(Ph. Eur. monograph 2084)
C256H381N65O79S6 5826
Action and use
Hormone; treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Preparation
Biphasic Insulin Aspart Injection
DEFINITION
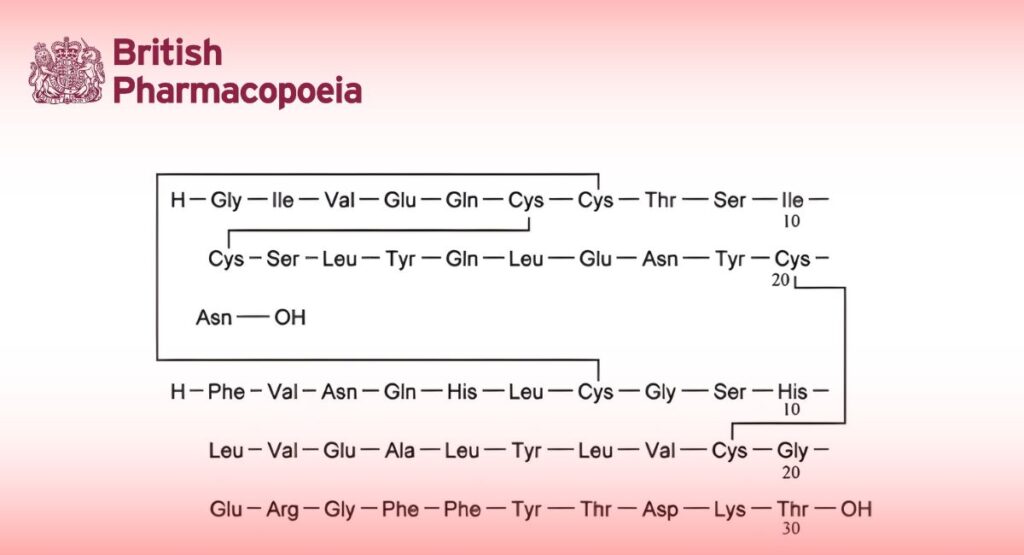
28 -L-Aspartate insulin (human).
Insulin aspart is a 2-chain peptide containing 51 amino acids. The A-chain is composed of 21 amino acids and the B-chain is composed of 30 amino acids. It is identical in primary structure to human insulin, except that it has aspartic acid instead of proline at position 28 of the B-chain. As in human insulin, insulin aspart contains 2 interchain disulfide bonds and 1 intrachain disulfide bond.
Content
90.0 per cent to 104.0 per cent of insulin aspart C256H381N65O79S6 plus A21Asp insulin aspart, B3Asp insulin aspart, B3isoAsp insulin aspart and B28isoAsp insulin aspart (dried substance).
By convention, for the purpose of labelling insulin aspart preparations, 0.0350 mg of insulin aspart is equivalent to 1 unit.
PRODUCTION
Insulin aspart is produced by a method based on recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology under conditions designed to minimise the degree of microbial contamination.
Prior to release, the following tests are carried out on each batch of insulin aspart, unless exemption has been granted by the competent authority.
Host-cell-derived proteins
The limit is approved by the competent authority.
Single-chain precursor
The limit is approved by the competent authority. Use a suitably sensitive method.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent), in methanol and in aqueous solutions with a pH around 5.1. In aqueous solutions below pH 3.5 or above pH 6.5, the solubility is greater than or equal to 25 mg/mL.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results: The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in retention time to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
B. Peptide mapping (2.2.55).
SELECTIVE CLEAVAGE OF THE PEPTIDE BONDS
Test solution: Prepare a 2.0 mg/mL solution of the substance to be examined in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and transfer 25 μL of this solution to a clean tube. Add 100 μL of HEPES buffer solution pH 7.5 R and 20 μL of a 1 mg/mL solution of Staphylococcus aureus strain V8 protease, type XVII-B R. Cap the tube and incubate at 25 °C for 6 h. Stop the reaction by adding 145 μL of sulfate buffer solution pH 2.0 R.
Reference solution: Prepare at the same time and in the same manner as for the test solution, but using insulin aspart CRS instead of the substance to be examined.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm,
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm) with a pore size of 8 nm,
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 100 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R, 200 mL of sulfate buffer solution pH 2.0 R and 700 mL of water R; filter and degas;
— mobile phase B: mix 200 mL of sulfate buffer solution pH 2.0 R, 400 mL of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 400 mL of water R; filter and degas;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 60 | 90 → 30 | 10 → 70 |
| 60 – 65 | 30 → 0 | 70 → 100 |
| 65 – 70 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Equilibration: At initial conditions for at least 15 min. Carry out a blank run using the above-mentioned gradient.
Injection: 50 μL.
System suitability:
— the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution is qualitatively similar to the chromatogram of insulin aspart digest supplied with insulin aspart CRS,
— in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution, identify the peaks due to digest fragments I, II and III: symmetry factor Maximum 1.5, for the peaks due to fragments II and III, resolution Minimum 8.0, between the peaks due to fragments II and III.
Results: The profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
NOTE: the retention times of fragments I, II and IV are the same as for human insulin. The retention time of fragment III differs from human insulin due to substitution of proline by aspartic acid.
TESTS
Impurities with molecular masses greater than that of insulin aspart
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution: Prepare a solution containing 4 mg/mL of the substance to be examined in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid.
Maintain the solution at 2-8 °C and use within 48 h.
Resolution solution: Use a solution of insulin (about 4 mg/mL), containing more than 0.4 per cent of high molecular mass proteins. An injectable insulin preparation, whether a solution or a suspension, that has been clarified with a sufficient amount of 6 M hydrochloric acid R, containing the indicated percentage of high molecular mass proteins, or a solution prepared from insulin, dissolved in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid may be used. Insulin containing the indicated percentage of high molecular mass proteins may be prepared by allowing insulin powder to stand at room temperature for about 10 days.
Maintain the solution at 2-8 °C and use within 7 days.
Column:
— size: l = 0.3 m, Ø = 7.8 mm,
— stationary phase: hydrophilic silica gel for chromatography R (5-10 μm) with a pore size of 12-12.5 nm, of a grade suitable for the separation of insulin monomer from dimer and polymers.
Mobile phase: Mix 15 volumes of glacial acetic acid R, 20 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 65 volumes of a 1.0 g/L solution of arginine R; filter and degas.
Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 276 nm.
Equilibration: At least 3 injections of the resolution solution; the column is equilibrated when repeatable results are obtained from 2 subsequent injections.
Injection: 100 μL.
Run time: About 35 min.
Retention time: Insulin aspart polymers = 13-17 min; insulin aspart dimer = about 17.5 min; insulin aspart monomer = about 20 min; salts = about 22 min.
System suitability Resolution solution:
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to the dimer and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to the monomer.
Limits: The sum of the areas of the peaks with a retention time less than that of the principal peak is not more than 0.5 per cent of the total area of the peaks. Disregard any peak with a retention time greater than that of the peak due to insulin aspart monomer.
Related proteins
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described under Assay: use the normalisation procedure.
Limits:
— B28isoAsp insulin aspart: maximum 1.0 per cent,
— total of the peaks due to A21Asp insulin aspart, B3Asp insulin aspart and B3isoAsp insulin aspart: maximum 2.0 per cent,
— total of other impurities: maximum 1.5 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 10.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 6.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g (dried substance).
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 10 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve the substance to be examined in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid to obtain a concentration of 4.0 mg/mL.
Maintain the solution at 2-8 °C and use within 24 h.
Reference solution: Dissolve the contents of a vial of insulin aspart CRS in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid to obtain a concentration of 4.0 mg/mL. Maintain the solution at 2-8 °C and use within 48 h.
Resolution solution: Use an appropriate solution with a content of B3Asp insulin aspart and A21Asp insulin aspart of not
less than 1 per cent. This may be achieved by storing reference solution at room temperature for about 1-3 days. Maintain the solution at 2-8 °C and use within 72 h.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm,
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm),
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 142.0 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R in water R; add 13.5 mL of phosphoric acid R and dilute to 5000 mL with water R; adjust to pH 3.6, if necessary, with strong sodium hydroxide solution R; filter and degas; mix 9 volumes of the solution with 1 volume of acetonitrile for chromatography R; filter and degas;
— mobile phase B: mix equal volumes of water R and acetonitrile for chromatography R; filter and degas;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 35 | 58 | 42 |
| 35 – 40 | 58 → 20 | 42 → 80 |
| 40 – 45 | 20 | 80 |
| 45 – 46 | 20 → 58 | 80 → 42 |
| 46 – 60 | 58 | 42 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to insulin aspart (retention time = 20-24 min): B28isoAsp insulin aspart = about 0.9; B3Asp insulin aspart plus A21Asp insulin aspart (generally coeluted) = about 1.3; B3isoAsp insulin aspart = about 1.5.
System suitability: Resolution solution:
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peak due to insulin aspart and the peak due to A21Asp insulin aspart and to B3Asp insulin aspart.
Calculate the content of insulin aspart C256H381N65O79S6, plus B28isoAsp insulin aspart, A21Asp insulin aspart, B3Asp insulin aspart and B3isoAsp insulin aspart using the areas of the corresponding peaks in the chromatograms obtained with the test solution and reference solution and the declared content of insulin aspart plus B28isoAsp insulin aspart, A21Asp insulin aspart, B3Asp insulin aspart and B3isoAsp insulin aspart in insulin aspart CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light, at or below -18 °C until released by the manufacturer. When thawed, insulin aspart is stored at 5 ± 3 °C and used for manufacturing preparations within a short period of time. To avoid absorption of humidity from the air during weighing, insulin aspart must be at room temperature before opening the container.