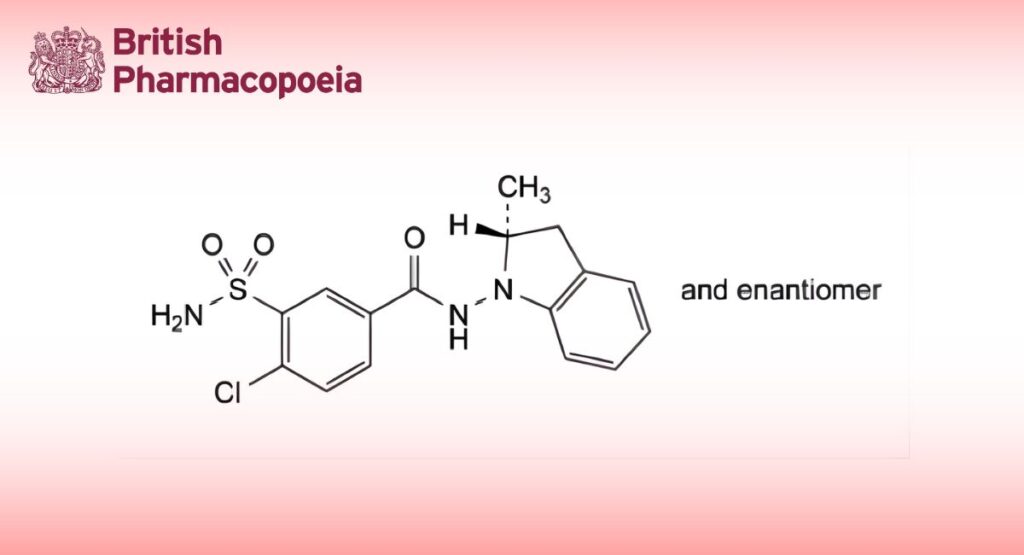
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1108)
C16H16ClN3O3S 365.8 26807-65-8
Action and use
Thiazide-like diuretic.
Preparations
Indapamide Tablets
Indapamide Prolonged-release Tablets
DEFINITION
4-Chloro-N-[(2RS)-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-yl]-3-sulfamoylbenzamide.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Spectral range: 220-350 nm.
Absorption maximum: At 242 nm.
Shoulders: At 279 nm and 287 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum 590 to 630.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: indapamide CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20 mg of indapamide CRS in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of indometacin R in 5 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 10 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Plate: TLC silica gel GF254 plate R.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, acetone R, toluene R (1:20:79 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection:Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.02° to + 0.02°.
Dissolve 0.250 g in anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light and prepare the solutions immediately before use
or maintain them at 4 °C.
Solvent mixture: acetonitrile R, methanol R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 7 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 3.0 mg of indapamide impurity B CRS in 3.5 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R. To 1.0 mL of the solution add 35 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (b): To 1.0 mL of the test solution add 17.5 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R. To 1.0 mL of this solution add 7 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 20.0 mg of indapamide CRS in 7 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (d): Dissolve 25 mg of indapamide CRS and 45 mg of methylnitrosoindoline CRS (impurity A) in 17.5 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 50 mL with a 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.20 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase: glacial acetic acid R, acetonitrile R, methanol R, 0.2 g/L solution of sodium edetate R (0.1:17.5:17.5:65 V/V/V/V).
Flow rate: 2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 10 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (a), (b) and (d).
Run time: 2.5 times the retention time of indapamide.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peak due to impurity A, use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity B.
Relative retention: With reference to indapamide (retention time = about 11 min): impurity A = about 1.4; impurity B = about 1.7.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to indapamide and impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d).
Limits:
— impurity B: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Impurity A
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the test protected from light.
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. Shake for 15 min. Allow to stand at 4 °C for 1 h and filter.
Reference solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 1.0 mL of a 0.125 mg/L solution of methylnitrosoindoline CRS (impurity A) in acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. Shake for 15 min. Allow to stand at 4 °C for 1 h and filter.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase: Mix 7 volumes of acetonitrile R, 20 volumes of tetrahydrofuran R and 73 volumes of a 1.5 g/L solution of triethylamine R adjusted to pH 2.8 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate: 1.4 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 305 nm.
Injection: 0.1 mL.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 3 for the peak due to impurity A appearing just before the peak due to indapamide;
— peak-to-valley-ratio: minimum 6.7, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to indapamide.
Limit:
— impurity A: the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is not more than the difference between the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution and the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution (5 ppm).
Impurity C
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Maintain the solutions at 10 °C after preparation.
Solution A: Dissolve 0.20 g of sodium edetate R in water for chromatography R, add 1.5 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution: Dissolve 75.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 7.5 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 9.0 mg of indapamide impurity C CRS in 1.0 mL of water R, add 6.0 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 20.0 mL with water R. To 1.0 mL of the solution add 7.5 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b): To 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) add 3.0 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): To 1 mL of reference solution (a) add 3 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 10 mL with the test solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 2.1 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography compatible with 100 per cent aqueous mobile phases R (1.8 μm);
— temperature: 50 °C.
Mobile phase: acetonitrile for chromatography R, solution A (30:70 V/V).
Flow rate: 0.7 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 235 nm.
Injection: 2 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Run time: 3 times the retention time of indapamide.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity C.
Relative retention: With reference to indapamide (retention time = about 1.3 min): impurity C = about 0.5.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to impurity C and indapamide;
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 20 for the peak due to impurity C.
Calculation of content:
— for impurity C, use the concentration of impurity C in reference solution (b).
Limit:
— impurity C: maximum 600 ppm.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C16H16ClN3O3S taking into account the assigned content of indapamide CRS.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
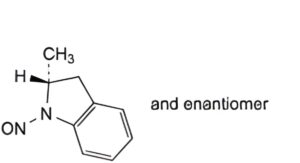
A. (2RS)-2-methyl-1-nitroso-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole,
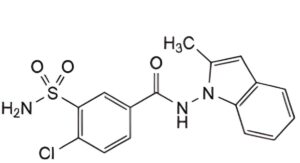
B. 4-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1H-indol-1-yl)-3-sulfamoylbenzamide,
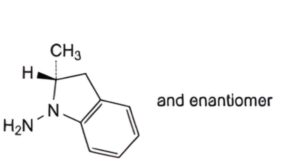
C. (2RS)-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-amine.