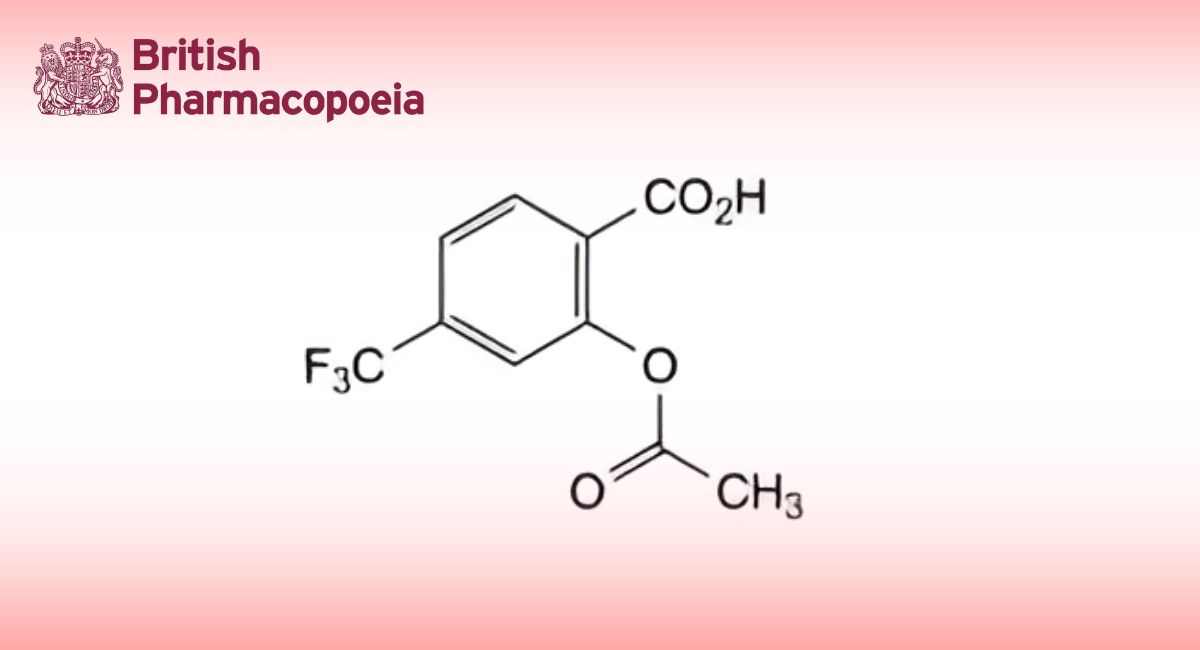
Reference solution: Dissolve 5.0 mg of iopamidol impurity A CRS in water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 25 mL volumetric flask and add 19.0 mL of water R.
Blank solution: Place 20.0 mL of water R in a 25 mL volumetric flask.
Procedure: Cool the test solution, reference solution and blank solution in a bath of iced water for 5 min. Add 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid R1 to each solution and cool again for 5 min in a bath of iced water. Add 1.0 mL of a 20 g/L solution of sodium nitrite R, shake vigorously and cool for another 5 min in a bath of iced water. To each solution add 0.50 mL of an 80 g/L solution of sulfamic acid R. Over the next 5 min, shake vigorously several times, raising the stoppers to vent the gas that evolves. Afterwards add to each solution 1.0 mL of a 1 g/L solution of naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride R in a mixture of 300 volumes of water R and 700 volumes of propylene glycol R, shake, allow to cool to room temperature for 10 min and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R. Degas the solutions in an ultrasonic bath for 1 min and measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the test solution and the reference solution at 495 nm against the blank, within 5 min.
System suitability:
— absorbance of the reference solution: minimum 0.40.
Limit:
— absorbance of the test solution: not more than the absorbance of the reference solution (0.05 per cent).
Related substances
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 200.0 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve the contents of a vial of iotrolan for system suitability CRS (containing about 0.05 per cent of each of impurities A and B) in 50 μL of a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Pretreatment: Over 3/4 of the plate with methylene chloride R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, water R, dioxan R (4:20:80 V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: In a current of air until the solvents have evaporated.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. Expose the plate to the ultraviolet light for 2-5 min until the principal spots appear clearly as yellow spots. Spray with ferric chloride-ferricyanide-arsenite reagent R and examine in daylight.
RF values Iotrolan = about 0.25; impurity A = about 0.4; impurity B = about 0.5.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— the chromatogram shows 3 clearly separated spots.
Limits:
— impurities A, B: any spot due to impurity A or B is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: any other spot is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent).
Isomer distribution
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described under Assay. Use the normalisation procedure.
Identification of peaks: Use the chromatogram supplied with iotrolan CRS and the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution to identify the peaks due to the 3 isomer groups.
Calculate the percentage content of each of the isomer groups G1, G2 and G3, with reference to the total area of all of the peaks due to the 3 isomer groups, using the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
Limits:
— isomer group G1: 53.0 per cent to 70.0 per cent;
— isomer group G2: 3.0 per cent to 11.0 per cent;
— isomer group G3: 25.0 per cent to 39.0 per cent.
Free iodine
Dissolve 0.20 g in 1 mL of water R in a glass-stoppered test tube. Add 4 mL of a 370 g/L solution of sulfuric acid R and 5 mL of toluene R, close and shake vigorously. The upper layer remains colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Iodide
Maximum 20 ppm.
Dissolve 10.0 g in 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Adjust to pH 3-4 adding about 0.15 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Titrate with 0.001 M silver nitrate, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Not more than 1.5 mL of 0.001 M silver nitrate is required to reach the end-point.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 3.5 per cent, determined on 0.250 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 0.7 IU/g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of iotrolan CRS in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase: methanol R, water for chromatography R (10:90 V/V).
Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 40 min.
Retention time: Isomer group G1 = about 8 min to 12 min; isomer group G2 = about 15 min to 22 min; isomer group G3 = about 22 min to 32 min.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— the chromatogram obtained is similar to the chromatogram supplied with iotrolan CRS.
Calculate the percentage content of iotrolan from the total area of all of the peaks of the 3 isomer groups G1, G2 and G3 and the declared content of iotrolan CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by
the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) C, D, E, F, G,
H, I, J.
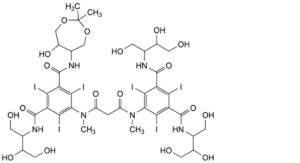
A. N,N′-bis[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]-5-[[3-[[3-[[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]carbamoyl]-5-[(6- hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxepan-5-yl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]methylamino]-3-oxopropanoyl]methylamino]-2,4,6-
triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
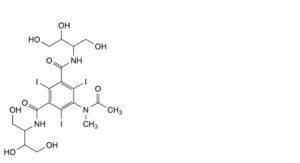
B. 5-(acetylmethylamino)-N,N′-bis[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
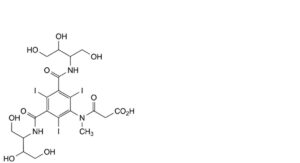
C. 3-[[3,5-bis[[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]methylamino]-3-oxopropanoic acid,
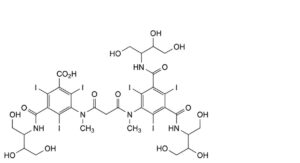
D. 3-[[3-[[3,5-bis[[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]methylamino]-3- oxopropanoyl]methylamino]-5-[[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic acid,
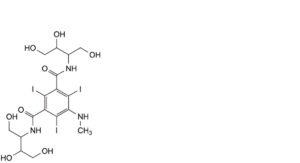
E. N,N′-bis[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]-2,4,6-triiodo-5-(methylamino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
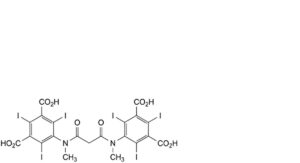
F. 5,5′-[propanedioylbis(methylimino)]bis[2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic] acid,
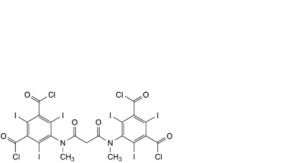
G. 5,5′-[propanedioylbis(methylimino)]bis[2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarbonyl] tetrachloride,
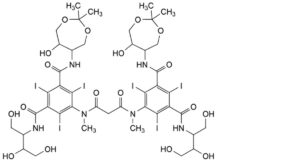
H. 5,5′-[propanedioylbis(methylimino)]bis[N-[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]-N′-(6-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-1,3- dioxepan-5-yl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide],
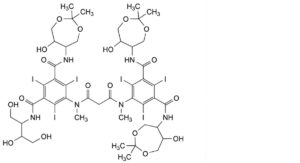
I. 5-[[3-[[3-[[2,3-dihydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]carbamoyl]-5-[(6-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxepan-5- yl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]methylamino]-3-oxopropanoyl]methylamino]-N,N′-bis(6-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-1,3- dioxepan-5-yl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
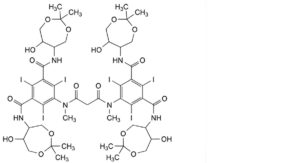
J. 5,5′-[propanedioylbis(methylimino)]bis[N,N′-bis(6-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxepan-5-yl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3- dicarboxamide].