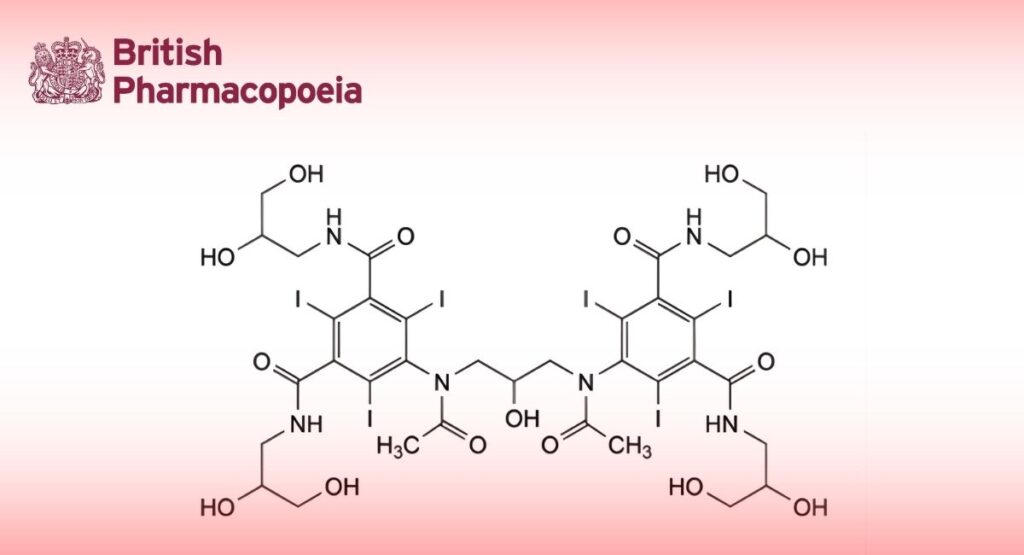
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2215)
C35H44I6N6O15 1550 92339-11-2
Action and use
Iodinated contrast medium.
DEFINITION
Mixture of stereoisomers of 5,5′-[(2-hydroxypropane-1,3-diyl)bis(acetylimino)]bis[N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6- triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide].
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder, hygroscopic.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: iodixanol CRS.
B. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection: Test solution and reference solution (b).
Results: The 3 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in retention time to the 3 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Heat solution S at about 98 °C for 30 min without boiling, then allow to cool to room temperature. The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Impurities: E and H
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of iodixanol impurity H CRS in water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve the contents of a vial of iodixanol impurity E CRS in a mixture of 100 μL of the test solution, 100 μL of reference solution (b) and 800 μL of water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: aminopropylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile R, water for chromatography R (50:50 V/V);
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2 | 30 | 70 |
| 2 – 27 | 30 → 68 | 70 → 32 |
Flow rate: 1.7 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 10 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a) and (c).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities E and H.
Relative retention With reference to iodixanol (1 peak) (retention time = about 16 min): impurity E (1 peak) = about 0.7; impurity E (2 peak) = about 0.8; impurity H = about 1.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the 1 peak due to impurity E and the 1 peak due to iodixanol.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of the total content of impurity E, multiply the peak area of the 1 peak due to impurity E by 1.7;
— impurity H: not more than 0.6 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.6 per cent);
— impurity E: not more than 0.3 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent).
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 25 mg of iodixanol CRS in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of iodixanol impurity C CRS and 5 mg of iopentol CRS in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 100 mL with water R.
Reference solution (d): Mix 5 mL of the test solution and 5 mL of reference solution (c) and dilute to 50 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R, water for chromatography R (50:50 V/V);
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2 | 94 | 6 |
| 2 – 32 | 94 → 80 | 6 → 20 |
| 32 – 72 | 80 → 0 | 20 → 100 |
| 72 – 82 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 10 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a), (c) and (d).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurity C and iopentol.
Relative retention: With reference to iodixanol (1 peak) (retention time = about 27 min): iopentol (1 peak) = about 0.8; iopentol (2 peak) = about 0.9; impurity C (1 peak) = about 1.04; overalkylated impurities (a group of peaks) = 1.33-1.70.
System suitability: Reference solution (d):
— resolution: baseline separation between the 2 peaks due to iopentol;
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 1.3, where Hp = height above the baseline of the 1 peak due to impurity C and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the 1 peak due to iodixanol.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of the total content of impurity C, multiply the peak area of the 1 peak due to impurity C by 1.3;
— impurity C: not more than 0.4 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.4 per cent);
— overalkylated impurities (such as impurity I): not more than the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.1 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 1.5 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the sum of the areas of the 2 principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
Free aromatic amine
Maximum 500 ppm.
Test solution: Transfer 0.200 g of the substance to be examined to a 25 mL volumetric flask and dissolve in 15.0 mL of water R.
Reference solution: Dissolve 5.0 mg of iohexol impurity J CRS in water R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R. Mix 10.0 mL of this solution and 5.0 mL of water R in a 25 mL volumetric flask.
Blank solution: Transfer 15.0 mL of water R to a 25 mL volumetric flask.
In conducting the following steps, keep the flasks in iced water and protected as much as possible from light until all the reagents have been added.
Place the 3 flasks containing respectively the test solution, the reference solution and the blank solution in iced water, protected from light, for 5 min. Add 1.5 mL of hydrochloric acid R1 and mix by swirling. Add 1.0 mL of a 20 g/L solution of sodium nitrite R, mix and allow to stand for 4 min. Add 1.0 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sulfamic acid R, swirl gently until gas liberation has ceased and allow to stand for 1 min. (CAUTION: considerable pressure is produced).
Add 1.0 mL of a freshly prepared 3 g/L solution of naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride R in a mixture of 30 volumes of water R and 70 volumes of propylene glycol R and mix. Remove the flasks from the iced water, dilute to 25.0 mL with water R, mix and examine the solutions after 5 min. The solution obtained from the test solution is less coloured than the solution obtained from the reference solution. If the solution obtained from the test solution is about the same colour or darker than the solution obtained from the reference solution, proceed as follows. Concomitantly determine the absorbance (2.2.25) at 495 nm of the solution obtained from the test solution and the reference solution in 5 cm cells, using the blank solution as the compensation liquid. The absorbance of the solution obtained from the test solution is not greater than that of the solution obtained from the reference solution.
Free iodine
Transfer 2.0 g to a glass-stoppered tube, add 20 mL of water R, 5 mL of toluene R and 5 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R, shake vigorously and allow the phases to separate: the toluene layer shows no red or pink colour.
Iodide
Maximum 10 ppm.
Dissolve 5.000 g in water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent. Titrate with 0.001 M silver nitrate. Determine the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20) using a silver indicator electrode and an appropriate reference electrode.
1 mL of 0.001 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 126.9 μg of iodide.
Ionic compounds (2.2.38)
Maximum 0.02 per cent m/m calculated as sodium chloride.
Rinse all glassware with distilled water R 5 times before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of sodium chloride R in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Measure the specific conductivity of the test solution and the reference solution using a suitable conductivity meter. The specific conductivity of the test solution is not greater than that of the reference solution.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 4.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g.
ASSAY
In a 125 mL round-bottomed flask, dissolve 0.200 g in 25 mL of a 50 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R, add 0.5 g of zinc powder R and a few glass beads. Boil under a reflux condenser for 1 h. Allow to cool and rinse the condenser with 20 mL of water R, adding the rinsings to the flask. Filter through a sintered-glass filter (40) (2.1.2) and wash the filter with several quantities of water R. Collect the filtrate and washings. Add 5 mL of glacial acetic acid R and titrate immediately with 0.1 M silver nitrate. Determine the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 25.84 mg of C35H44I6N6O15.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities C, E, H, overalkylated impurities.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.
They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities. It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, F, G.
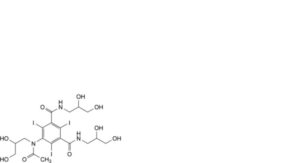
A. 5-[acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide (iohexol),

B. 5-acetamido-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
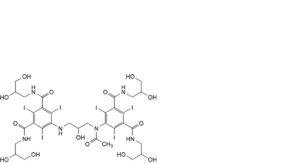
C. 5-[acetyl[3-[[3,5-bis[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]-N,N′-bis(2,3- dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
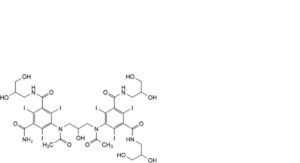
E. 5-[acetyl[3-[acetyl[3-carbamoyl-5-[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
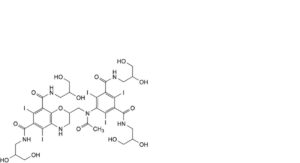
F. 2-[[acetyl[3,5-bis[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]methyl]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5,7-diiodo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazine-6,8-dicarboxamide,
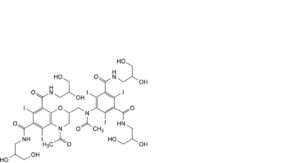
G. 4-acetyl-2-[[acetyl[3,5-bis[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]methyl]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5,7-diiodo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazine-6,8-dicarboxamide,
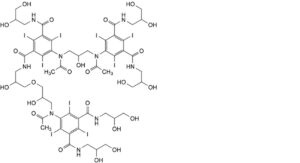
H. 5-[acetyl[3-[acetyl[3-[[3-[3-[acetyl[3,5-bis[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropoxy]-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamoyl]-5-[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide,
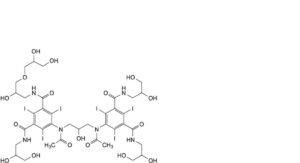
I. overalkylated impurities (an example): 5-[acetyl[3-[acetyl[3,5-bis[(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl]-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]-N-[3-(2,3-dihydroxypropoxy)-2-hydroxypropyl]-N′-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide.