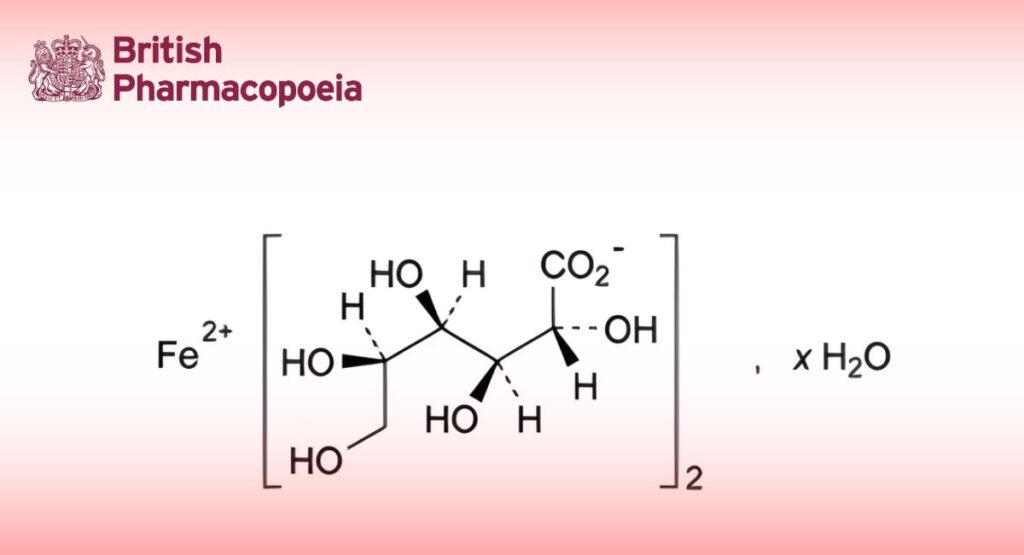
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0493)
C12H22FeO14,xH2O 446.1 (anhydrous substance)
Action and use
Used in prevention and treatment of iron deficiency.
Preparation
Ferrous Gluconate Tablets
DEFINITION
Iron(II) bis[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate] (iron(II) di(D-gluconate)) hydrate.
Content
11.8 per cent to 12.5 per cent of iron(II) (dried substance).
It contains a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Greenish-yellow or grey powder or granules.
Solubility
Freely but slowly soluble in water giving a greenish-brown solution, more readily soluble in hot water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in 2 mL of water R, heating if necessary in a water-bath at 60 °C.
Reference solution: Dissolve 20 mg of ferrous gluconate CRS in 2 mL of water R, heating if necessary in a water-bath at 60 °C.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 μm) [or TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 μm)].
Mobile phase: concentrated ammonia R, ethyl acetate R, water R, ethanol (96 per cent) R (10:10:30:50 V/V/V/V).
Application: 1 μL.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: At 105 °C for 20 min; allow to cool.
Detection: Spray with a solution containing 10 g/L of cerium sulfate R and 25 g/L of ammonium molybdate R in dilute sulfuric acid R and heat at 105 °C for about 10 min.
Results: After 5 min, the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. 1 mL of solution S (see Tests) gives reaction (a) of iron (2.3.1).
TESTS
Solution S
Dissolve 2.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R and heated to about 60 °C, allow to cool and dilute to 20 mL with carbon dioxide-free water R prepared from distilled water R.
Appearance of solution
The solution is clear (2.2.1).
Dilute 2 mL of solution S to 10 mL with water R. Examine the solution against the light.
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 5.5 for solution S, measured 3-4 h after preparation.
Sucrose and reducing sugars
Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 mL of warm water R and add 1 mL of dilute ammonia R1. Pass hydrogen sulfide R through the solution and allow to stand for 30 min. Filter and wash the precipitate with 2 quantities, each of 5 mL, of water R. Acidify the combined filtrate and washings to blue litmus paper R with dilute hydrochloric acid R and add 2 mL in excess. Boil until the vapour no longer darkens lead acetate paper R and continue boiling, if necessary, until the volume is reduced to about 10 mL. Cool, add 15 mL of sodium carbonate solution R, allow to stand for 5 min and filter. Dilute the filtrate to 100 mL with
water R. To 5 mL of this solution add 2 mL of cupri-tartaric solution R and boil for 1 min. Allow to stand for 1 min. No red precipitate is formed.
Chlorides (2.4.4)
Maximum 0.06 per cent.
Dilute 0.8 mL of solution S to 15 mL with water R.
Oxalates
Dissolve 5.0 g in a mixture of 10 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 40 mL of water R. Shake the solution with 50 mL of ether R for 5 min. Separate the aqueous layer and shake it with 20 mL of ether R for 5 min. Combine the ether layers, evaporate to dryness and dissolve the residue in 15 mL of water R. Filter, boil the filtrate until the volume is reduced to 5 mL and add 1 mL of dilute acetic acid R and 1.5 mL of calcium chloride solution R. Allow to stand for 30 min. No precipitate is formed.
Sulfates (2.4.13)
Maximum 500 ppm.
To 3.0 mL of solution S add 3 mL of acetic acid R and dilute to 15 mL with distilled water R. Examine the solutions against the light.
Elemental impurities
Any method that fulfils the requirements of general chapter 2.4.20. Determination of elemental impurities may be used.
| Element | Maximum content (ppm) |
| Arsenic | 2 |
| Cobalt | 25 |
| Nickel | 50 |
| Vanadium | 50 |
Ferric ions
Maximum 1.0 per cent.
In a ground-glass-stoppered flask, dissolve 5.00 g in a mixture of 10 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 100 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Add 3 g of potassium iodide R, close the flask and allow to stand protected from light for 5 min.
Titrate with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate, using 0.5 mL of starch solution R, added towards the end of the titration, as indicator.
Carry out a blank titration. Not more than 9.0 mL of 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate is used.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
5.0 per cent to 10.5 per cent, determined on 0.500 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 5 h.
Microbial contamination
TAMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
TYMC: acceptance criterion 10 CFU/g (2.6.12).
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.5 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate R in a mixture of 30 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 70 mL of water R. When the effervescence stops, dissolve 1.00 g of the substance to be examined with gentle shaking. Using 0.1 mL of ferroin R as indicator, titrate with 0.1 M ammonium and cerium nitrate until the red colour disappears.
1 mL of 0.1 M ammonium and cerium nitrate is equivalent to 5.585 mg of iron(II).
STORAGE
Protected from light.