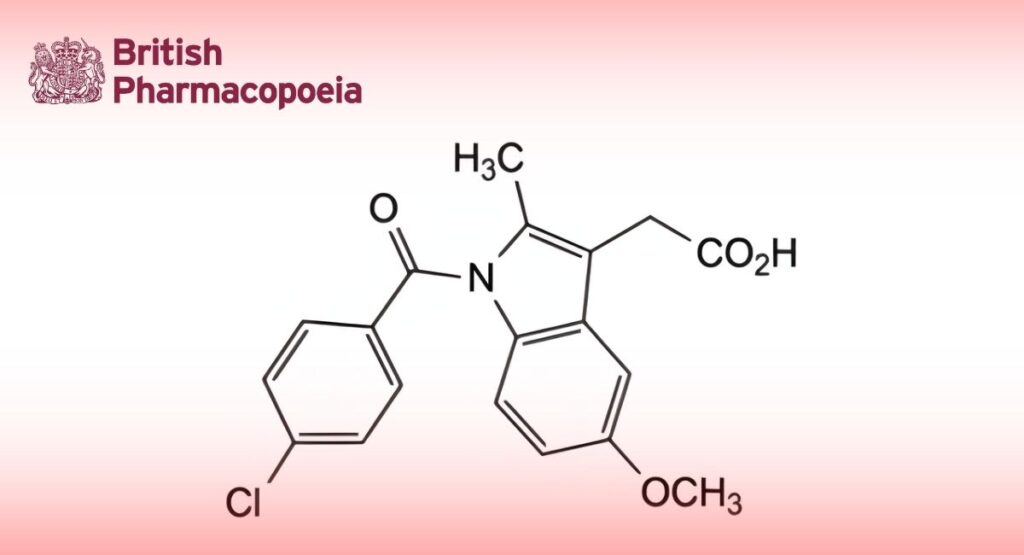
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0092)
C19H16ClNO4 357.8 53-86-1
Action and use
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
Preparations
Indometacin Capsules
Indometacin Suppositories
DEFINITION
[1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid.Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
It shows polymorphism (5.9). The acceptable crystalline form corresponds to indometacin CRS.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 158 °C to 162 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), without recrystallisation.
Comparison: indometacin CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 1.0 mL of methanol R.
Reference solution: Dissolve 10 mg of indometacin CRS in 1.0 mL of methanol R.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: formic acid R, ethyl acetate R, toluene R (2:28:70 V/V/V).
Application: 2 μL.
Development: Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection A: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results A: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
Detection B: Spray with anisaldehyde solution R; heat the plate at 120 °C till the spots become visible (about 30 s) and examine in daylight and in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results B: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour in daylight, fluorescence in ultraviolet light at 365 nm and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture, using sonication if necessary, and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve the contents of a vial of indometacin impurity mixture CRS (impurities I and J) in 1 mL of the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 2.1 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped ethylene-bridged phenylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (hybrid material) R (1.7 μm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 5 g/L solution of formic acid R;
— mobile phase B: 5 g/L solution of formic acid R in acetonitrile R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 5.5 | 60 | 40 |
| 5.5 – 5.6 | 60 → 30 | 40 → 70 |
| 5.6 – 9 | 30 | 70 |
Flow rate: 0.3 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 1.4 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with indometacin impurity mixture CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities I and J.
Relative retention: With reference to indometacin (retention time = about 6 min): impurity I = about 1.3; impurity J = about 1.4.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to impurities I and J.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of indometacin in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of indometacin CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.10 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped solid core octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (2.6 μm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 10 g/L solution of acetic acid R;
— mobile phase B: 10 g/L solution of acetic acid R in acetonitrile R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 5 | 50 | 50 |
| 5 – 5.5 | 50 → 0 | 50 → 100 |
| 5.5 – 8 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 0.8 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Retention time: Indometacin = about 4 min.
Calculate the percentage content of C19H16ClNO4 taking into account the assigned content of indometacin CRS.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J.
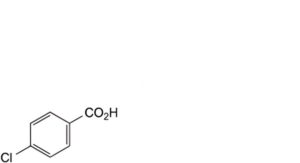
A. 4-chlorobenzoic acid,
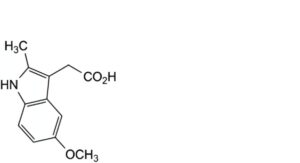
B. (5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid,
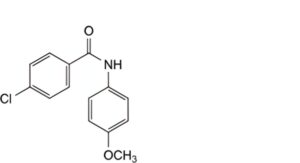
C. 4-chloro-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzamide,
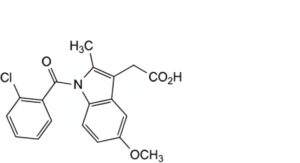
D. [1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid,
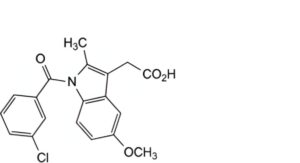
E. [1-(3-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid,
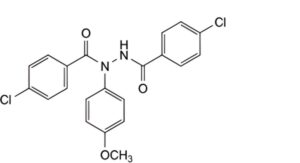
F. 4-chloro-N′-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzohydrazide,
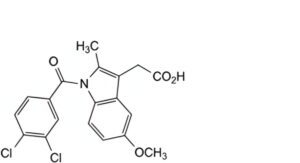
G. [1-(3,4-dichlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid,
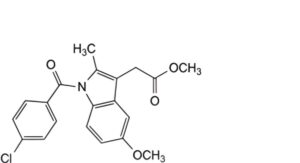
H. methyl [1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetate,
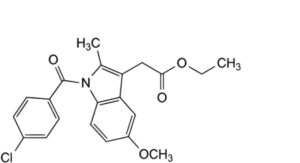
I. ethyl [1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetate,
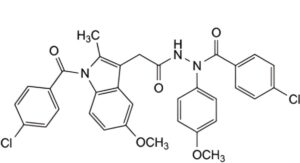
J. 4-chloro-N′-[[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetyl]-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzohydrazide.