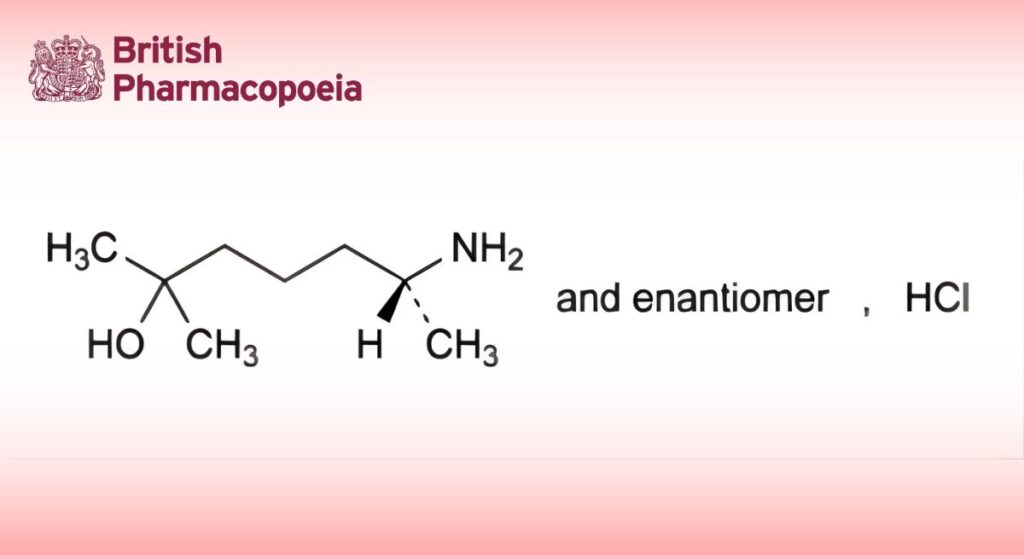
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1980)
C8H20ClNO 181.7 543-15-7
Action and use
Non-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor; treatment of reversible airways obstruction.
DEFINITION
(6RS)-6-Amino-2-methylheptan-2-ol hydrochloride.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B, D.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. To 1 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 4 mL of water R and 2 mL of a 200 g/L solution of ammonium and cerium nitrate R in dilute nitric acid R1. An orange-brown colour develops.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: heptaminol hydrochloride CRS.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Detection: Examine in daylight.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Acidity or alkalinity
To 10 mL of solution S add 0.1 mL of methyl red solution R and 0.3 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. The solution is red.
Add 0.6 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide. The solution is yellow.
Related substances
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.50 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 10 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 3.0 mL of test solution (a) to 10.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 0.10 g of heptaminol hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 10.0 mg of heptaminol impurity A CRS in methanol R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (e): To 2.5 mL of reference solution (c) add 0.5 mL of test solution (b) and dilute to 5 mL with methanol R.
Plate: TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, dioxan R, 2-propanol R (10:50:50 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL; apply test solutions (a) and (b) and reference solutions (a), (b), (d) and (e).
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Expose the plate to iodine vapour for at least 15 h.
System suitability: The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (e) shows 2 clearly separated principal spots and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) shows a single principal spot.
Limits: In the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a):
— impurity A: any spot corresponding to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.2 per cent),
— any other impurity: any spot, apart from the principal spot and any spot corresponding to impurity A is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.6 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 4 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.140 g in 50 mL of alcohol R and add 5.0 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Carry out a potentiometric titration (2.2.20), using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Read the volume added between the 2 points of inflexion.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 18.17 mg of C8H20ClNO.
IMPURITIES
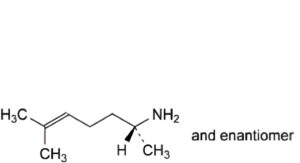
A. (2RS)-6-methylhept-5-en-2-amine.