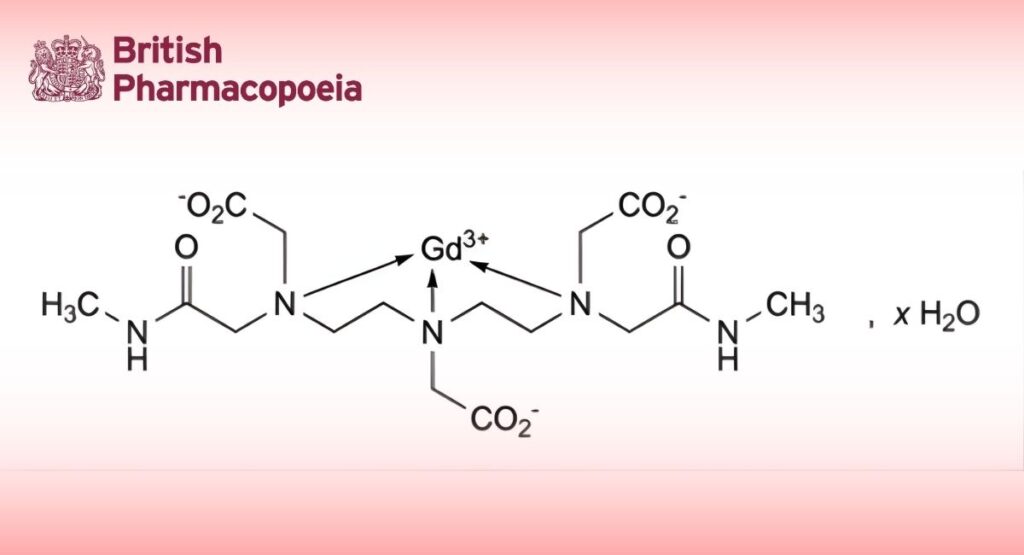
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2225)
C16H26GdN5O8 ,xH2O with x = 2 to 5 573.7 (anhydrous substance)
Anhydrous gadodiamide 131410-48-5
Action and use
Paramagnetic contrast enhancing medium for magnetic resonance imaging.
DEFINITION
6-(Carboxylatomethyl)-3,9-bis[(methylcarbamoyl)methyl]-3,6,9-triazaundecanedioato-κ N ,N ,N -gadolinium(III) hydrate (Gd-DTPA-BMA).
Content
— gadolinium (Gd; Mr 157.3): 26.0 per cent to 29.0 per cent (anhydrous substance);
— gadodiamide (C16H26GdN5O8; Mr 573.7): 96.5 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder, slightly hygroscopic.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: gadodiamide CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
B. Gadolinium (see Assay).
Results: The test solution exhibits the characteristic emission of gadolinium at 342.247 nm.
TESTS
Appearance of solution
The solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II (2.2.1). If this is not the case, heat the solution at 60- 70 °C for 2-3 min, cool to room temperature and compare the solutions again.
Dissolve 7.5 g (anhydrous substance) in water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 6.5.
Dissolve 0.50 g (anhydrous substance) in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b): Dissolve 60.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 5.0 mg of gadodiamide impurity A CRS and 5.0 mg of gadodiamide impurity B CRS in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 20 mg of gadodiamide CRS in water R, add 0.5 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to 10 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 60.0 mg of gadodiamide CRS in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (a) to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (e): Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with water R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: base-deactivated end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase: To 980 mL of water for chromatography R add 287 μL of glacial acetic acid R and 700 μL of triethylamine R, adjust to pH 6.8 with a 0.6 g/L solution of acetic acid R or with a 42 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R, then dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R; use within 2 days.
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Post-column solution: Dissolve 0.120 g of arsenazo III R in about 400 mL of water for chromatography R, add 0.650 g of urea R and mix to dissolve; add 6.3 mL of nitric acid R and sonicate for 15 min, filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 μm) and wash the filter with about 550 mL of water for chromatography R; dilute the filtrate and washings to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R; use within 1 week.
Flow rate: of post-column solution 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 658 nm.
Injection: 10 μL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (b), (d) and (e).
Run time: 5 times the retention time of gadodiamide.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A and B.
Relative retention: With reference to gadodiamide (retention time = about 5 min): impurity A = about 2.6; impurity B = about 4.0. The peak due to gadodiamide shows a shoulder due to an isomer that is to be integrated with the main peak.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to gadodiamide and impurity A; minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurities A and B.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for impurities A and B, use the concentration of each substance in reference solution (e);
— for impurities other than A and B, use the concentration of gadodiamide hydrate in reference solution (d).
Limits:
— impurity A: maximum 1.0 per cent;
— impurity B: maximum 0.2 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent;
— sum of unspecified impurities: maximum 0.3 per cent;
— total: maximum 1.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.10 per cent.
The thresholds indicated under Related substances (Table 2034.-1) in the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034) do not apply.
Excess of gadolinium or DTPA-BMA
Maximum 20 ppm (anhydrous substance) for the excess of gadolinium and maximum 0.1 per cent (anhydrous substance) for the excess of diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid bis-(methylamide) (DTPA-BMA).
Test solution: Dissolve 2.0 g of the substance to be examined in 25.0 mL of 1 M morpholinoethanesulfonate buffer solution pH 6.0 R. Add 50 μL of a 1.5 g/L solution of arsenazo III R.
Blank solution: To 25.0 mL of 1 M morpholinoethanesulfonate buffer solution pH 6.0 R, add 50 μL of a 1.5 g/L solution of arsenazo III R. The solution is violet-pink.
Standard solution: Dissolve 18.6 g of gadolinium chloride hexahydrate R in a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with the same acid solution. Dilute 20.0 mL of this solution to 1000.0 mL with water R (0.001 M solution). Standardise 10.0 mL of 0.001 M sodium edetate, using a mixture of 25.0 mL of 1 M morpholinoethanesulfonate buffer solution pH 6.0 R and 50 μL of a 1.5 g/L solution of arsenazo III R. Titrate with the standard solution until a greenish-blue colour is obtained.
Excess of DTPA-BMA If the test solution is violet-pink, there is no excess of gadolinium. Determine the excess of DTPA- BMA by titrating the test solution and the blank solution with the standard solution until a greenish-blue colour is obtained.
Calculate the excess of DTPA-BMA, in per cent, using the following expression:
V0 = volume of standard solution used in the blank titration, in millilitres;
V1 = volume of standard solution used in the titration of the test solution, in millilitres;
M1 = molarity of the gadolinium solution, in moles per litre;
m = mass of the substance to be examined (anhydrous substance) used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams.
Excess of gadolinium If the test solution is greenish-blue, there is no excess of DTPA-BMA. Determine the excess of gadolinium by titrating the test solution with 0.001 M sodium edetate until a violet-pink colour is obtained. Calculate the excess of gadolinium, in parts per million, using the following expression:
V2 = volume of 0.001 M sodium edetate used in the titration of the test solution, in millilitres;
M2 = molarity of the sodium edetate solution, in moles per litre;
m = mass of the substance to be examined (anhydrous substance) used to prepare the test solution, in milligrams.
Impurity C
Maximum 0.02 per cent (anhydrous substance).
Phthalaldehyde solution Introduce 0.100 g of phthalaldehyde R into a brown-glass vessel and dissolve in 3 mL of methanol R. Add 220 mL of borate buffer solution pH 10.0 R and 100 μL of 2-mercaptoethanol R and mix. Keep refrigerated and use within 24 h.
Test solution: Dissolve 1.5 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions: Prepare a series of reference solutions for calibration in the range of 1 μg/mL to 35 μg/mL of methylamine (impurity C) from a 0.220 g/L solution of methylamine hydrochloride R.
Calculate the concentrations of methylamine by multiplying the concentrations of methylamine hydrochloride by 0.46.
Blank solution A: freshly prepared mixture of 3.0 mL of phthalaldehyde solution and 3.0 mL of water R.
Introduce 3.0 mL of the test solution and of each reference solution into separate test tubes. Add 3.0 mL of phthalaldehyde solution to each tube and mix. Immediately transfer each solution to a cell and immediately measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at 335 nm using the blank solution as compensation liquid. Calculate the linear regression curve from the absorbances obtained with the reference solutions: the coefficient of determination r is not less than 0.99. If the absorbance obtained with the test solution is outside the calibration range, dilute the test solution with water R and repeat the procedure.
Water (2.5.12)
6.0 per cent to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.150 g.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
Bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)
Less than 3.50 IU/g.
ASSAY
Gadolinium
Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (2.2.57). An external calibration curve is used for quantification.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.600 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with a 20 g/L solution of nitric acid R.
Reference solutions: Into 3 volumetric flasks, introduce 10.0 mL, 15.0 mL and 20.0 mL of a certified reference solution containing 1000 μg/mL of gadolinium. Dilute each flask to 100.0 mL with a 20 g/L solution of nitric acid R. Mix to obtain reference solutions containing respectively 100 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL and 200 μg/mL of gadolinium.
The standard operating conditions prescribed by the manufacturer of the apparatus are to be followed. The following operating conditions are cited as an example of conditions found suitable for a given apparatus:
— flush time: 15 s;
— pure gas (N2) flow: 1 mL/min;
— plasma flow: 15 L/min;
— auxiliary flow: 1.0 mL/min;
— nebuliser flow: 1.0 mL/min;
— pump rate: 1.0 mL/min;
— power: 1160 W;
— read delay: 25 s;— wavelength: 342.247 nm;
— viewing height: 14.0 mm;
— background correction: none;
— nebuliser: cross-flow nebuliser.
System suitability:
— the correlation coefficient of the calibration curve is not less than 0.999.
Gadodiamide
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection 10 μL of test solution (b) and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C16H26GdN5O8 taking into account the assigned content of gadodiamide CRS.
STORAGE
In an airtight container.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
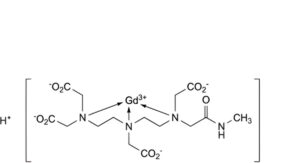
A. hydrogen[3,6-bis(carboxylatomethyl)-9-[(methylcarbamoyl)methyl]-3,6,9-triazaundecanedioato-κ N ,N ,N -gadolinate] (1-) (Gd-DTPA-MMA),
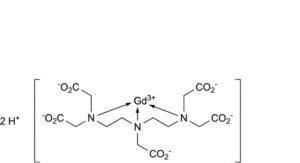
B. dihydrogen[3,6,9-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-3,6,9-triazaundecanedioato-κ N ,N ,N -gadolinate](2-) (Gd-DTPA),

C. methanamine (methylamine).