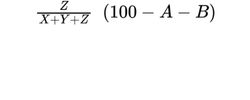(Ph. Eur. monograph 1427)
Action and use
Excipient.
DEFINITION
Mixture of diacylglycerols, mainly dibehenoylglycerol, together with variable quantities of mono- and triacylglycerols, obtained by esterification of Glycerol (0496) with behenic (docosanoic) acid.
Content
— monoacylglycerols: 15.0 per cent to 23.0 per cent;
— diacylglycerols: 40.0 per cent to 60.0 per cent;
— triacylglycerols: 21.0 per cent to 35.0 per cent.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Hard, waxy mass, or powder or white or almost white, unctuous flakes.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride, partly soluble in hot ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 65 °C to 77 °C.
B. Composition of fatty acids (see Tests).
C. It complies with the assay (content of diacylglycerols).
TESTS
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 4.0, determined on 1.0 g using a mixture of equal volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R and toluene R as solvent and with gentle heating.
Iodine value (2.5.4, Method A)
Maximum 3.0.
Saponification value (2.5.6)
145 to 165.
Carry out the titration with heating.
Free glycerol
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined as described under Assay.
Composition of fatty acids
Gas chromatography (2.4.22, Method C) with the following modifications. Raise the temperature of the column to 240 °C and use the mixture of calibrating substances in Table 2.4.22.-3.
Composition of the fatty acid fraction of the substance:
— palmitic acid: maximum 3.0 per cent;
— stearic acid: maximum 5.0 per cent;
— arachidic acid: maximum 10.0 per cent;
— behenic acid: minimum 83.0 per cent;
— erucic acid: maximum 3.0 per cent;
— lignoceric acid: maximum 3.0 per cent.
Water (2.5.12)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.00 g. Use pyridine R as the solvent.
Total ash (2.4.16)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.00 g.
ASSAY
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30).
Stock solution: Place 0.100 g of glycerol R in a flask and dilute to 25.0 mL with tetrahydrofuran R.
Test solution: In a 15 mL flask, weigh 0.200 g (m) of the substance to be examined and add 5.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran R.
Heat gently, at about 35 °C, and shake to dissolve. Reweigh the flask and calculate the total mass of solvent and substance (M); use immediately.
Reference solutions: Into four 15 mL flasks, introduce respectively 0.25 mL, 0.5 mL, 1.0 mL and 2.5 mL of the stock solution and add 5.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran R. Weigh each flask and calculate the concentration of glycerol in milligrams per gram of each reference solution.
Column:
— size: l = 0.6 m, Ø = 7 mm;
— stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (5 μm) with a pore size of 10 nm.
Mobile phase: tetrahydrofuran R.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Differential refractive index.
Injection: 40 μL; when injecting the test solution, maintain the flask at about 35 °C to avoid precipitation.
Relative retention: With reference to glycerol (retention time = about 15 min): triacylglycerols = about 0.73; diacylglycerols = about 0.76; monoacylglycerols = about 0.82.
Calculations:
— free glycerol: from the calibration curve obtained with the reference solutions, determine the concentration (C) in milligrams per gram in the test solution and calculate the percentage content (A) in the substance to be examined using the following expression:
(C x M)/ (m x 10)
— free fatty acids: calculate the percentage content of free fatty acids (D) using the following expression:
(IA x 340)/ 561.1
IA = acid value;
— monoacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of monoacylglycerols using the following expression:
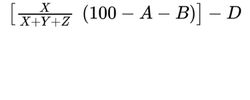
A = percentage content of free glycerol (see Tests);
B = percentage content of water (see Tests);
D = percentage content of free fatty acids;
X = area of the peak due to monoacylglycerols;
Y = area of the peak due to diacylglycerols;
Z = area of the peak due to triacylglycerols;
— diacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of diacylglycerols using the following expression:
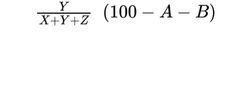
— triacylglycerols: calculate the percentage content of triacylglycerols using the following expression: