(Ph. Eur. monograph 1429)
Action and use
Excipient.
DEFINITION
Mixture of monoacylglycerols, mainly mono-oleoyl- and monolinoleoylglycerol, together with variable quantities of di- and triacylglycerols, obtained by partial glycerolysis of vegetable oils mainly containing triacylglycerols of linoleic ((9Z,12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoic) acid. A suitable antioxidant may be added.
Content
— monoacylglycerols: 32.0 per cent to 52.0 per cent;
— diacylglycerols: 40.0 per cent to 55.0 per cent;
— triacylglycerols: 5.0 per cent to 20.0 per cent.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Amber, oily liquid which may be partially solidified at room temperature.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Iodine value (see Tests).
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of the substance to be examined in methylene chloride R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution: Dissolve 1.0 g of glycerol monolinoleate CRS in methylene chloride R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase hexane R, ether R (30:70 V/V).
Application 10 μL.
Development: Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying In air.
Detection: Spray with a 0.1 g/L solution of rhodamine B R in ethanol (96 per cent) R and examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results: The spots in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in position to those in the
chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. Composition of fatty acids (see Tests).
TESTS
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 6.0, determined on 1.0 g.
Iodine value (2.5.4, Method A)
100 to 140.
Peroxide value (2.5.5, Method A)
Maximum 12.0, determined on 2.0 g.
Saponification value (2.5.6)
160 to 180, determined on 2.0 g.
Free glycerol
Maximum 6.0 per cent, determined as described in the assay.
Composition of fatty acids (2.4.22, Method C)
Composition of the fatty acid fraction of the substance:
— palmitic acid: 4.0 per cent to 20.0 per cent;
— stearic acid: maximum 6.0 per cent;
— oleic acid: 10.0 per cent to 35.0 per cent;
— linoleic acid: minimum 50.0 per cent;
— linolenic acid: maximum 2.0 per cent;
— arachidic acid: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— eicosenoic acid: maximum 1.0 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.00 g. Use as the solvent a mixture of equal volumes of anhydrous methanol R and methylene chloride R.
Total ash (2.4.16)
Maximum 0.1 per cent.
ASSAY
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30).
Test solution: Into a 15 mL flask, weigh about 0.2 g (m), to the nearest 0.1 mg. Add 5 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and shake to dissolve. Reweigh the flask and calculate the total mass of solvent and substance (M).
Reference solutions: Into four 15 mL flasks, respectively weigh, to the nearest 0.1 mg, about 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg and 20 mg of glycerol R. Add 5 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and shake until well mixed. Weigh the flasks again and calculate the concentration of glycerol in milligrams per gram for each reference solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.6 m, Ø = 7 mm,
— stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (5 μm) with a pore size of 10 nm.
Mobile phase tetrahydrofuran R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection: Differential refractometer.
Injection 40 μL.
Relative retention: With reference to glycerol (retention time = about 15.6 min): triacylglycerols = about 0.76;
diacylglycerols = about 0.80; monoacylglycerols = about 0.86.
Calculations:
— free glycerol: from the calibration curve obtained with the reference solutions, determine the concentration of glycerol (C) in milligrams per gram in the test solution and calculate the percentage content of free glycerol (A) in the substance to be examined using the following expression:
C×M/m×10
— free fatty acids: calculate the percentage content of free fatty acids (D) using the following expression:
IA×280/56.11×10
IA = acid value (see Tests);
280 = rounded molar mass of linoleic acid, in grams per mole;
56.11 = molar mass of potassium hydroxide, in grams per mole.
— monoacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of monoacylglycerols using the following expression:
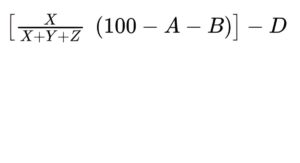
A = percentage content of free glycerol;
B = percentage content of water (see Tests);
D = percentage content of free fatty acids;
X = area of the peak due to monoacylglycerols and free fatty acids;
Y = area of the peak due to diacylglycerols;
Z = area of the peak due to triacylglycerols.
— diacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of diacylglycerols using the following expression:
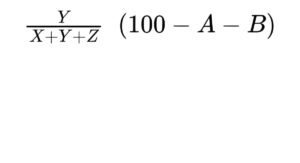
— triacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of triacylglycerols using the following expression:
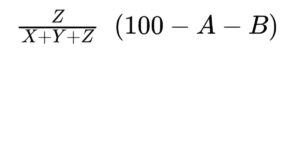
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.






