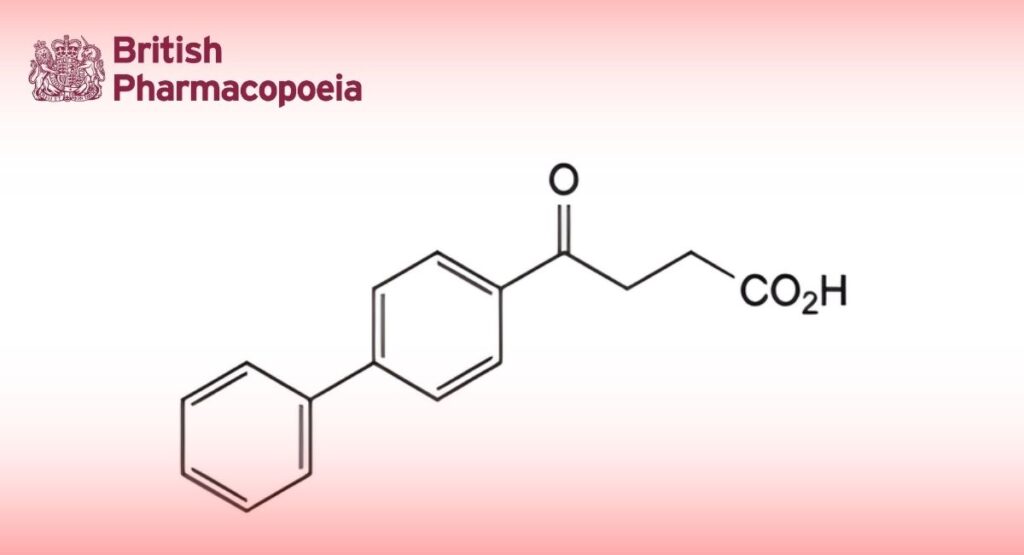
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1209)
C16H14O3 254.3 36330-85-5
Action and use
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
DEFINITION
4-(Biphenyl-4-yl)-4-oxobutanoic acid.
Content
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, fine, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone, in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B.
Second identification: A, C.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 186 °C to 189 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: fenbufen CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution: Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 10 mg of fenbufen CRS in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 10 mg of ketoprofen CRS in methylene chloride R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. To 5 mL of this solution, add 5 mL of reference solution (a).
Plate: TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous acetic acid R, ethyl acetate R, hexane R (5:25:75 V/V/V).
Application: 10 μL.
Development: Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying: In air.
Detection: Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture dimethylformamide R, mobile phase A (40:60 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 0.5 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 25 mg of fenbufen CRS and 6 mg of ketoprofen CRS in the solvent mixture and dilute to 10 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1 mL of this solution to 100 mL with the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: mix 32 volumes of acetonitrile R and 68 volumes of a mixture of 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R and 55 volumes of water R;
— mobile phase B: mix 45 volumes of acetonitrile R and 55 volumes of a mixture of 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R and 55 volumes of water R;
| Time
(min) |
Mobile phase A
(per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B
(per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 15 | 100 | 0 |
| 15 – 20 | 100 → 0 | 0 → 100 |
| 20 – 35 | 0 | 100 |
Flow rate: 2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to ketoprofen and fenbufen.
Limits:
— any impurity: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
— total: not more than 5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.02 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 75 mL of acetone R previously neutralised with phenolphthalein solution R1 and add 50 mL of water R.
Add 0.2 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1 and titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 25.43 mg of C16H14O3.
IMPURITIES
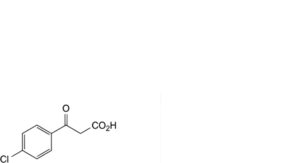
A. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-oxopropanoic acid,
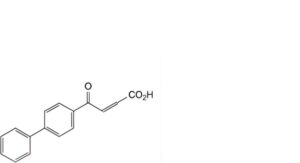
B. 4-(biphenyl-4-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid,
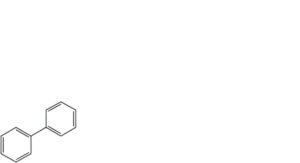
C. biphenyl,
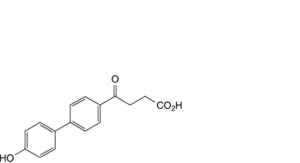
D. 4-(4′-hydroxybiphenyl-4-yl)-4-oxobutanoic acid.