(Ph. Eur. monograph 2771)
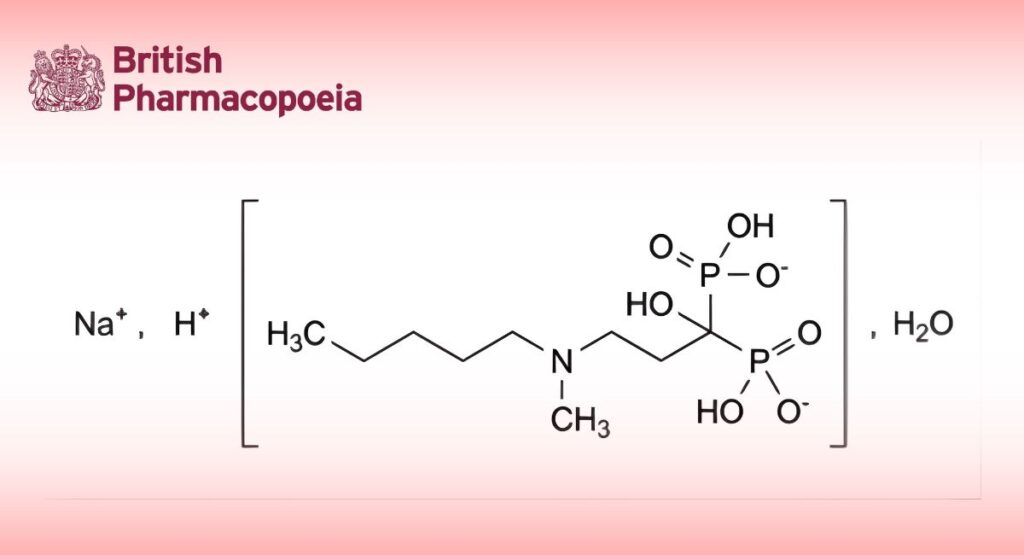
C9H22NNaO7P2,H2O 359.2 138926-19-9
Action and use
Bisphosphonate; treatment of osteolytic lesions; osteoporosis; hypercalcaemia in malignancy
DEFINITION
Monosodium trihydrogen [1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]propane-1,1-diyl]bisphosphonate monohydrate.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white or yellowish powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in acetone.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison ibandronate sodium monohydrate CRS.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in 2 mL of water R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 0.5 g in water R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension IV (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution B4 (2.2.2, Method II).
pH (2.2.3)
3.9 to 4.2 for solution S.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R, ethanol (96 per cent) R (50:50 V/V).
Buffer solution pH 2.3: Dissolve 0.25 g of sodium edetate R in 900 mL of water for chromatography R, add 1 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R and 1 mL of triethylamine R; adjust to pH 2.3 with trifluoroacetic acid R or triethylamine R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Solution A: Dissolve 0.25 g of sodium edetate R in water R, add 10 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water R.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.40 g of the substance to be examined in solution A and dilute to 10.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 25 μL of acetone R to 50 mL with solution A (solution B). Dissolve 40 mg of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of solution B.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped phenylhexylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase Solvent mixture, buffer solution pH 2.3 (6:94 V/V).
Flow rate 1.2 mL/min.
Detection Differential refractometer maintained at 40 °C.
Injection 30 μL.
Run time 4 times the retention time of ibandronate.
Relative retention With reference to ibandronate (retention time = about 6.5 min): acetone = about 0.7.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to acetone and ibandronate.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of ibandronate sodium monohydrate in reference solution (a).
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Water (2.5.32)
4.4 per cent to 5.6 per cent, determined on 50.0 mg using the evaporation technique at 150 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.500 g in 50 mL of water R. Carry out a potentiometric titration (2.2.20), using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Read the volume added at the 1 inflexion point (not systematically detected) and continue the titration to the 2 inflexion point.
Calculate the percentage content of C9H22NNaO7P2 using the following expression:
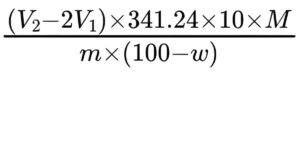
V1 = volume of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide added at the 1 inflexion point (at about pH about 2 to 5), in millilitres (only detected if free phosphates and phosphites are present);
V2 = volume of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide added at the 2 inflexion point (at pH of about 11), in millilitres;
341.24 = relative molecular mass of anhydrous ibandronate sodium;
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in grams;
M = molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution, in moles per litre;
w = percentage content of water.
IMPURITIES
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, C.
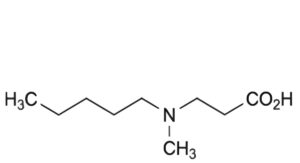
A. 3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]propanoic acid,
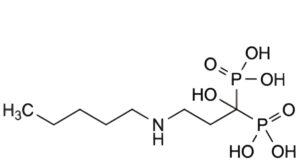
C. [1-hydroxy-3-(pentylamino)propane-1,1-diyl]bis(phosphonic acid).