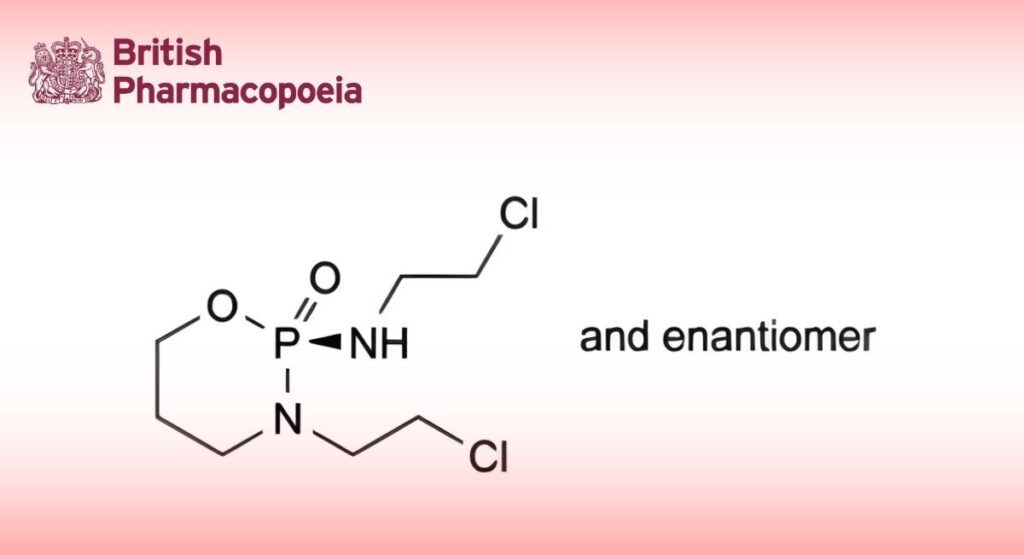
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1529)
C7H15Cl2N2O2P 261.1 3778-73-2
Action and use
Cytotoxic alkylating agent.
Preparation
Ifosfamide Injection
DEFINITION
Ifosfamide contains not less than 98.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 102.0 per cent of (RS)-N,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amine 2-oxide, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white, fine, crystalline powder, hygroscopic, soluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of ifosfamide.
Examine the substance prepared as a disc.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 50 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R. To 10 mL of this solution add 0.1 mL of methyl red solution R. Not more than 0.1 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator to red. To another 10 mL of the solution add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R. Not more than 0.3 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator to pink.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
The angle of optical rotation, determined on solution S, is -0.10° to + 0.10°.
Related substances
A. Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel plate R.
Test solution: Dissolve 1.00 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 25 mg of ifosfamide impurity A CRS and 25 mg of chloroethylamine hydrochloride R (impurity C) ina mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 15 mg of ifosfamide impurity B CRS ina mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of ethanolamine R (impurity D), 20 mg of ifosfamide impurity A CRS and 80 mg of chloroethylamine hydrochloride R (impurity C) in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R and dilute to 100 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Apply to the plate 10 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 10 volumes of water R, 15 volumes of methanol R, 25 volumes of anhydrous acetic acid R and 50 volumes of methylene chloride R. Dry the plate at 115 °C for 45 min. At the bottom of a chromatographic tank, place an evaporating dish containing a 3.2 g/L solution of potassium permanganate R and add an equal volume of dilute hydrochloric acid R, close the tank and allow to stand for 10 min. Place the plate whilst still hot in the tank, avoiding contact of the stationary phase with the solution, and close the tank. Leave the plate in contact with the chlorine vapour for 20 min. Withdraw the plate and place it in a current of cold air until the excess of chlorine is removed (about 20 min) and an area of coating below the points of application does not give a blue colour with a drop of potassium iodide and starch solution R. Avoid prolonged exposure to cold air. Immerse the plate in a 1 g/L solution of tetramethylbenzidine R in alcohol R for 5 s. Allow the plate to dry and examine. In the chromatogram obtained with the test solution: any spot corresponding to impurity A or impurity C is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent); any spot corresponding to impurity B is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent); any other spot is not more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows 3 clearly separated spots.
B. Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel plate R.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5 mg of ifosfamide impurity E CRS and 5 mg of ifosfamide impurity F CRS in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and methylene chloride R and dilute to 100 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10 mg of ifosfamide impurity E CRS and 10 mg of ifosfamide CRS in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and methylene chloride R and dilute to 100 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Apply to the plate: 5 μL of each solution. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 1 volume of methylene chloride R and 10 volumes of acetone R. Dry the plate at 115 °C for 45 min. Proceed as described in test A for related substances.
Any spot corresponding to impurity E or impurity F in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R. The freshly prepared solution complies with the limit test for chlorides (100 ppm).
Water (2.5.12)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.00 g by the semi-micro determination of water.
ASSAY
Examine by liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use the solutions within 24 h.
Solution A: Dissolve 50.0 mg of ethyl parahydroxybenzoate R in 25 mL of alcohol R, dilute to 100.0 mL with water R and mix.
Test solution: To 0.150 g of the substance to be examined add 10.0 mL of solution A and dilute to 250.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution: To 15.0 mg of ifosfamide CRS add 1.0 mL of solution A and dilute to 25.0 mL with water R.
The chromatography may be carried out using:
— a stainless steel column 0.25 m long and 4.6 mm in internal diameter packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm),
— as mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of water R,
— as detector a spectrophotometer set at 195 nm.
Inject 1 μL of the reference solution six times. The assay is not valid unless the resolution between the peaks due to ifosfamide and to ethyl parahydroxybenzoate is not less than 6.0 and the relative standard deviation of the peak area for ifosfamide is at most 2.0 per cent.
Inject 1 μL of the test solution. Calculate the percentage content of C7H15Cl2N2O2P from the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained and the declared content of ifosfamide CRS.
STORAGE
Store in an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Test A for related substances A, B, C, D.
Test B for related substances E, F.
Specified impurities A, B, C, E, F.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) D.
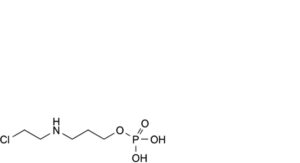
A. 3-[(2-chloroethyl)amino]propyl dihydrogen phosphate,
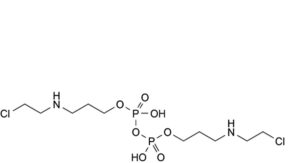
B. bis[3-[(2-chloroethyl)amino]propyl] dihydrogen diphosphate,

C. 2-chloroethanamine,

D. 2-aminoethanol.
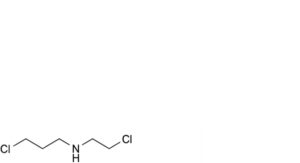
E. 3-chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)propan-1-amine,
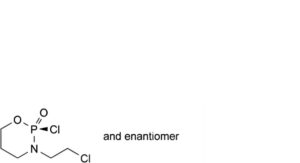
F. (RS)-2-chloro-3-(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinane 2-oxide.