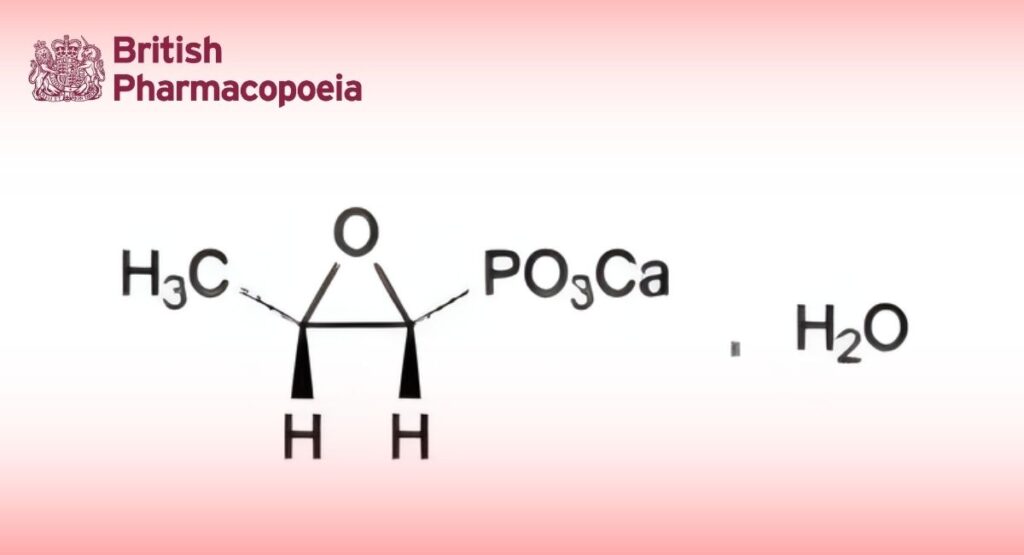
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1328)
C3H5CaO4P,H2O 194.1 26469-67-0
Action and use
Phosphonic acid derivative; antibacterial.
DEFINITION
Calcium (2R,3S)-(3-methyloxiran-2-yl)phosphonate monohydrate.
Substance produced by certain strains of Streptomyces fradiae or obtained by any other means.
Content
95.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone, in methanol and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, D.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: fosfomycin calcium CRS.
B. Dissolve about 0.1 g in 3 mL of a 25 per cent V/V solution of perchloric acid R. Add 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium periodate and heat on a water-bath for 30 min. Allow to cool and add 50 mL of water R.
Neutralise with a saturated solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate R and add 1 mL of a freshly prepared 400 g/L solution of potassium iodide R. Prepare a blank at the same time and in the same manner. The test solution remains colourless and the blank is orange.
C. To about 8 mg add 2 mL of water R, 1 mL of perchloric acid R and 2 mL of 0.1 M sodium periodate. Heat on a water-bath for 10 min and add, without cooling, 1 mL of ammonium molybdate solution R5 and 1 mL of aminohydroxynaphthalenesulfonic acid solution R. Allow to stand for 30 min. A blue colour develops.
D. It gives reaction (a) of calcium (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
8.1 to 9.6.
Dissolve 20 mg in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
-11.0 to -13.0 (anhydrous substance), determined at 405 nm using a mercury lamp.
Dissolve 2.5 g in a 125 g/L solution of sodium edetate R previously adjusted to pH 8.5 with strong sodium hydroxide solution R, and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Impurity A
Maximum 1.5 per cent.
In a glass-stoppered flask, dissolve 0.200 g in 100.0 mL of water R. Add 50 mL of 0.5 M phthalate buffer solution pH 6.4 R and 5.0 mL of 0.005 M sodium periodate, close and shake. Allow to stand protected from light for 90 min. Add 10 mL of a freshly prepared 400 g/L solution of potassium iodide R, close and shake for 2 min. Titrate with 0.0025 M sodium arsenite until the yellow colour almost disappears. Add 2 mL of starch solution R and slowly continue the titration until the colour is completely discharged. Carry out a blank test under the same conditions.
Calculate the percentage content of C3H7CaO5P using the following expression:
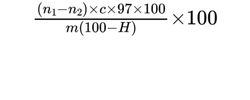
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in milligrams;
n1 = volume of 0.0025 M sodium arsenite used in the blank titration, in millilitres;
n2 = volume of 0.0025 M sodium arsenite used in the titration of the test solution, in millilitres;
c = molarity of the sodium arsenite solution;
H = percentage content of water.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 0.2 per cent.
Dissolve 0.500 g in water R, add 2 mL of nitric acid R and dilute to 50 mL with the same acid. To 2.5 mL of this solution add 12.5 mL of water R.
Water (2.5.12)
8.5 per cent to 11.5 per cent, determined on 0.250 g. Use as the solvent a mixture of 1 volume of pyridine R and 3 volumes of ethylene glycol R.
ASSAY
In a glass-stoppered flask, dissolve 0.120 g in 20.0 mL of 0.1 M sodium periodate. Add 5 mL of a 50 per cent V/V solution of perchloric acid R and shake. Heat in a water-bath at 37 °C for 105 min. Add 50 mL of water R and immediately adjust to pH 6.4 with a saturated solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate R. Add 10 mL of a freshly prepared 400 g/L solution of potassium iodide R, close and allow to stand for 2 min. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium arsenite until the yellow colour almost disappears. Add 2 mL of starch solution R and slowly continue the titration until the colour is completely discharged. Carry
out a blank test under the same conditions.
Calculate the percentage content of C3H5CaO4P using the following expression:
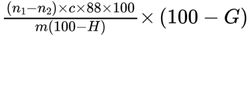
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in milligrams;
n1 = volume of 0.1 M sodium arsenite used in the blank titration, in millilitres;
n2 = volume of 0.1 M sodium arsenite used in the titration of the test solution, in millilitres;
c = molarity of the sodium arsenite solution;
G = percentage content of impurity A;
H = percentage content of water.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A.
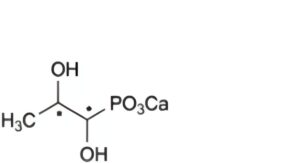
A. calcium (1,2-dihydroxypropyl)phosphonate.