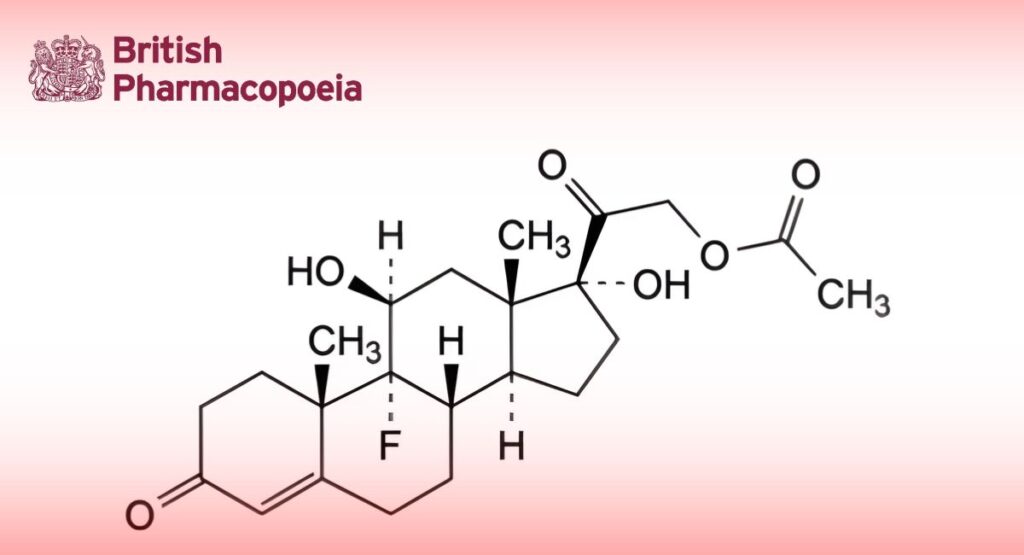
C23H31FO6 422.5 514-36-3
Action and use
Mineralocorticoid.
Preparation
Fludrocortisone Tablets
DEFINITION
9-Fluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-21-yl acetate.
Content
97.0 per cent to 103.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, B.
Second identification: C, D, E.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: fludrocortisone acetate CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of acetone R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Solvent mixture methanol R, methylene chloride R (1:9 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of fludrocortisone acetate CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of cortisone acetate CRS in 5 mL of reference solution (a).
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: Add a mixture of 1.2 volumes of water R and 8 volumes of methanol R to a mixture of 15 volumes of ether R and 77 volumes of methylene chloride R.
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection A: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results A: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
Detection B: Spray with alcoholic solution of sulfuric acid R. Heat at 120 °C for 10 min or until the spots appear. Allow to cool. Examine in daylight and in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results B: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour in daylight, fluorescence in ultraviolet light at 365 nm and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution (a): Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent (solution A). Dilute 2 mL of the solution to 10 mL with methylene chloride R.
Test solution (b): Transfer 2 mL of solution A to a 15 mL glass tube with a ground-glass stopper or a polytetrafluoroethylene cap. Add 10 mL of saturated methanolic potassium hydrogen carbonate solution R and immediately pass a stream of nitrogen R through the solution for 5 min. Stopper the tube. Heat on a water-bath at 45 °C
protected from light for 2.5 h. Allow to cool.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 25 mg of fludrocortisone acetate CRS in methanol R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent (solution B). Dilute 2 mL of the solution to 10 mL with methylene chloride R.
Reference solution (b): Transfer 2 mL of solution B to a 15 mL glass tube with a ground-glass stopper or a polytetrafluoroethylene cap. Add 10 mL of saturated methanolic potassium hydrogen carbonate solution R and immediately pass a stream of nitrogen R through the solution for 5 min. Stopper the tube. Heat on a water bath at 45 °C protected from light for 2.5 h. Allow to cool.
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: Add a mixture of 1.2 volumes of water R and 8 volumes of methanol R to a mixture of 15 volumes of ether R and 77 volumes of methylene chloride R.
Application: 5 μL.
Development: Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection A: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results A: The principal spot in each of the chromatograms obtained with the test solutions is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the corresponding reference solution.
Detection B: Spray with alcoholic solution of sulfuric acid R. Heat at 120 °C for 10 min or until the spots appear. Allow to cool. Examine in daylight and in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results B: The principal spot in each of the chromatograms obtained with the test solutions is similar in position, colour in daylight, fluorescence in ultraviolet light at 365 nm and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the corresponding reference solution. The principal spots in the chromatograms obtained with test solution (b) and reference solution (b) have RF values distinctly lower than those of the principal spots in the chromatograms obtained with test solution (a) and reference solution (a).
D. Mix about 5 mg with 45 mg of heavy magnesium oxide R and ignite in a crucible until an almost white residue is obtained (usually less than 5 min). Allow to cool, add 1 mL of water R, 0.05 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1 and about 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R to render the solution colourless. Filter and add to the filtrate a freshly prepared mixture of 0.1 mL of alizarin S solution R and 0.1 mL of zirconyl nitrate solution R. Mix, allow to stand for 5 min and compare the colour of the solution with that of a blank prepared in the same manner. The colour of the solution to be examined changes from red to yellow.
E. About 10 mg gives the reaction of acetyl (2.3.1).
TESTS
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 148 to + 156 (dried substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in dioxan R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 2.0 mg of fludrocortisone acetate CRS and 2.0 mg of hydrocortisone acetate CRS in the mobile phase, then dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.2 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: tetrahydrofuran R, water R (35:65 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Equilibration: With the mobile phase for about 30 min.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: Twice the retention time of fludrocortisone acetate.
Retention time: Hydrocortisone acetate = about 8.5 min; fludrocortisone acetate = about 10 min.
System suitability: Reference solution (a):
— resolution: minimum 1.0 between the peaks due to hydrocortisone acetate and fludrocortisone acetate; if necessary, adjust slightly the concentration of tetrahydrofuran in the mobile phase (an increase in the concentration of tetrahydrofuran reduces the retention times).
Limits:
— any impurity: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— total: not more than 0.75 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.025 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
ASSAY
Dissolve 10.0 mg in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 238 nm.
Calculate the content of C23H31FO6 taking the specific absorbance to be 405.