(Ph. Eur. monograph 0721)
C13H18O2 206.3 15687-27-1
Action and use
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
Preparations
Ibuprofen Capsules
Ibuprofen Effervescent Granules
Ibuprofen Gel
Ibuprofen Oral Suspension
Ibuprofen Orodispersible Tablets
Ibuprofen Prolonged-release Capsules
Ibuprofen Prolonged-release Tablets
Ibuprofen Tablets
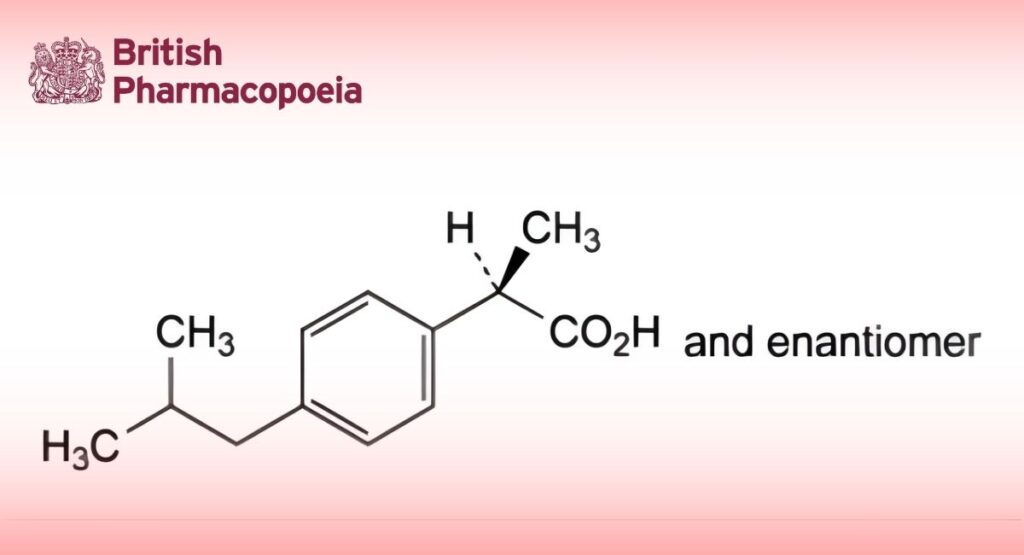
DEFINITION
(2RS)-2-[4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Ibuprofen
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone, in methanol and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, C.
Second identification: A, B, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 75 °C to 78 °C.
B. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg in a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same alkaline solution.
Spectral range 240-300 nm, using a spectrophotometer with a band width of 1.0 nm and a scan speed of not more than 50 nm/min.
Absorption maxima: At 264 nm and 272 nm.
Shoulder: At 258 nm.
Absorbance ratio:
— A264 / A258 = 1.20 to 1.30;
— A272 / A258 = 1.00 to 1.10.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: ibuprofen CRS.
D. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 50 mg of ibuprofen CRS in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous acetic acid R, ethyl acetate R, hexane R (5:24:71 V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying: At 120 °C for 30 min.
Detection: Lightly spray with a 10 g/L solution of potassium permanganate R in dilute sulfuric acid R and heat at 120 °C for 20 min; examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.0 g in methanol R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-0.05° to + 0.05°.
Dissolve 0.50 g in methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with mobile phase A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of ibuprofen impurity B CRS to 10.0 mL with acetonitrile R (solution A). Dissolve 20 mg of ibuprofen CRS in 2 mL of acetonitrile R, add 1.0 mL of solution A and dilute to 10.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve the contents of a vial of ibuprofen for peak identification CRS (mixture of impurities A, J and N) in 1 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 5 mL with mobile phase A.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl amorphous organosilica polymer for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 0.5 volumes of phosphoric acid R, 340 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 600 volumes of water for chromatography R; allow to equilibrate and dilute to 1000 volumes with water for chromatography R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R1;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 25 | 100 | 0 |
| 25 – 55 | 100 → 15 | 0 → 85 |
| 55 – 70 | 15 | 85 |
Flow rate: 2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 214 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with ibuprofen for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, J and N.
Relative retention: With reference to ibuprofen (retention time = about 21 min): impurity J = about 0.2; impurity N = about 0.3; impurity A = about 0.9; impurity B = about 1.1.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 1.5, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity B, and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to ibuprofen. If necessary, adjust the concentration of acetonitrile in mobile phase A.
Limits:
— impurities A, J, N: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent);
— total: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.03 per cent).
Impurity F
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Methylating solution: Dilute 1 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide dimethylacetal R and 1 mL of pyridine R to 10 mL with ethyl acetate R.
Test solution: Weigh about 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined into a sealable vial, dissolve in 1.0 mL of ethyl acetate R, add 1 mL of the methylating solution, seal and heat at 100 °C in a block heater for 20 min. Allow to cool.
Remove the reagents under a stream of nitrogen at room temperature. Dissolve the residue in 5 mL of ethyl acetate R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 0.5 mg of ibuprofen impurity F CRS in ethyl acetate R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Weigh about 50.0 mg of ibuprofen CRS into a sealable vial, dissolve in 1.0 mL of reference solution (a), add 1 mL of the methylating solution, seal and heat at 100 °C in a block heater for 20 min. Allow to cool.
Remove the reagents under a stream of nitrogen at room temperature. Dissolve the residue in 5 mL of ethyl acetate R.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 25 m, Ø = 0.53 mm;
— stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness 2 μm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 5.0 mL/min.
Temperature:
— column: 150 °C;
— injection port: 200 °C;
— detector: 250 °C.
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1 μL of the test solution and reference solution (b).
Run time: Twice the retention time of ibuprofen.
System suitability:
— relative retention with reference to ibuprofen (retention time = about 17 min): impurity F = about 1.5.
Limit:
— impurity F: maximum 0.1 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.450 g in 50 mL of methanol R. Add 0.4 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide until a red colour is obtained. Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 20.63 mg of C13H18O2.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, F, J, N.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) B, C, D, E,
G, H, I, K, L, M, O, P, Q, R.
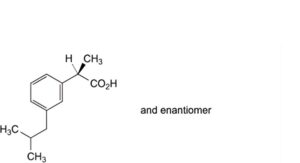
A. (2RS)-2-[3-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
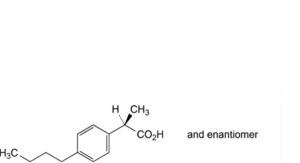
B. (2RS)-2-(4-butylphenyl)propanoic acid,
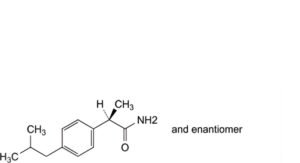
C. (2RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanamide,
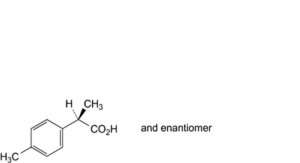
D. (2RS)-2-(4-methylphenyl)propanoic acid,
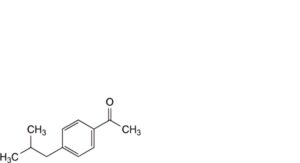
E. 1-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]ethanone,
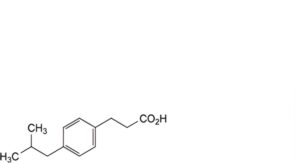
F. 3-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
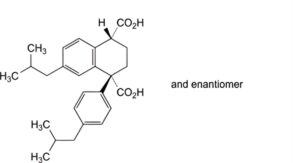
G. (1RS,4RS)-7-(2-methylpropyl)-1-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid,
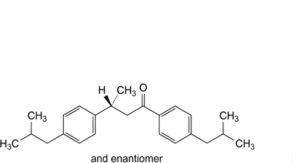
H. (3RS)-1,3-bis[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]butan-1-one,
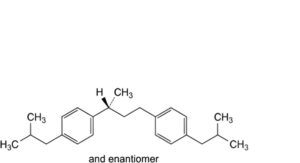
I. 1-(2-methylpropyl)-4-[(3RS)-3-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]butyl]benzene,
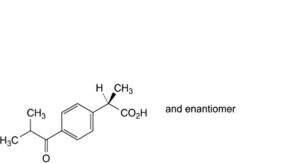
J. (2RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropanoyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
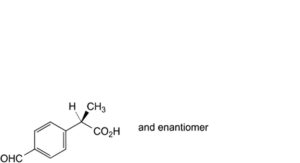
K. (2RS)-2-(4-formylphenyl)propanoic acid,
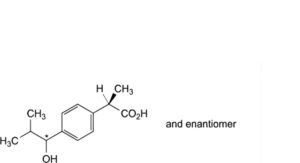
L. (2RS)-2-[4-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
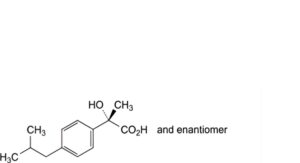
M. (2RS)-2-hydroxy-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
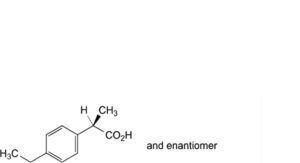
N. (2RS)-2-(4-ethylphenyl)propanoic acid,
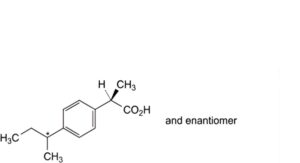
O. (2RS)-2-[4-(1-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid,
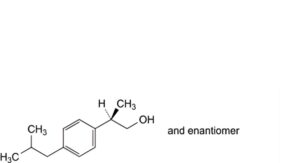
P. (2RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propan-1-ol,
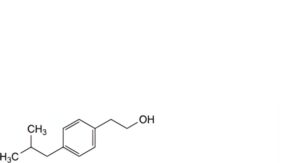
Q. 2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]ethanol,
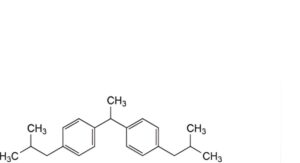
R. 1,1′-(ethane-1,1-diyl)-4,4′-(2-methylpropyl)dibenzene.