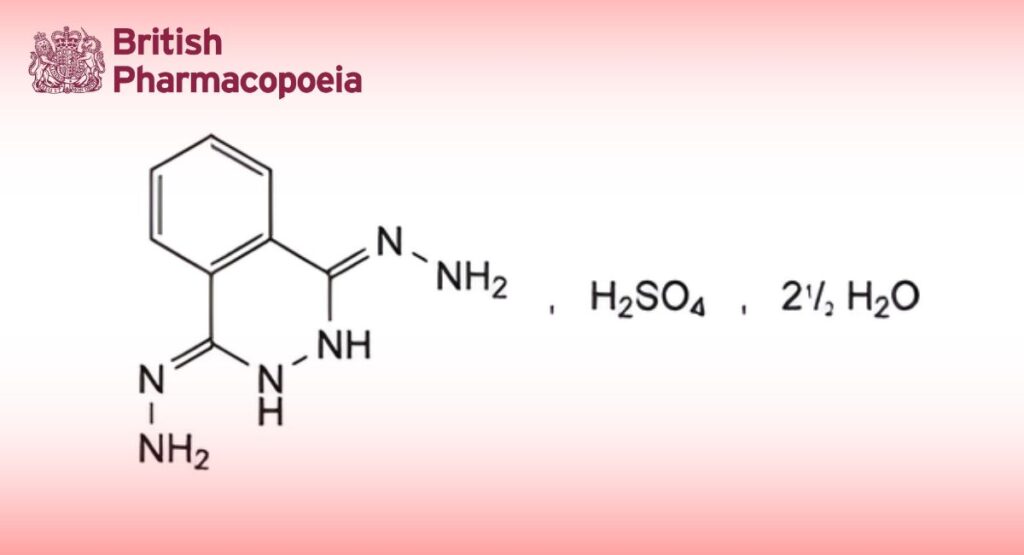
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1310)
C8H12N6O4S,2 1⁄2H2O 333.3
Dihydralazine sulfate, anhydrous 7327-87-9
Action and use
Vasodilator.
DEFINITION
(Phthalazine-1,4(2H,3H)-diylidene)dihydrazine sulfate 2.5-hydrate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or slightly yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol. It dissolves in dilute mineral acids.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of dihydralazine sulfate hydrated.
B. Dissolve about 50 mg in 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. The solution gives reaction (a) of sulfates (2.3.1).
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 0.20 g in dilute nitric acid R and dilute to 10 mL with the same acid.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in a 6 g/L solution of glacial acetic acid R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase containing 0.5 g/L of sodium edetate R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase containing 0.5 g/L of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase containing 0.5 g/L of sodium edetate R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 5 mg of dihydralazine for system suitability CRS in a 6 g/L solution of glacial acetic acid R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped cyanosilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 22 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R and 78 volumes of a solution containing 1.44 g/L of sodium laurilsulfate R and 0.75 g/L of tetrabutylammonium bromide R, then adjust to pH 3.0 with dilute sulfuric acid R1.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of dihydralazine.
Relative retention: With reference to dihydralazine: impurity A = about 0.8.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— the peaks due to impurity A and dihydralazine are baseline separated as in the chromatogram supplied with dihydralazine for system suitability CRS.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— sum of impurities other than A: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.01 per cent).
Impurity B
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of hydrazine sulfate R (impurity B) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with water R. To 0.50 mL of this solution, add 0.200 g of the substance to be examined and dissolve in 6 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R, then dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. In a centrifuge tube with a ground-glass stopper, place immediately 0.50 mL of this solution and 2.0 mL of a 60 g/L solution of benzaldehyde R in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R. Shake for 90 s. Add 1.0 mL of water R and 5.0 mL of heptane R. Shake for 1 min and centrifuge. Use the upper layer.
Reference solution: Dissolve 40.0 mg of hydrazine sulfate R (impurity B) in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 25.0 mL with water R. To 0.50 mL of this solution, add 6 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. In a centrifuge tube with a ground-glass stopper, place 0.50 mL of this solution and 2.0 mL of a 60 g/L solution of benzaldehyde R in a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R. Shake for 90 s. Add 1.0 mL of water R and 5.0 mL of heptane R. Shake for 1 min and centrifuge. Use the upper layer.
Blank solution: Prepare in the same manner as for the reference solution but replacing the 0.50 mL of hydrazine sulfate solution by 0.50 mL of water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: 0.3 g/L solution of sodium edetate R, acetonitrile R (30:70 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 305 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to benzaldehyde: benzaldehyde azine (benzalazine) corresponding to impurity B = about 1.8.
Limit:
— impurity B: the area of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine is not greater than twice the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (10 ppm).
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 20 ppm.
To the residue obtained in the test for sulfated ash add 0.2 mL of sulfuric acid R and heat carefully until the acid is almost completely eliminated. Allow to cool and dissolve the residue with heating in 5.5 mL of hydrochloric acid R1. Filter the hot solution through a filter previously washed 3 times with dilute hydrochloric acid R. Wash the crucible and the filter with 5 mL of water R. Combine the filtrate and the washings and neutralise with about 3.5 mL of strong sodium hydroxide solution R. Adjust to pH 3-4 with acetic acid R and dilute to 20 mL with water R. Prepare the standard with 5 mL of iron
standard solution (2 ppm Fe) R and 5 mL of water R.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
13.0 per cent to 15.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo at 50 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 5 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 60.0 mg in 25 mL of water R. Add 35 mL of hydrochloric acid R and titrate slowly with 0.05 M potassium iodate, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20), using a suitable reference electrode and a platinum indicator electrode.
1 mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 7.208 mg of C8H12N6O4S.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
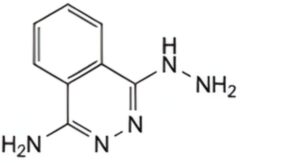
A. 4-hydrazinophthalazin-1-amine,
B. H2N-NH2: hydrazine,
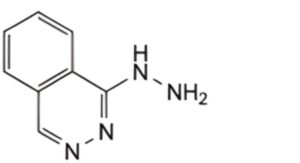
C. (phthalazin-1-yl)hydrazine (hydralazine).