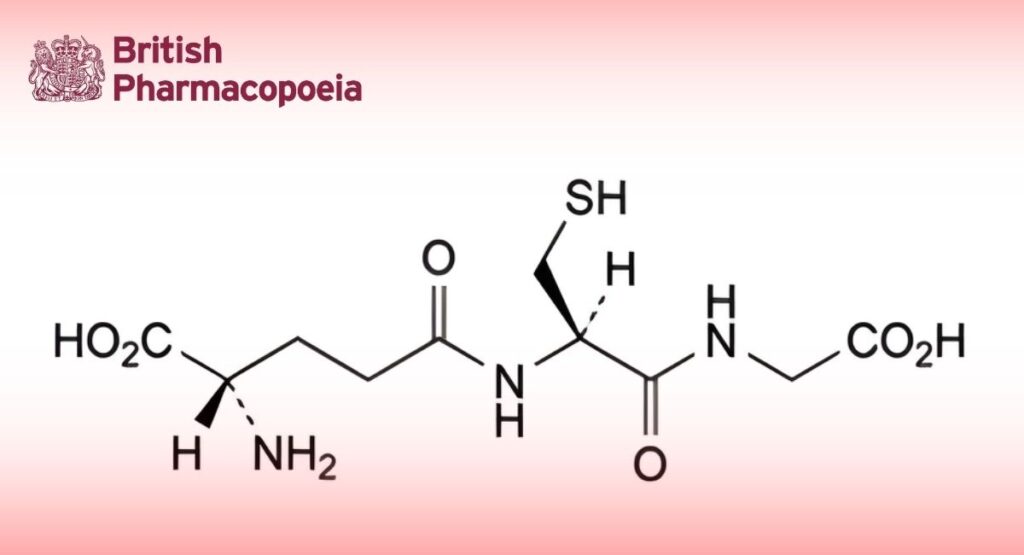
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1670)
C10H17N3O6S 307.3 70-18-8
DEFINITION
L-γ-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine.
Fermentation product.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: glutathione CRS.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.0 g in distilled water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-17.5 to -15.5 (dried substance).
Dissolve 1.0 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Capillary electrophoresis (2.2.47). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Internal standard solution (a): Dissolve 0.100 g of phenylalanine R in the electrolyte solution and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Internal standard solution (b): Dilute 10.0 mL of internal standard solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the electrolyte solution.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in the electrolyte solution and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Test solution (b): Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in internal standard solution (b) and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in internal standard solution (a) and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 50.0 mL with the electrolyte solution.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of the electrolyte solution. Add 1.0 mL of internal standard solution (a), 0.5 mL of a 2 mg/mL solution of L-cysteine R (impurity B) in the electrolyte solution, 0.5 mL of a 2 mg/mL solution of oxidised L-glutathione R (impurity C) in the electrolyte solution and 0.5 mL of a 2 mg/mL solution of L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteine R (impurity D) in the electrolyte solution. Dilute to 10.0 mL with the electrolyte solution.
Capillary:
— material: uncoated fused silica;
— size: length to the detector cell = 0.5 m; total length = 0.6 m; Ø = 75 μm.
Temperature 25 °C.
Electrolyte solution: Dissolve 1.50 g of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in 230 mL of water R and adjust to pH 1.80 with phosphoric acid R. Dilute to 250.0 mL with water R. Check the pH and, if necessary, adjust with phosphoric acid R or dilute sodium hydroxide solution R.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 200 nm.
Preconditioning of a new capillary: Rinse the new capillary before the first injection with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid at 138 kPa for 20 min and with water R at 138 kPa for 10 min; for complete equilibration, condition the capillary with the electrolyte solution at 350 kPa for 40 min, and subsequently at a voltage of 20 kV for 60 min.
Preconditioning of the capillary: Rinse the capillary with the electrolyte solution at 138 kPa for 40 min.
Between-run rinsing: Rinse the capillary with water R at 138 kPa for 1 min, with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide at 138 kPa for 2 min, with water R at 138 kPa for 1 min, with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid at 138 kPa for 3 min and with the electrolyte solution at 138 kPa for 10 min.
Injection: Test solutions (a) and (b), reference solutions (b) and (c) and the electrolyte solution (blank): under pressure (3.45 kPa) for 5 s.
Migration: Apply a voltage of 20 kV.
Run time 45 min.
Relative migration With reference to the internal standard (about 14 min): impurity A = about 0.77; impurity B = about 1.04; impurity E = about 1.2; impurity C = about 1.26; impurity D = about 1.3.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to the internal standard and impurity B in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (c); if necessary, increase the pH with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R;
— peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 2.5, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to glutathione in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (c); if necessary, lower the pH with phosphoric acid R;
— check that in the electropherogram obtained with test solution (a) there is no peak with the same migration time as the internal standard (in such case correct the area of the phenylalanine peak).
Limits Test solution (b):
— corrected areas: divide all the peak areas by the corresponding migration times;
— correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the ratio of time-corrected peak areas of impurity and the internal standard by the corresponding correction factor: impurity B = 3.0; impurity D = 1.4;
— impurity C: not more than 1.5 times the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent);
— impurity D: not more than the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— impurities A, B, E: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than 0.2 times the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
— total: not more than 2.5 times the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the ratio of the area of the peak due to glutathione to the area of the peak due to the internal standard in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Chlorides
Maximum 200 ppm.
Dissolve 0.5 g in 5 mL of dilute nitric acid R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. Add 10 mL of strong hydrogen peroxide solution R and heat on a water-bath for 30 min. Cool and dilute to 50 mL with water R. Add 1 mL of silver nitrate solution R2 and mix. Allow to stand for 5 min protected from light. Any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a standard prepared at the same time and in the same manner using 2 mL of chloride standard solution (50 ppm Cl) R. Examine the tubes laterally against a black background.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 300 ppm.
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R.
Ammonium (2.4.1, Method B)
Maximum 200 ppm, determined on 50 mg.
Prepare the standard using 0.1 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R.
Iron (2.4.9)
Maximum 10 ppm.
In a separating funnel, dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methyl isobutyl ketone R1, shaking for 3 min each time. To the combined organic layers, add 10 mL of water R and shake for 3 min. The aqueous layer complies with the test.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
In a ground-glass-stoppered flask, dissolve 0.500 g of the substance to be examined and 2 g of potassium iodide R in 50 mL of water R. Cool the solution in iced water and add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid R1 and 20.0 mL of 0.05 M iodine. Stopper the flask and allow to stand in the dark for 15 min. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate using 1 mL of starch solution R, added towards the end of the titration, as indicator. Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.05 M iodine is equivalent to 30.73 mg of C10H17N3O6S.
STORAGE
Protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
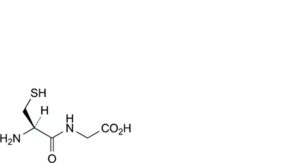
A. L-cysteinylglycine,
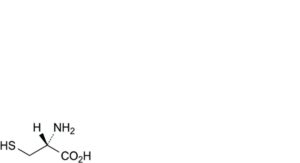
B. (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid (cysteine),
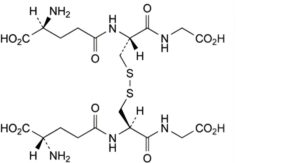
C. bis(L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine) disulfide (L-glutathione oxidised),
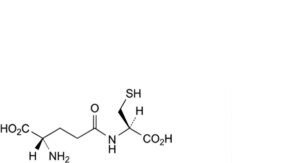
D. L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteine,
E. unknown structure (product of degradation).