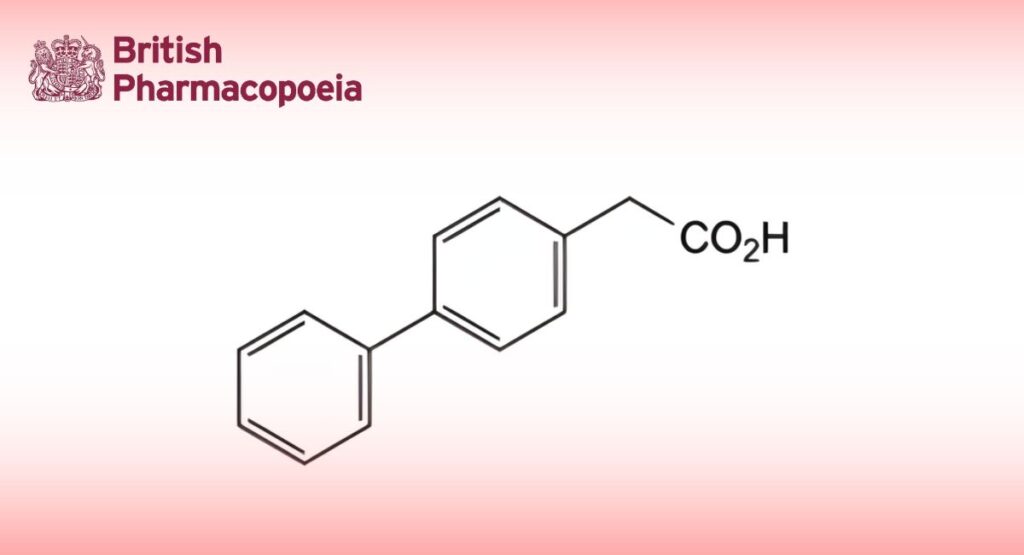
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2304)
C14H12O2 212.2 5728-52-9
Action and use
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
DEFINITION
(Biphenyl-4-yl)acetic acid.
Content
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
mp
About 164 °C.
IDENTIFICATION
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: felbinac CRS.
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Protect the solutions from light and inject within 20 min of preparation.
Test solution: Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 5.0 mg of felbinac impurity A CRS and 5.0 mg of biphenyl R (impurity B) in methanol R, add 0.5 mL of the test solution and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: Mix 45 volumes of a 0.1 per cent V/V solution of glacial acetic acid R and 55 volumes of methanol R.
Flow rate: 2 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 254 nm.
Injection: 20 μL.
Run time: 3.5 times the retention time of felbinac.
Relative retention: With reference to felbinac (retention time = about 15 min): impurity A = about 1.3; impurity B = about 2.8.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to felbinac and impurity A.
Limits:
— impurity A: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent);
— impurity B: not more than the area of the peak due to felbinac in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the peak due to felbinac in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than twice the area of the peak due to felbinac in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.2 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the peak due to felbinac in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.05 per cent).
Chlorides
Maximum 110 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 40 mL of acetone R, add 6 mL of a 10 per cent V/V solution of nitric acid R, dilute to 50.0 mL with water R and mix. Pour 15.0 mL of this solution as a single addition into 1 mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate and allow to stand for 5 min protected from light. When viewed horizontally against a black background, any opalescence produced is not more intense than that obtained by treating in the same manner 15.0 mL of a mixture of 1.5 mL of 0.002 M hydrochloric acid, 40 mL of acetone R, 6 mL of 10 per cent V/V solution of nitric acid R, diluted to 50.0 mL with water R.
Sulfates
Maximum 130 ppm.
Dissolve 1.5 g in 40 mL of dimethylformamide R, add 1 mL of a 10 per cent V/V solution of hydrochloric acid R, dilute to 50.0 mL with dimethylformamide R and mix. To 15.0 mL of this solution add 2.0 mL of a 120 g/L solution of barium chloride R and allow to stand for 5 min. Any opalescence produced is not more intense than that of a standard prepared in the same manner but using 2.0 mL of 0.001 M sulfuric acid instead of the substance to be examined.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.160 g in 50 mL of methanol R. Titrate with 0.1 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide determining the end-point
potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide is equivalent to 21.23 mg of C14H12O2.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B.
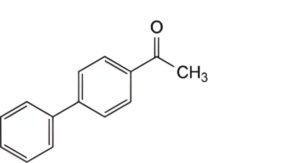
A. 4-acetyl biphenyl,
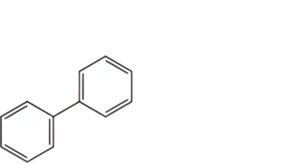
B. biphenyl.