(Ph. Eur. monograph 2928)
Mr approx. 145 kDa (dimer without glycosylation)
C6462H9960N1728O2036S44 (dimer without glycosylation)
Action and use
Monoclonal antibody (TNF alfa).
DEFINITION
Solution of a monoclonal antibody consisting of a bisdisulfide dimer of 1328 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of approximately 145 kDa, which binds with high affinity to both soluble and transmembrane forms of TNF-α.
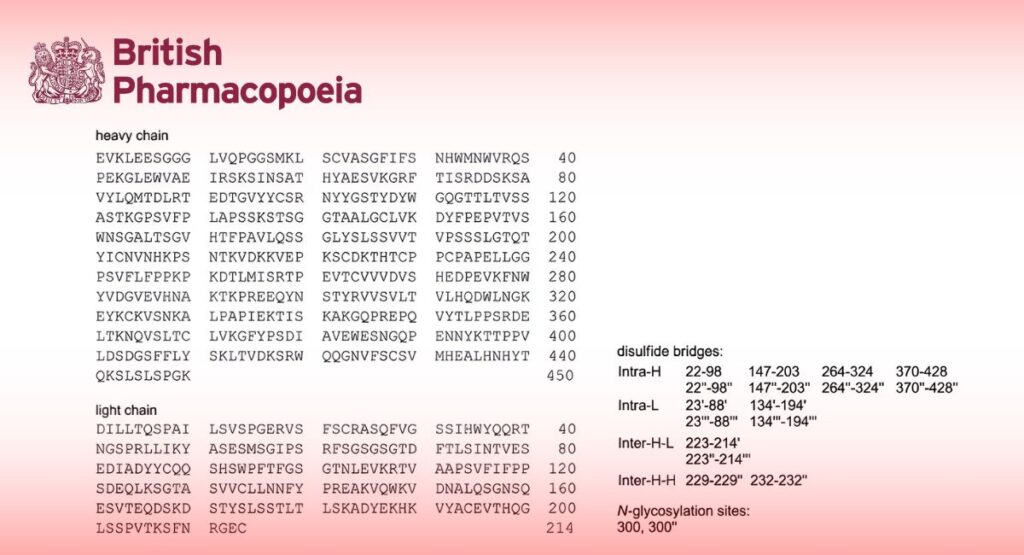
Infliximab is a chimeric human-murine IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody representing a glycosylated immunoglobulin with 1 N-linked glycosylation site (Asn 300) in the CH2 domain of each heavy chain. The detected oligosaccharides are mostly G0F (absence of terminal galactose) and G1F (1 terminal galactose) structures. Each heavy chain consists of 450 amino acids with 11 cysteine residues, and each light chain consists of 214 amino acids with 5 cysteine residues. All cysteine residues in heavy and light chains are involved in either intra- or inter-disulfide bonding.
Content (milligrams of protein per millilitre) As approved by the competent authority.
Potency
8 × 103 to 12 × 103 IU per milligram of protein.
PRODUCTION
Infliximab is produced in a suitable mammalian cell expression system by a method based on recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. In the course of product development, it must be demonstrated that the manufacturing process consistently produces a product with the expected N-glycan occupancy and Fc-effector functions (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC)) using suitably qualified assay(s).
Prior to release, the following tests are carried out on each batch of infliximab concentrated solution, unless an exemption has been granted by the competent authority.
Host-cell-derived proteins (2.6.34)
The limit is approved by the competent authority.
Host-cell- and vector-derived DNA
The limit is approved by the competent authority.
Residual Protein A
Use a suitable immunochemical method (2.7.1) based on an ELISA. To determine residual Protein A, the preparation to be examined is transferred to an ELISA microplate coated with an anti-protein A capture antibody. Peroxidase-conjugated polyclonal anti-protein A antibody is added followed by a peroxidase substrate. Optical density is measured and the amount of residual Protein A is calculated using a standard curve and the usual statistical methods (for example, 5.3).
Limit As approved by the competent authority.
Glycan analysis
Use a suitable procedure developed according to general chapter 2.2.59. Glycan analysis of glycoproteins, section 2-3:
— after desalting, release the glycans using one of the agents described in Table 2.2.59.-1, for example peptide N- glycosidase F (PNGase F);
— if needed, label the released glycans with one of the fluorescent labelling agents described in Table 2.2.59.-2;
— analyse the labelled or unlabelled glycans using a suitable technique.
The following procedure is given as an example.
Solution A: Dissolve 0.17 g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and 0.53 g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R in water R. Adjust to pH 7.6 with sodium hydroxide solution R or hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: Desalt a volume of the preparation to be examined by a suitable method (for example, using a suitable centrifugal filter with water for chromatography R as elution buffer), and dilute with solution A to obtain a concentration of about 1 mg/mL. To 200 μL of this solution add 0.3 μL of a 500 000 U/mL solution of peptide N-glycosidase F R. Incubate at 37 °C for at least 16 hours.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in water R. Desalt a volume of this preparation and carry out the glycan release at the same time and in the same manner as for the test solution.
Reference solution (b): Use a suitable infliximab in-house reference preparation shown to be representative of batches tested clinically and batches used to demonstrate consistency of production. Desalt a volume of this preparation and carry out the glycan release at the same time and in the same manner as for the test solution.
Blank solution Use 200 μL of solution A to proceed to glycan release.
Analyse the native glycans by liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Precolumn:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 3.0 mm;
— stationary phase: strongly basic anion-exchange resin for chromatography R2 (5.5 μm).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 3.0 mm;
— stationary phase: strongly basic anion-exchange resin for chromatography R2 (5.5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 2 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R;
— mobile phase B: solution containing 2 g/L of sodium hydroxide R and 10.25 g/L of anhydrous sodium acetate R;
— mobile phase C: solution containing 2 g/L of sodium hydroxide R and 41 g/L of anhydrous sodium acetate R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase C
(per cent V/V) |
Flow rate
(mL/min) |
| 0 – 5 | 99.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.35 |
| 5 – 45 | 99.2 → 95.2 | 0.8 → 4.8 | 0 | 0.35 |
| 45 – 50 | 95.2 → 72 | 4.8 → 28 | 0 | 0.35 |
| 50 – 77 | 72 → 4 | 28 → 96 | 0 | 0.35 |
| 77 – 77.1 | 4 → 0 | 96 → 0 | 0 → 100 | 0.35 |
| 77.1 – 87 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.40 |
Detection: Electrochemical detector (pulsed amperometry).
Autosampler: Set at 2-8 °C.
Injection: 25 μL.
Identification of peaks: Use the chromatogram in Figure 2928.-1 to identify the 7 peaks corresponding to fucosylated (peaks 1, 4 and 5), afucosylated (peaks 2 and 3) and sialylated (peaks 6 and 7) glycans; record the retention time of each peak.
System suitability:
— the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) is qualitatively similar to the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS and peaks 1 to 7 are clearly visible;
— no significant peaks are observed in the chromatogram obtained with the blank solution.
Results:
— the profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— the retention times of the peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution correspond to those in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— no additional peaks are observed in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution in comparison with the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Calculate the relative peak areas of the individual peaks corresponding to fucosylated, afucosylated and sialylated glycans with reference to the sum of the areas of all retained glycan peaks.
Calculate the percentage contents of fucosylated, afucosylated and sialylated glycans, using the following expressions:
A/ (A + B + C) x 100
B/ (A + B + C) x 100
C/ (A + B + C) x 100
A = sum of the areas of the peaks due to fucosylated glycans;
B = sum of the areas of the peaks due to afucosylated glycans;
C = sum of the areas of the peaks due to sialylated glycans.
NOTE: sialylated glycans elute as peak clusters and are integrated as such.
Limits:
— percentage of fucosylated glycans: as authorised by the competent authority;
— percentage of afucosylated glycans: as authorised by the competent authority;
— percentage of sialylated glycans: as authorised by the competent authority.
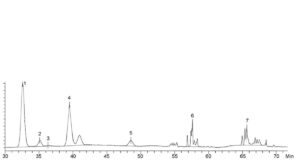
| Peak | Charged | Glycoform | Peak | Charged | Glycoform |
| 1. | No | Fucosylated G0F (absence of terminal galactose) | 5. | No | Fucosylated G2F (2 terminal galactoses) |
| 2. | No | Afucosylated Man5 (addition of 2 mannoses instead of terminal N- acetylglucosamine) | 6. | Yes | Sialylated SA1 (addition of 1 sialic acid) |
| 3. | No | No Afucosylated G0 (absence of fucose) | 7. | Yes | Yes Sialylated SA2 (addition of 2 sialic acids) |
| 4. | No | Fucosylated G1F (1 terminal galactose) |
Figure 2928.-1. – Chromatogram for glycan analysis of infliximab
Charged variants
A. Isoelectric focusing (2.2.54): use suitable agarose gels.
The following procedure is given as an example.
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with water R to obtain a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in water R to obtain a concentration of
0.5 mg/mL.
Reference solution (b): Use a suitable infliximab in-house reference preparation shown to be representative of batches tested clinically and batches used to demonstrate consistency of production. Dilute with water R to obtain a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL.
Reference solution (c): Use an isoelectric point (pI) calibration solution, in the pI range of 3-10, prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Adjust the concentration to allow detection of all marker proteins.
Focusing:
— pH gradient: 3-10;
— catholyte: 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R;
— anolyte: 2.87 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R;
— application: 15 μL.
For each gel, run 2 lanes with reference solution (a), 2 lanes with reference solution (b) and 2 lanes with reference solution (c); use the remaining lanes for the test solution. Proceed with the isoelectric focusing by applying the electrical parameters according to the manufacturer’s instructions (the following parameters have been found suitable: 1500 V, 7 mA, 25 W and 80 min).
Detection: As described in general chapter 2.2.54, with the following modifications.
Immerse the gel in a solution containing 36 g/L of sulfosalicylic acid R, 60 g/L of trichloroacetic acid R and 285 g/L of methanol R. Incubate with gentle shaking at room temperature for 30 min. Drain off the solution and transfer the gel to a mixture of 80 volumes of glacial acetic acid R, 250 volumes of anhydrous ethanol R and 670 volumes of water R (mixture A); while shaking, rinse for 10 min at room temperature. Immerse the gel in a staining solution (1 g/L solution of acid blue 83 R in mixture A) and incubate for 20 min at room temperature.
Destain the gel by passive diffusion (for at least 6 h) with mixture A until the bands are well visualised against a clear background. Soak and wash the gel for 1 h with water R.
System suitability:
— in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (a), 7 bands (4 major and 3 minor) in the pI region 7.35-8.30 are clearly visible;
— in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (c), the relevant pI markers are distributed along the entire length of the gel.
Results:
— the electropherogram obtained with the test solution is similar to the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b). Plot the migration distances of the relevant pI markers versus their pI and determine the isoelectric points of the principal components of the test solution and reference solution (b); they do not differ by more than 0.05 pI units;
— no additional bands are observed in the electropherogram obtained with the test solution in comparison to the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Alternatively, use a suitable capillary isoelectric focusing procedure developed according to general chapter 2.2.47.
Capillary electrophoresis.
B. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with mobile phase A to obtain a concentration of about 1 mg/mL.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in mobile phase A to obtain a concentration of about 1 mg/mL.
Reference solution (b): Use a suitable infliximab in-house reference preparation shown to be representative of batches tested clinically and batches used to demonstrate consistency of production. Dilute with mobile phase
A to obtain a concentration of about 1 mg/mL.
Precolumn:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: weak cation-exchange resin R (10 μm).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: weak cation-exchange resin R (10 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: dissolve 0.56 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and 1.14 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R in 800 mL of water for chromatography R, and adjust to pH 7.25, if necessary, with sodium hydroxide solution R or hydrochloric acid R; dilute to 1000.0 mL with water for chromatography R and degas;
— mobile phase B: dissolve 0.56 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R, 1.14 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R and 58.44 g of sodium chloride R in 800 mL of water for chromatography R, and adjust to pH 7.25, if necessary, with sodium hydroxide solution R or hydrochloric acid R; dilute to 1000.0 mL with water for chromatography R and degas;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 15 | 100 → 92 | 0 → 8 |
| 15 – 16 | 92 → 60 | 8 → 40 |
| 16 – 21 | 60 | 40 |
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Autosampler: Set at 10 °C.
Injection: 50 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to the peak due to isoform 6 (retention time = about 9.2 min): isoform 1 = 0.68; isoform 2 = 0.74; isoform 3 = 0.80; isoform 4 = 0.87; isoform 5 = 0.95.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— the chromatogram obtained is similar to the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS;
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to isoforms 3 and 4.
Results:
— the profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— the relative retentions of the peaks due to isoforms 2, 3 and 4 in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are within 1 per cent of those of the corresponding peaks in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Calculate the relative peak areas of the individual peaks due to isoforms with reference to the total area of all peaks eluting between 3 min and 11 min.
Limits:
— sum of isoforms 1 and 2: as authorised by the competent authority;
— sum of isoforms 3, 4 and 6: as authorised by the competent authority;
— isoform 5: as authorised by the competent authority.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Opalescent or slightly opalescent, colourless or light yellow liquid.
IDENTIFICATION
A. It complies with the limits of the assay (potency).
B. Peptide mapping (2.2.55).
SELECTIVE CLEAVAGE OF THE PEPTIDE BONDS
Dilution buffer: Dissolve 50.00 g of sucrose R, 0.22 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R, 0.61 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate R and 0.05 g of polysorbate 80 R in water R. Adjust to pH 7.2, if necessary, and dilute to 500.0 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with the dilution buffer to obtain a concentration of about 5 mg/mL.
Reference solution: Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in the dilution buffer to obtain a concentration of about 5 mg/mL.
Reduction and alkylation: Dilute the test solution with guanidine-tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-EDTA buffer solution pH 8.6 R to obtain a concentration of 2 mg/mL. To 1 mL of this solution add 10 μL of a 154 g/L solution of dithiothreitol R and incubate at 37 °C for 1 h. Add 20 μL of a freshly prepared 185 g/L solution of iodoacetamide R and incubate at room temperature for 15 min, protected from light. Add 10 μL of a 154 g/L of solution of dithiothreitol R and mix well.
Digestion: Desalt a volume of the reduced solution prepared previously by a suitable method (for example, using a suitable centrifugal filter unit with tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH 7.5 R1 as elution buffer), and adjust the concentration to 1 mg/mL with tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH 7.5 R1. Prepare a 0.5 mg/mL solution of trypsin for peptide mapping R, and add 10 μL of the solution to 100 μL of the desalted solution. Incubate at 37 °C for 16 h. Add 2 μL of a 150 g/L solution of trifluoroacetic acid R and mix gently using a vortex mixer.
NOTE: a protease/protein ratio of 1:20 (m/m) is recommended.
Carry out the reduction/alkylation and digestion steps for the reference solution in the same manner as for the test solution.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm) with a pore size of 30 nm;
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: add 0.6 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R to 1000 mL of water for chromatography R; degas;
— mobile phase B: add 0.6 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R to a mixture of 100 mL of water for chromatography R and 900 mL of acetonitrile R1; degas;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 3 | 100 | 0 |
| 3 – 115 | 100 → 50 | 0 → 50 |
| 115 – 115.5 | 50 → 10 | 50 → 90 |
| 115.5 – 135 | 10 | 90 |
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Autosampler: Set at 2-8 °C.
Injection: 80 μL.
Identification of peaks: Use the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS to identify peaks 1 to 20.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— the chromatogram obtained is qualitatively similar to the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS and peaks 1 to 20 are clearly visible;
— peaks 5 and 6 are separated as shown in the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS.
Results:
— the profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
— no additional peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution has an area greater than 0.5 per cent of the sum of the areas of peaks 1 to 20.
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
As approved by the competent authority.
Related proteins
Capillary electrophoresis (2.2.47) under both reducing and non-reducing conditions.
Sample buffer: Dissolve 1 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate R in tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer solution pH 9.0 R1 and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solution.
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with water R to obtain a concentration of 2 mg/mL. Mix 27 μL of this solution and 30 μL of sample buffer.
— reducing conditions: add 3 μL of 2-mercaptoethanol R and incubate at 80 °C for 10 min; allow to cool for 5 min and transfer 60 μL to the autosampler vial;
— non-reducing conditions: add 3 μL of a 46.3 g/L solution of iodoacetamide R and incubate at 60-65 °C for 5 min; allow to cool for 5 min and transfer 60 μL to the autosampler vial.
Reference solution: Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in water R to obtain a concentration of 2 mg/mL. Mix 27 μL of the solution and 30 μL of sample buffer. Proceed at the same time and in the same manner as for the test solution.
Capillary:
— material: uncoated fused silica;
— size: total length = about 30 cm, effective length = 20 cm, Ø = 50 μm.
Temperature 25 °C.
Gel buffer Use a formulation suitable for a sieving range of approximately 10-225 kDa.
Acidic wash solution dilute hydrochloric acid R3.
Basic wash solution 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Autosampler Set at 25 °C.
Preconditioning of the capillary: Rinse the capillary with the basic wash solution for 10 min at 138 kPa, with the acidic wash solution for 5 min at 138 kPa, with water R for 2 min at 138 kPa and with the gel buffer for 10 min at 483 kPa. Apply voltage for 10 min (15 kV reversed polarity).
Between-run rinsing: Rinse the capillary with the basic wash solution for 3 min at 483 kPa, with the acidic wash solution for 1 min at 483 kPa, with water R for 1 min at 483 kPa and with the gel buffer for 10 min at 483 kPa.
Injection: Electrokinetically at 5 kV reversed polarity for 20 s.
Migration: Apply a voltage of 15 kV reversed polarity for 35 min using the gel buffer as the electrolyte in both buffer reservoirs.
Migration time:
— reducing conditions: light chain = 14 min to 17 min; non-glycosylated heavy chain = 17 min to 20 min; heavy
chain = 18 min to 21 min;
— non-reducing conditions: intact IgG = 26 min to 32 min.
Calculate corrected areas of all peaks with a migration time greater than 11 min, using the following expression:
(Ld x A)/t
Ld = capillary length to detector;
A = uncorrected peak area;
t = migration time.
System suitability Reference solution:
— reducing conditions: the electropherogram obtained is qualitatively similar to the electropherogram supplied with infliximab CRS;
— non-reducing conditions: the electropherogram obtained is qualitatively similar to the electropherogram supplied with infliximab CRS.
Result:
— the profile of the electropherogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the electropherogram obtained with the reference solution, except for minor peaks, that may be absent in the electropherogram obtained with the test solution.
Calculate individual peak areas expressed as a percentage of the sum of all corrected peak areas with a migration time greater than 11 min.
Limits:
Reducing conditions:
— sum of all peaks other than heavy chain and light chain: maximum 2 per cent, unless otherwise justified and
authorised;
Non-reducing conditions:
— sum of all peaks other than the principal peak: maximum 8 per cent.
Impurities with molecular masses differing from that of infliximab
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with the mobile phase to obtain a concentration of 8 mg/mL.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve the contents of a vial of infliximab CRS in the mobile phase to obtain a concentration of 8 mg/mL.
Reference solution (b): Reconstitute a mixture of thyroglobulin, gamma-globulin, ovalbumin, myoglobin and vitamin B12 in water R to obtain an 18 mg/mL solution of molecular mass markers suitable for calibration in the range of 1350-670 000 Da. Further dilute 10 μL of the solution with water for chromatography R to obtain a concentration of 0.9 mg/mL.
Column:
— size: l = 0.30 m, Ø = 7.8 mm;
— stationary phase: hydrophilic silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm) with a pore size of 25 nm and of a grade suitable for fractionation of globular proteins in the relative molecular mass range of 10 000 to 500 000.
Mobile phase: Dissolve 0.78 g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate R, 1.92 g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R and 8.77 g of sodium chloride R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water for chromatography R; filter and degas.
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Autosampler: Set at 10 °C.
Injection: 10 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to infliximab monomer (retention time = about 8 min): high molecular weight species = about 0.88; low molecular weight species = about 1.28.
Calculate individual peak areas expressed as a percentage relative to the sum of the areas of all peaks eluting between 5 min and 11 min. Individual relative per cent peak areas are calculated as the average of 3 injections.
NOTE: protein species that elute between 5 min and the monomer peak are classified as high molecular weight species, while those that elute after the monomer peak and before 11 min are classified as low molecular weight species.
System suitability:
— the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) is qualitatively similar to the chromatogram supplied with infliximab CRS;
— resolution: minimum 1.2 between the peaks due to gamma-globulin and ovalbumin in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
Result:
— the retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
Limit:
— sum of all peaks other than the monomer peak: maximum 2 per cent.
ASSAY
Protein (2.5.33, Method 1)
Test solution: Dilute the preparation to be examined with a suitable buffer to obtain a concentration of about 1 mg/mL.
Prepare and analyse each preparation in duplicate.
Record the UV spectrum between 280 nm and 350 nm. Measure the value at the absorbance maximum of 280 nm, after correction for any light scattering measured up to 350 nm. Calculate the protein content, taking the specific absorbance to be 14.5.
Potency
The potency of infliximab is determined by comparison of dilutions of the test preparation with dilutions of infliximab BRP using a suitable cell-based assay based on the inhibitory action of infliximab on the biological activity of TNF-α with a suitable readout for assessing this inhibitory effect.
The following procedure is given as an example.
WEHI-164 cytotoxicity assay (2.7.26, Procedure B)
Carry out the assay as described with the following modifications.
Reference solution: Reconstitute the contents of 1 vial of infliximab BRP with sterilised water for injections R to obtain a concentration of 500 IU/mL. Further dilute with assay medium to obtain a concentration of 6.4 IU/mL.
Analyse 2 independent dilutions per plate.
Result: The estimated potency is not less than 80 per cent and not more than 120 per cent relative to the reference solution. The confidence limits (P = 0.95) are not less than 80 per cent and not more than 125 per cent of the estimated potency.
In addition, the following procedures have been found suitable:
U937 apoptosis assay (2.7.26, Procedure A)
Carry out the assay as described with the following modifications.
Reference solution: Reconstitute the contents of 1 vial of infliximab BRP with sterilised water for injections R to obtain a concentration of 500 IU/mL. Further dilute with assay medium to obtain a concentration of 12.5 IU/mL.
Use this solution to prepare 10 additional reference sample dilutions on a dilution plate to generate the standard curve (a dilution step of 2 has been found suitable). Analyse 2 independent dilutions per plate.
NF-κB-inducible reporter gene assay (2.7.26, Procedure C)
Carry out the assay as described with the following modifications.
Reference solution: Reconstitute the contents of 1 vial of infliximab BRP with sterilised water for injections R to obtain a concentration of 500 IU/mL. Further dilute with assay medium to obtain a concentration of 8 IU/mL.
Use this solution to prepare 10 additional reference sample dilutions (a dilution step of 1.7 has been found suitable) on a dilution plate.
Analyse 2 independent dilutions per plate.
L929 cytotoxicity assay (2.7.26, Procedure D)
Carry out the assay as described with the following modifications.
Reference solution Reconstitute the contents of 1 vial of infliximab BRP with sterilised water for injections R to obtain a concentration of 500 IU/mL. Further dilute with assay medium to obtain a concentration of 1.0 IU/mL.
Use this solution to prepare 10 additional reference sample dilutions (a dilution step of 1.7 has been found suitable) on a dilution plate.
Analyse 2 independent dilutions per plate.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, under approved conditions.
LABELLING
The label states the content in milligrams of protein per millilitre.