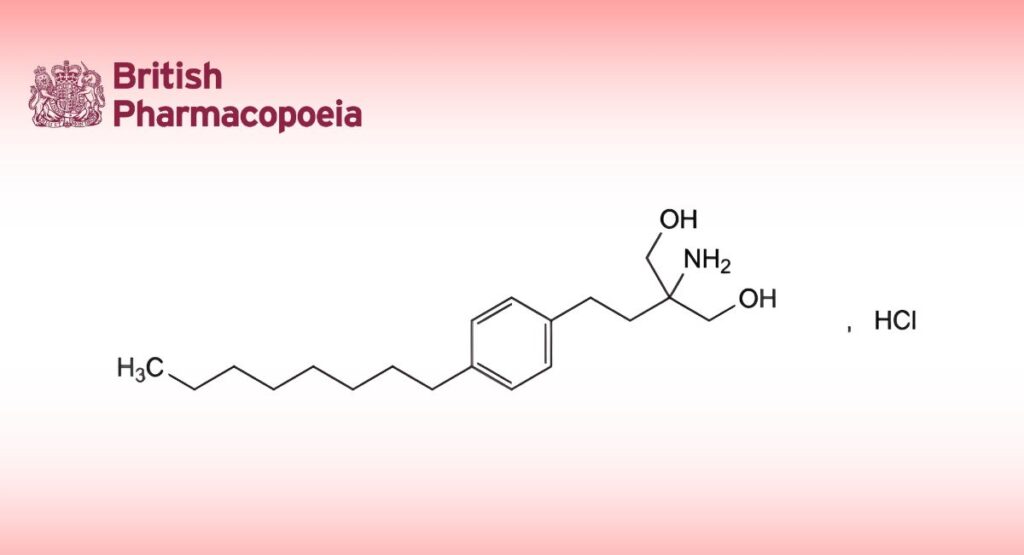
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2988)
C19H34ClNO2 343.9 162359-56-0
Action and use
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator; immunomodulator.
DEFINITION
2-Amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol hydrochloride.
Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white powder.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in heptane.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Mulls in liquid paraffin R if recording by transmission.
Comparison fingolimod hydrochloride CRS.
If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in anhydrous ethanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
B. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
If precipitation is observed after addition of dilute nitric acid R, centrifuge and use the supernatant in the remainder of the test.
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R1, 0.1 per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 30.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 30.0 mg of fingolimod hydrochloride CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (c): Dissolve 3 mg of fingolimod for system suitability CRS (containing impurities C and G) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.0 mm;
— stationary phase: encapsulated polar-embedded octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 μm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 0.1 per cent V/V solution of phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R1;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2 | 80 | 20 |
| 2 – 22 | 80 → 5 | 20 → 95 |
| 22 – 25 | 5 | 95 |
Flow rate 0.8 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection 5 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with fingolimod for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities C and G.
Relative retention: With reference to fingolimod (retention time = about 11 min): impurity G = about 1.08;
impurity C = about 1.10.
System suitability: Reference solution (c):
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities G and C.
Calculation of percentage contents:
— for each impurity, use the concentration of fingolimod hydrochloride in reference solution (b).
Limits:
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Water (2.5.32)
Maximum 0.3 per cent, determined on 0.200 g by direct sample introduction.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection Test solution and reference solution (a).
System suitability Reference solution (a):
— symmetry factor: maximum 5.0.
Calculate the percentage content of C19H34ClNO2 taking into account the assigned content of fingolimod hydrochloride CRS.
IMPURITIES
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I.
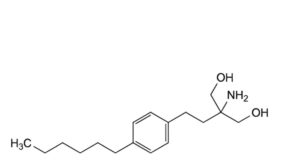
A. 2-amino-2-[2-(4-hexylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
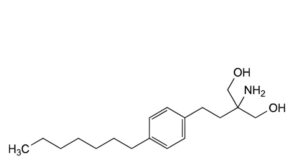
B. 2-amino-2-[2-(4-heptylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
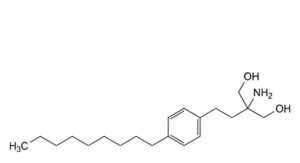
C. 2-amino-2-[2-(4-nonylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
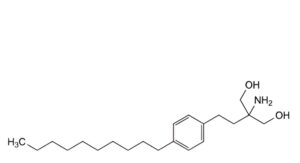
D. 2-amino-2-[2-(4-decylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
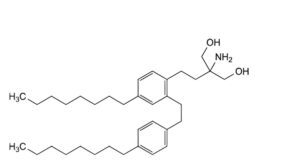
E. 2-amino-2-[2-[4-octyl-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]phenyl]ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
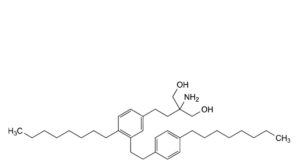
F. 2-amino-2-[2-[4-octyl-3-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]phenyl]ethyl]propane-1,3-diol,
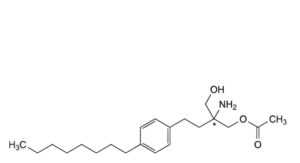
G. (2Ξ)-2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-octylphenyl)butyl acetate,
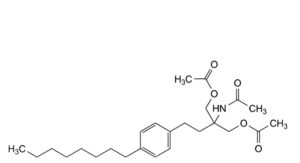
H. 2-acetamido-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diyl diacetate,
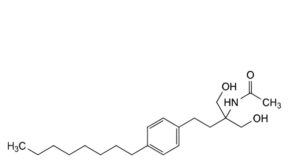
I. N-[1-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-octylphenyl)butan-2-yl]acetamide.