(Ph. Eur. monograph 0700)
C11H12I3NO2 571 96-83-3
Action and use
Iodinated contrast medium.
DEFINITION
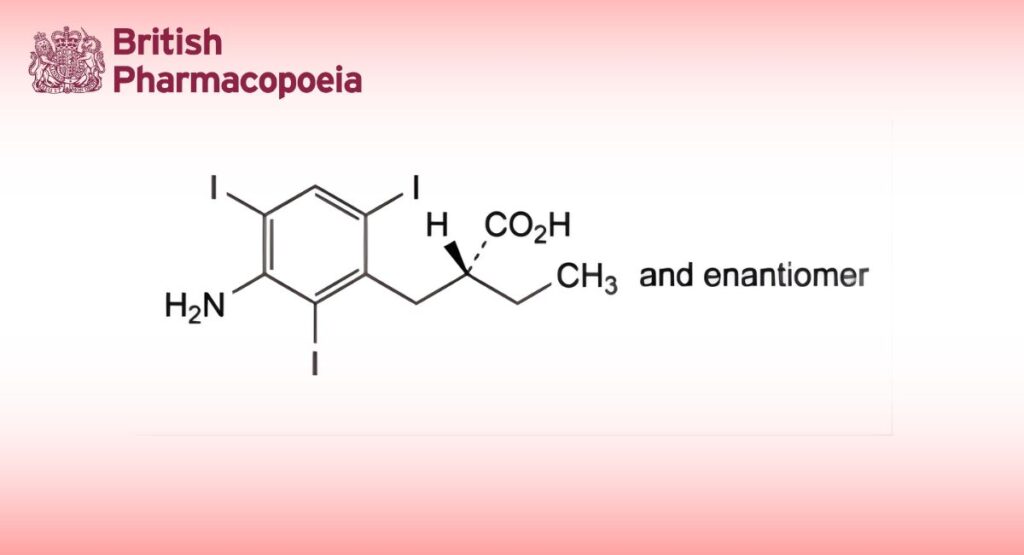
Iopanoic acid contains not less than 98.5 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of (RS)-2-(3-amino- 2,4,6-tri-iodobenzyl)butanoic acid, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or yellowish-white powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methanol. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): about 155 °C, with decomposition.
B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with iopanoic acid CRS.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances (see Tests). Spray the plate with a 1 g/L solution of 4-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde R in a mixture of 1 volume of hydrochloric acid R and 99 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. Heat 50 mg carefully in a small porcelain dish over a flame. Violet vapour is evolved.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
Dissolve 1.0 g in 1 M sodium hydroxide and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent. The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y3 (2.2.2, Method II).
Related substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using silica gel GF254 R as the coating substance.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 1.0 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 3 volumes of ammonia R and 97 volumes of methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 10 mL with a mixture of 3 volumes of ammonia R and 97 volumes of methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50 mg of iopanoic acid CRS in a mixture of 3 volumes of ammonia R and 97 volumes of methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (b) to 50 mL with a mixture of 3 volumes of ammonia R and 97 volumes of methanol R.
Apply separately to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 10 cm using a mixture of 10 volumes of concentrated ammonia R, 20 volumes of methanol R, 20 volumes of toluene R and 50 volumes of dioxan R. Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent).
Halides
To 0.46 g add 10 mL of nitric acid R and 15 mL of water R. Shake for 5 min and filter. 15 mL of the filtrate complies with the limit test for chlorides (2.4.4) (180 ppm, expressed as chloride).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 1 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
To 0.150 g in a 250 mL round-bottomed flask add 5 mL of strong sodium hydroxide solution R, 20 mL of water R, 1 g of zinc powder R and a few glass beads. Boil under a reflux condenser for 60 min. Allow to cool and rinse the condenser with 20 mL of water R, adding the rinsings to the flask. Filter through a sintered-glass filter (2.1.2) and wash the filter with several quantities of water R. Collect the filtrate and washings. Add 40 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and titrate immediately with 0.1 M silver nitrate. Determine the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 19.03 mg of C11H12I3NO2.
STORAGE
Store protected from light.