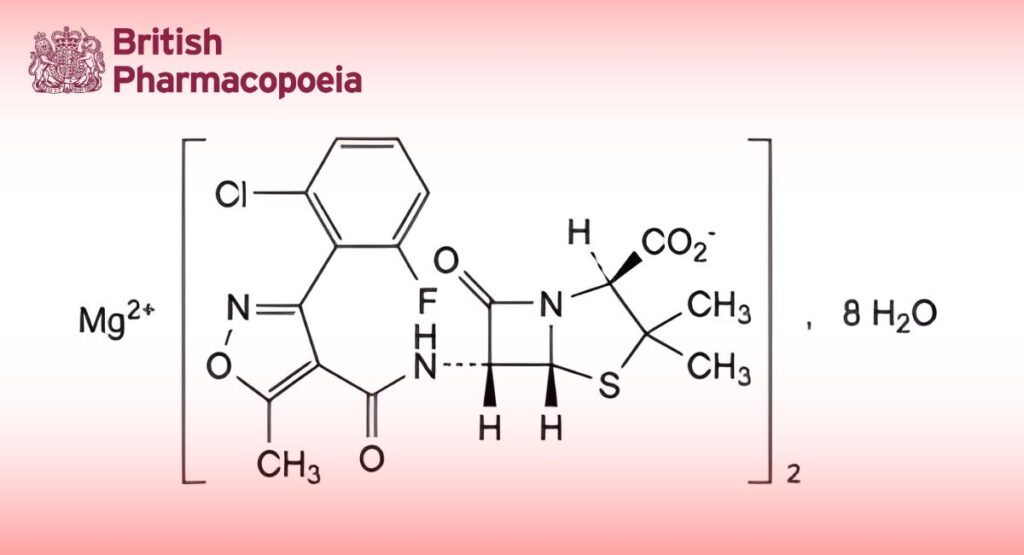
Flucloxacillin Magnesium
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2346)
C38H32Cl2F2MgN6O10S2,8H2O 1074 58486-36-5
Action and use
Penicillin antibacterial.
Preparations
Flucloxacillin Oral Suspension
Co-fluampicil Oral Suspension
DEFINITION
Magnesium bis[(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate] octahydrate.
Semi-synthetic product derived from a fermentation product.
Content
95.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A, C.
Second identification: B, C.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: flucloxacillin magnesium octahydrate CRS.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of water R.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 25 mg of flucloxacillin sodium CRS in 5 mL of water R.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 25 mg of cloxacillin sodium CRS, 25 mg of dicloxacillin sodium CRS and 25 mg of flucloxacillin sodium CRS in 5 mL of water R.
Plate: TLC silanised silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: Mix 30 volumes of acetone R and 70 volumes of a 154 g/L solution of ammonium acetate R previously adjusted to pH 5.0 with glacial acetic acid R.
Application: 1 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Expose the plate to iodine vapour until the spots appear.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 3 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
C. It gives the reaction of magnesium (2.3.1).
TESTS
pH (2.2.3)
4.5 to 6.5.
Dissolve 0.25 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7)
+ 163 to + 175 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 0.250 g in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Test solution (b): Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (a) to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 50.0 mg of flucloxacillin sodium CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (b) to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c): In order to prepare impurity A in situ, add 1 mL of sodium carbonate solution R to 10 mg of the substance to be examined, dilute to 25 mL with water R and place in an oven at 70 °C for 20 min.
Reference solution (d): Dilute 1 mL of reference solution (c) to 10 mL with a 27 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 3.5 with dilute phosphoric acid R.
Reference solution (e): In order to prepare impurity B in situ, add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R to 10 mL of reference solution (c), dilute to 25 mL with water R and place in an oven at 70 °C for 1 h. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 5 mL with a 27 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 7.0 with phosphoric acid R.
Reference solution (f): Dilute 2 mL of reference solution (a) to 10 mL with reference solution (e).
Reference solution (g): Dissolve 1.5 mg of flucloxacillin impurity C CRS in 1 mL of the mobile phase and dilute to 50 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (h): Dissolve 1 mg of flucloxacillin impurity D CRS in 100 mL of the mobile phase.
Reference solution (i): Dissolve 1 mg of flucloxacillin impurity E CRS in 100 mL of the mobile phase.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase: Mix 25 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 75 volumes of a 2.7 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 5.0 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution R.
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 225 nm.
Injection: 20 μL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (b), (d), (e), (f), (g), (h) and (i).
Run time: 7 times the retention time of flucloxacillin.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatograms obtained with reference solutions (d), (e), (g), (h) and (i) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, D and E respectively.
Relative retention: With reference to flucloxacillin (retention time = about 8 min): impurity C = about 0.2; impurity A (isomer 1) = about 0.3; impurity A (isomer 2) = about 0.5; impurity D = about 0.6; impurity B (isomer 1) = about 0.8; impurity B (isomer 2) = about 0.9; impurity E = about 6.
System suitability Reference solution (f):
— resolution: minimum 2.0 between the 2 peak due to impurity B (isomer 2) and the peak due to flucloxacillin.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity C by 3.3;
— impurity A (sum of the 2 isomers): the sum of the areas of the 2 peaks is not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2.0 per cent);
— impurity B (sum of the 2 isomers): the sum of the areas of the 2 peaks is not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— impurity C: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
— impurities D, E: for each impurity, not more than 0.3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
— any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than 0.3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
— total: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (3.0 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
2-Ethylhexanoic acid (2.4.28)
Maximum 0.8 per cent m/m.
Water (2.5.12)
12.0 per cent to 15.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C38H32Cl2F2MgN6O10S2 from the declared content of flucloxacillin sodium CRS, multiplying by 0.9773.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
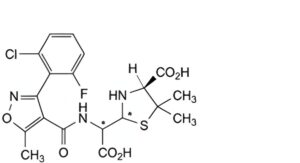
A. (4S)-2-[carboxy[[[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]methyl]-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4- carboxylic acid (penicilloic acids of flucloxacillin),
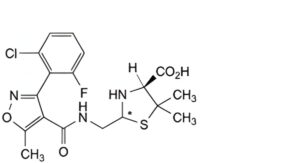
B. (2RS,4S)-2-[[[[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]methyl]-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4- carboxylic acid (penilloic acids of flucloxacillin),
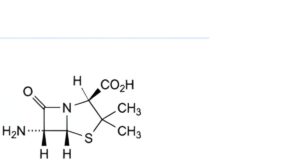
C. (2S,5R,6R)-6-amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (6-aminopenicillanic acid),
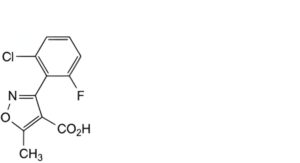
D. 3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylic acid,
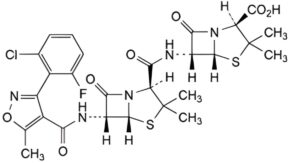
E. (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo- 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (6-APA flucloxacillin amide).