(Ph. Eur. monograph 3101)
71138-97-1
Action and use
Artificial tears; excipient.
DEFINITION
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate hydrogen butanedioate.
A mixture of acetic acid and monosuccinic acid esters of hypromellose, containing methoxy (-OCH3; Mr 31.03), 2-hydroxypropoxy (-OCH2CHOHCH3; Mr 75.1), acetyl (-COCH3; Mr 43.04) and succinyl (3-carboxypropanoyl; -COCH2CH2CO2H; Mr 101.1) groups.
Content
— methoxy groups: 12.0 per cent to 28.0 per cent (dried substance);
— 2-hydroxypropoxy groups: 4.0 per cent to 23.0 per cent (dried substance);
— acetyl groups: 2.0 per cent to 16.0 per cent (dried substance);
— succinyl groups: 4.0 per cent to 28.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or yellowish white, hygroscopic powder or granules.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, in anhydrous ethanol and in hexane. It dissolves in an 8 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24). Examine by attenuated total reflection (ATR).
Comparison hypromellose acetate succinate CRS.
TESTS
Viscosity (2.2.9)
80.0 per cent to 120.0 per cent of the nominal value.
To a quantity of the substance to be examined equivalent to 2.00 g of dried substance, add an appropriate volume of a 4.3 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R in carbon dioxide-free water R to make 100.0 g of suspension; stopper tightly and dissolve by shaking for a minimum of 30 min.
Free acetic and succinic acids
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Acetic acid stock solution: Introduce about 20 mL of water R into a stoppered volumetric flask, place the flask on a balance and tare. Transfer 2.0 mL of glacial acetic acid R to the flask and record the mass of the acid added. Dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 6.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Succinic acid stock solution 1.3 mg/mL solution of succinic acid R.
Solution A: 2.72 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 7.5 with a 42.0 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Test solution: Weigh 0.100 g of the substance to be examined into a vial, add 4.0 mL of solution A and stir for 2 h. Add 4.0 mL of a 2.9 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, mix well and filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.22 μm). Use the filtrate.
Reference solution: Mix 4.0 mL of the acetic acid stock solution and 4.0 mL of the succinic acid stock solution and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: polar end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase: 2.72 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 2.8 with a 700 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Equilibration: After each run sequence, flush the column with a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R1 and water for chromatography R for 60 min and then with methanol R2 for 60 min. Store the column in methanol R2.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection: 10 μL.
Run time: 4 times the retention time of acetic acid.
Relative retention: With reference to acetic acid (retention time = about 4 min): succinic acid = about 2.0.
System suitability:
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 2.0 per cent for the areas of the peaks due to acetic acid and succinic acid, determined on 6 injections of the reference solution.
Calculate the percentage content of free acetic acid (Afree) using the following expression:
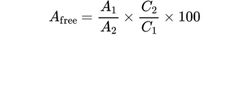
A1 = area of the peak due to acetic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A2 = area of the peak due to acetic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
C1 = ratio between the mass of the substance to be examined and the total extraction volume used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams per millilitre;
C2 = concentration of acetic acid in the reference solution, in milligrams per millilitre.
Calculate the percentage content of free succinic acid (Sfree) using the following expression:
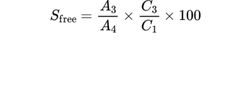
A3 = area of the peak due to succinic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A4 = area of the peak due to succinic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
C1 = ratio between the mass of the substance to be examined and the total extraction volume used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams per millilitre;
C3 = concentration of succinic acid in the reference solution, in milligrams per millilitre.
Limit:
— sum of free acetic and succinic acids: maximum 1.0 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 5.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 1 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Methoxy and 2-hydroxypropoxy groups
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Apparatus:
— reaction vial: 5 mL pressure-tight vial equipped with a pressure-tight butyl rubber membrane stopper coated with polytetrafluoroethylene and secured with an aluminium crimp cap or another sealing system providing a sufficient air-tightness;
— heater: heating module with a square aluminium block having holes into which the reaction vials fit; mixing of the contents of the vial is effected using a magnetic stirrer equipped in the heating module or using a reciprocal shaker that performs approximately 100 cycles/min.
Internal standard solution 30 g/L solution of octane R in o-xylene R.
Test solution: Weigh 65.0 mg of the substance to be examined, place in a reaction vial, add 0.06-0.10 g of adipic acid R, 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and 2.0 mL of hydriodic acid R, immediately cap and seal the vial, and weigh accurately. Mix the contents of the vial continuously for 60 min while heating the block so that the temperature of the contents is maintained at 130 ± 2 °C. If a reciprocal shaker or magnetic stirrer cannot be used, shake the vial thoroughly by hand at 5 min intervals during the initial 30 min of the heating time. Allow the vial to cool, and again weigh accurately. If the loss of mass is less than 26 mg and there is no evidence of a leak, use the upper layer of the mixture as the test
solution.
Reference solution: Place 0.06-0.10 g of adipic acid R, 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and 2.0 mL of hydriodic acid R in another reaction vial, cap and seal the vial, and weigh accurately. Add 15-22 μL of isopropyl iodide R through the septum with a syringe, weigh accurately, add 45 μL of methyl iodide R in the same manner, and weigh accurately. Shake the reaction vial thoroughly and use the upper layer as the reference solution.
Use a precolumn if needed.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.53 mm;
— stationary phase: methylpolysiloxane R (3 μm).
Carrier: gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 4.3 mL/min.
Split ratio: 1:40.
Temperature:
| Time
(min) |
Temperature
(°C) |
|
| Column | 0 – 3 | 50 |
| 3 – 8 | 50 → 100 | |
| 8 – 12.3 | 100 → 250 | |
| 12.3 – 20.3 | 250 | |
| Injection port | 250 | |
| Detector | 280 |
Detection: Flame ionisation or thermal conductivity.
Injection: 1-2 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to octane (retention time = about 10 min): methyl iodide = about 0.4; isopropyl iodide = about 0.7.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to methyl iodide and isopropyl iodide and between the peaks due to isopropyl iodide and octane;
— repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 2.0 per cent for the ratios of the areas of the peaks respectively due to methyl iodide and isopropyl iodide to the area of the peak due to octane, determined on 6 injections.
Calculate the response factor for methyl iodide (R1) using the following expression:
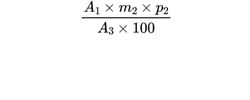
Calculate the response factor for isopropyl iodide (R2) using the following expression:
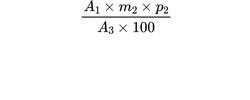
A1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
A2 = area of the peak due to methyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
A3 = area of the peak due to isopropyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
m1 = mass of methyl iodide in the reference solution, in milligrams;
m2 = mass of isopropyl iodide in the reference solution, in milligrams;
p1 = percentage content of methyl iodide R;
p2 = percentage content of isopropyl iodide R.
Calculate the percentage content m/m of the methoxy groups using the following expression:
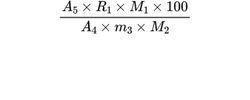
Calculate the percentage content m/m of 2-hydroxypropoxy groups using the following expression:
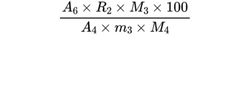
A4 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A5 = area of the peak due to methyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A6 = area of the peak due to isopropyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
R1 = response factor for methyl iodide;
R2 = response factor for isopropyl iodide;
M1 = molar mass of methoxy group (31.03);
M2 = molar mass of methyl iodide (141.9);
M3 = molar mass of 2-hydroxypropoxy group (75.1);
M4 = molar mass of isopropyl iodide (170.0);
m3 = mass of the sample (dried substance) in the test solution, in milligrams.
Acetyl and succinyl groups
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for free acetic and succinic acids with the following modifications.
Test solution: Introduce 30.0 mg of the substance to be examined into a vial, add 10.0 mL of a 42.0 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and stir for 4 h. Add 10.0 mL of a 144 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R, mix well and filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.22 μm). Use the filtrate.
Calculate the percentage content of acetic acid (A) using the following expression:
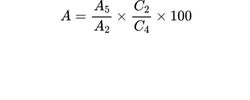
A2 = area of the peak due to acetic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
A5 = area of the peak due to acetic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
C2 = concentration of acetic acid in the reference solution, in milligrams per millilitre;
C4 = ratio between the mass of the substance to be examined and the total extraction volume used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams per millilitre.
Calculate the percentage content of acetyl groups using the following expression:
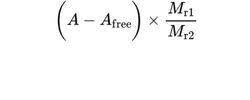
A = percentage content of acetic acid (see above);
Afree = percentage content of free acetic acid (see Tests);
Mr1 = molecular mass of the acetyl group (43.04);
Mr2 = molecular mass of acetic acid (60.1).
Calculate the percentage content of succinic acid (S) using the following expression:
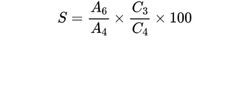
A4 = area of the peak due to succinic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
A6 = area of the peak due to succinic acid in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
C3 = concentration of succinic acid in the reference solution, in milligrams per millilitre;
C4 = ratio between the mass of the substance to be examined and the total extraction volume used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams per millilitre.
Calculate the percentage content of succinyl groups using the following expression:
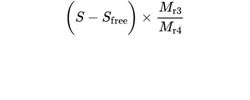
S = percentage content of succinic acid (see above);
Sfree = percentage content of free succinic acid (see Tests);
Mr3 = molecular mass of the succinyl group (101.1);
Mr4 = molecular mass of succinic acid (118.1).
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
LABELLING
The label states the nominal viscosity in millipascal seconds.






