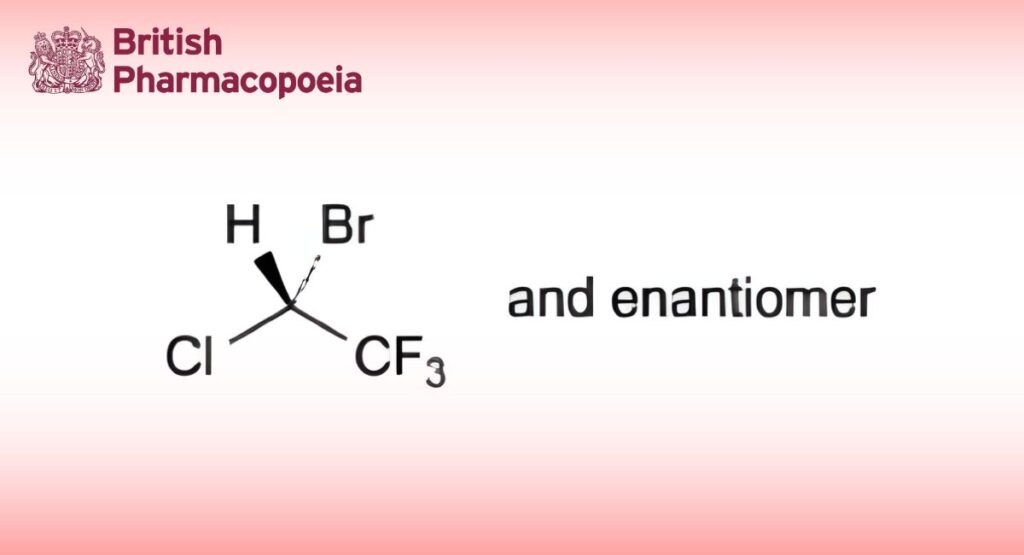
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0393)
C2HBrClF3 197.4 151-67-7
Action and use
General anaesthetic.
DEFINITION
(RS)-2-Bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane to which 0.01 per cent m/m of thymol has been added.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, colourless, mobile, heavy, non-flammable liquid.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, miscible with anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Distillation range (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation: Examine the substance in a 0.1 mm cell.
Comparison: Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of halothane.
C. Add 0.1 mL to 2 mL of 2-methyl-2-propanol R in a test-tube. Add 1 mL of copper edetate solution R, 0.5 mL of concentrated ammonia R and a mixture of 0.4 mL of strong hydrogen peroxide solution R and 1.6 mL of water R (solution A). Prepare a blank at the same time (solution B). Place both tubes in a water-bath at 50 °C for 15 min, cool and add 0.3 mL of glacial acetic acid R. To 1 mL of each of solutions A and B add 0.5 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of freshly prepared alizarin S solution R and zirconyl nitrate solution R. Solution A is yellow and solution B is red.
To 1 mL of each of solutions A and B add 1 mL of buffer solution pH 5.2 R, 1 mL of phenol red solution R diluted 1 to 10 with water R and 0.1 mL of chloramine solution R. Solution A is bluish-violet and solution B is yellow.
To 2 mL of each of solutions A and B add 0.5 mL of a mixture of 25 volumes of sulfuric acid R and 75 volumes of water R, 0.5 mL of acetone R and 0.2 mL of a 50 g/L solution of potassium bromate R and shake. Warm the tubes in a water-bath at 50 °C for 2 min, cool and add 0.5 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of nitric acid R and water R and 0.5 mL of silver nitrate solution R2. Solution A is opalescent and a white precipitate is formed after a few minutes; solution B remains clear.
TESTS
Acidity or alkalinity
To 20 mL add 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R, shake for 3 min and allow to stand. Separate the aqueous layer and add 0.2 mL of bromocresol purple solution R. Not more than 0.1 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide or 0.6 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator.
Relative density (2.2.5)
1.872 to 1.877.
Distillation range (2.2.11)
It distils completely between 49.0 °C and 51.0 °C and 95 per cent distills within a range of 1.0 °C.
Volatile related substances
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard: trichlorotrifluoroethane CRS.
Test solution (a): The substance to be examined.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of trichlorotrifluoroethane CRS to 20.0 mL with the substance to be examined. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the substance to be examined. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the substance to be examined.
Column:
— size: l = 2.75 m, Ø = 5 mm;
— stationary phase: silanised diatomaceous earth for gas chromatography R (180-250 μm), the first 1.8 m being impregnated with 30 per cent m/m of macrogol 400 R and the remainder with 30 per cent m/m of dinonyl phthalate R;
— temperature: 50 °C.
Carrier gas: nitrogen for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 30 mL/min.
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 5 μL.
Limit: Test solution (b):
— total: not more than the area of the peak due to the internal standard, corrected if necessary for any impurity with the same retention time as the internal standard (0.005 per cent).
Thymol
Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Internal standard solution: Dissolve 0.10 g of menthol R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution: To 20.0 mL of the substance to be examined add 5.0 mL of the internal standard solution.
Reference solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of thymol R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
To 20.0 mL of this solution, add 5.0 mL of the internal standard solution.
Column:
— material: fused silica;
— size: l = 15 m, Ø = 0.53 mm;
— stationary phase: methylpolysiloxane R (film thickness 1.5 μm).
Carrier gas: nitrogen for chromatography R.
Flow rate: 15 mL/min.
Temperature:
— column: 150 °C;
— injection port: 170 °C;
— detector: 200 °C.
Detection: Flame ionisation.
Injection: 1.0 μL.
Limit:
— thymol: 0.75 times to 1.15 times the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.008 per cent m/m to 0.012 per cent m/m).
Bromides and chlorides
To 10 mL add 20 mL of water R and shake for 3 min. To 5 mL of the aqueous layer add 5 mL of water R, 0.05 mL of nitric acid R and 0.2 mL of silver nitrate solution R1. The solution is not more opalescent than a mixture of 5 mL of the aqueous layer and 5 mL of water R.
Bromine and chlorine
To 10 mL of the aqueous layer obtained in the test for bromides and chlorides add 1 mL of potassium iodide and starch solution R. No blue colour is produced.
Non-volatile matter
Maximum 20 mg/L.
Evaporate 50 mL to dryness on a water-bath and dry the residue in an oven at 100-105 °C for 2 h. The residue weighs a maximum of 1 mg.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. The choice of material for the container is made taking into account the particular reactivity of halothane with certain metals.
IMPURITIES
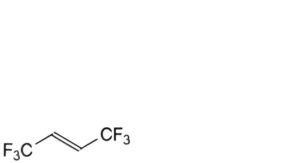
A. (E)-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluorobut-2-ene,
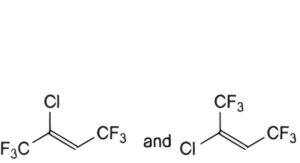
B. (EZ)-2-chloro-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluorobut-2-ene (cis and trans),
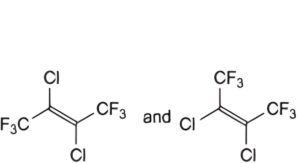
C. (EZ)-2,3-dichloro-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluorobut-2-ene (cis and trans),
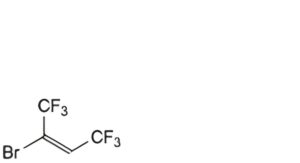
D. (E)-2-bromo-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluorobut-2-ene,
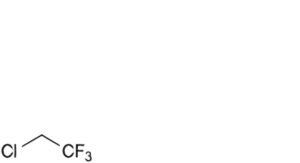
E. 2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane,
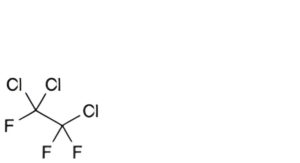
F. 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane,

G. 1-bromo-1-chloro-2,2-difluoroethene,

H. 2,2-dichloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane,
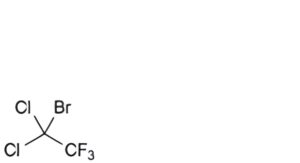
I. 1-bromo-1,1-dichloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethane,
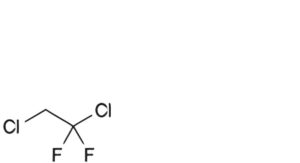
J. 1,2-dichloro-1,1-difluoroethane.