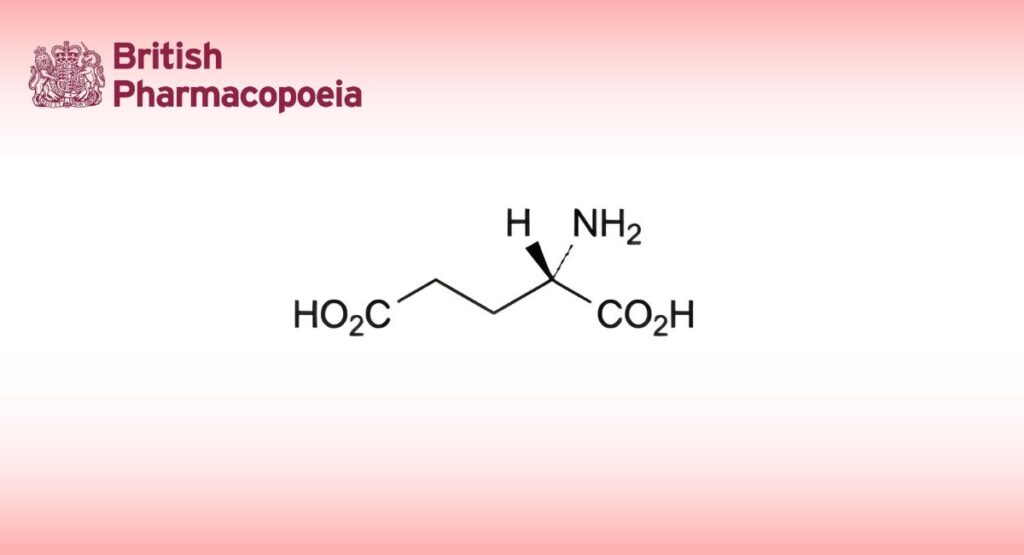
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0750)
C5H9NO4 147.1 56-86-0
Action and use
DEFINITION
Glutamic acid contains not less than 98.5 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 100.5 per cent of (2S)-2-aminopentanedioic acid, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
CHARACTERS
A white or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, freely soluble in boiling water, slightly soluble in cold water, practically insoluble in acetic acid, in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with glutamic acid CRS. Examine the substances prepared as discs. If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum quantity of water R, evaporate to dryness at 60 °C and record new spectra using the residues.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for ninhydrin-positive substances. The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. To 2.0 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R and 3.0 mL to 3.5 mL of 1 M sodium hydroxide to change the colour of the indicator to red. Add a mixture of 3 mL of formaldehyde solution R, 3 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R and 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R, to which sufficient 1 M sodium hydroxide has been added to produce a pink colour. The solution is decolourised. Add 1 M sodium hydroxide until a red colour is produced. The total volume of 1 M sodium hydroxide used is 4.0 mL to 4.7 mL.
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 5.00 g in 1 M hydrochloric acid with gentle heating, and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same acid.
Appearance of solution
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 30.5 to + 32.5, determined on solution S and calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Ninhydrin-positive substances
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel plate R.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of dilute ammonia R2 and dilute to 10 mL with water R.
Test solution (b): Dilute 1 mL of test solution (a) to 50 mL with water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of glutamic acid CRS in water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 5 mL of test solution (b) to 20 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 10 mg of glutamic acid CRS and 10 mg of aspartic acid CRS in water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Apply to the plate 5 μL of each solution. Dry the plate in a current of air for 15 min. Develop over a path of 15 cm using a mixture of 20 volumes of glacial acetic acid R, 20 volumes of water R and 60 volumes of butanol R. Allow the plate to dry in air, spray with ninhydrin solution R and heat at 100-105 °C for 15 min. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Dissolve 0.25 g in 3 mL of dilute nitric acid R and dilute to 15 mL with water R. The solution, to which 1 mL of water R is added instead of dilute nitric acid R, complies with the limit test for chlorides (200 ppm).
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Dilute 5 mL of solution S to 15 mL with distilled water R. The solution complies with the limit test for sulfates (300 ppm).
Ammonium (2.4.1)
50 mg complies with limit test B for ammonium (200 ppm). Prepare the standard using 0.1 mL of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R.
Iron (2.4.9)
In a separating funnel, dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. Shake with 3 quantities, each of 10 mL, of methyl isobutyl ketone R1, shaking for 3 min each time. To the combined organic layers add 10 mL of water R and shake for 3 min. The aqueous layer complies with the limit test for iron (10 ppm).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.130 g in 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R with gentle heating. Cool. Using 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue
solution R1 as indicator, titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide until the colour changes from yellow to blue.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 14.71 mg of C5H9NO4
.
STORAGE
Protected from light.