(Ph. Eur. monograph 2398)
Action and use
Source of vitamins A and D.
DEFINITION
Purified fatty oil obtained from the fresh livers of farmed cod, Gadus morhua L., solid substances being removed by cooling and filtering.
Content
— sum of the contents of EPA and DHA (expressed as triglycerides): 10.0 per cent to 28.0 per cent;
— vitamin A: 50 IU (15 μg) to 500 IU (150 μg) per gram;
— vitamin D3: maximum 50 IU (1.3 μg) per gram.
A suitable antioxidant may be added.
PRODUCTION
The fish shall only be given feed with a composition that is in accordance with the relevant European Union or other applicable regulations.
The content of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) is controlled using methods and limits in accordance with the requirements set in the European Union or other applicable regulations.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, pale yellowish liquid.
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, miscible with light petroleum, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
A. Examine the C NMR spectra obtained in the test for positional distribution (β(2)-acyl) of fatty acids (see Tests). The spectra contain peaks between 172 ppm and 173 ppm with shifts similar to those in the spectrum shown in Figure 2398.-1.
The positional distribution (β(2)-acyl) for cervonic (docosahexaenoic) acid (C22:6 n-3; DHA), timnodonic (eicosapentaenoic) acid (C20:5 n-3; EPA) and moroctic acid (C18:4 n-3) complies with the limits.
B. Linoleic acid (see Tests).
TESTS
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 2.0.
Anisidine value (2.5.36)
Maximum 10.0.
Peroxide value (2.5.5, Method B)
Maximum 5.0.
Unsaponifiable matter (2.5.7)
Maximum 1.5 per cent, determined on 2.0 g, and extracting with 3 quantities, each of 50 mL, of peroxide-free ether R.
Stearin
Heat at least 10 mL to 60-90 °C then allow to cool for 3 h in a bath of iced water or a thermostatically controlled bath at 0 ± 0.5 °C. If necessary, to eliminate insoluble matter, filter the sample after heating. The sample remains clear.
Positional distribution (β(2)-acyl) of fatty acids
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry (2.2.33).
Test solution: Dissolve 190-210 mg of the substance to be examined in 500 μL of deuterated chloroform R. Prepare at least 3 samples and examine within 3 days.
Apparatus: High-resolution FT-NMR spectrometer operating at minimum 300 MHz.
Acquisition of 13C NMR spectra: The following parameters may be used:
— sweep width: 200 ppm (-5 ppm to 195 ppm);
— irradiation frequency offset: 95 ppm;
— time domain: 64 K;
— pulse delay: 2 s;
— pulse program: zgig 30 (inverse gated, 30° excitation pulse);
— dummy scans: 4;
— number of scans: 4096.
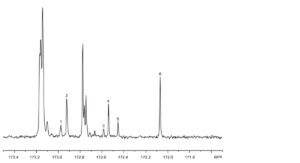
1. α C18:4 2. α EPA 3. β C18:4 4. β EPA 5. α DHA 6. β DHA
Figure 2398.-1. – 13C NMR spectrum: carbonyl region of farmed cod-liver oil
Processing and plotting: The following parameters may be used:
— size: 64 K (zero-filling);
— window multiplication: exponential;
— Lorentzian broadening factor: 0.2 Hz.
Use the CDCl3 signal for shift referencing. The shift of the central peak of the 1:1:1 triplet is set to 77.16 ppm.
Plot the spectral region δ 171.5-173.5 ppm. Compare the spectrum with the spectrum shown in Figure 2398.-1. The shift values lie within the ranges given in Table 2398.-1.
Table 2398.-1. – Shift values
| Signal | Shift range (ppm) |
| β DHA | 172.05 – 172.09 |
| α DHA | 172.43 – 172.47 |
| β EPA | 172.52 – 172.56 |
| α EPA | 172.90 – 172.94 |
| β C18:4 | 172.56 – 172.60 |
| α C18:4 | 172.95 – 172.99 |
System suitability:
— signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 5 for the smallest relevant peak corresponding to α C18:4 signal (in the range δ 172.95-172.99 ppm);
— peak width at half-height: maximum 0.02 ppm for the central CDCl3 signal (at δ 77.16 ppm).
Calculation of positional distribution (β(2)-acyl) Use the following expression:

α = peak area of the corresponding α-carbonyl peak;
β = peak area of β-carbonyl peak from C22:6 n-3, C20:5 n-3 or C18:4 n-3, respectively.
Limits:
— positional distribution (β(2)-acyl):
— cervonic (docosahexaenoic) acid (C22:6 n-3; DHA): 71 per cent to 81 per cent;
— timnodonic (eicosapentaenoic) acid (C20:5 n-3 EPA): 32 per cent to 40 per cent;
— moroctic acid (C18:4 n-3): 28 per cent to 38 per cent.
Composition of fatty acids (2.4.29)
For identification of the peaks, see the chromatogram shown in Figure 2398.-2.
The 24 largest peaks of the methyl esters account for more than 90 per cent of the total area (these correspond to, in common elution order: 14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 16:1 n-7, 16:4 n-1, 18:0, 18:1 n-9, 18:1 n-7, 18:2 n-6, 18:3 n-3, 18:4 n-3, 20:1 n-11, 20:1 n-9, 20:1 n-7, 20:2 n-6, 20:4 n-6, 20:3 n-3, 20:4 n-3, 20:5 n-3, 22:1 n-11, 22:1 n-9, 21:5 n-3, 22:5 n-3, 22:6 n-3).
Linoleic acid (2.4.29)
3.0 per cent to 11.0 per cent.
ASSAY
EPA and DHA (2.4.29)
See the chromatogram shown in Figure 2398.-2.
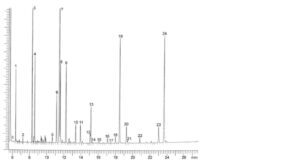
1. C14:0 5. C16:4 n-1 9. C18:2 n-6 13. C20:1 n-9 17. C20:3 n-3 21. C22:1 n-9
2. C15:0 6. C18:0 10. C18:3 n-3 14. C20:1 n-7 18. C20:4 n-3 22. C21:5 n-3
3. C16:0 7. C18:1 n-9 11. C18:4 n-3 15. C20:2 n-6 19. C20:5 n-3 23. C22:5 n-3
4. C16:1 n-7 8. C18:1 n-7 12. C20:1 n-11 16. C20:4 n-6 20. C22:1 n-11 24. C22:6 n-3
Figure 2398.-2. – Chromatogram for the test for composition of fatty acids of farmed cod-liver oil
Vitamin A
Carry out the test as rapidly as possible, avoiding exposure to actinic light and air, oxidising agents, oxidation catalysts (for example, copper and iron) and acids.
Use method A. If method A is found not to be valid, use method B.
METHOD A
Ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution To 1.00 g in a round-bottomed flask, add 3 mL of a freshly prepared 50 per cent m/m solution of potassium hydroxide R and 30 mL of anhydrous ethanol R. Boil under reflux in a current of nitrogen R for 30 min. Cool rapidly and add 30 mL of water R. Extract with 50 mL of ether R. Repeat the extraction 3 times and discard the lower layer after complete separation. Wash the combined upper layers with 4 quantities, each of 50 mL, of water R, and evaporate to dryness under a gentle current of nitrogen R at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C or in a rotary evaporator at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C under reduced pressure (water ejector). Dissolve the residue in sufficient 2-propanol R1
to give an expected concentration of vitamin A equivalent to 10-15 IU/mL.
Measure the absorbances of the solution at 300 nm, 310 nm, 325 nm and 334 nm and at the wavelength of maximum absorption with a suitable spectrophotometer in specially matched 1 cm cells, using 2-propanol R1 as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of vitamin A, as all-trans-retinol, in International Units per gram, using the following expression:
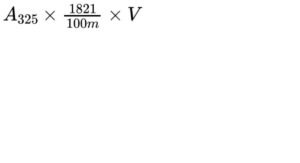
A325 = absorbance at 325 nm;
m = mass of the substance to be examined, in grams;
V = total volume of solution containing 10-15 IU of vitamin A per millilitre;
1821 = conversion factor for the specific absorbance of all-trans-retinol, in International Units.
The above expression can be used only if A325 has a value not greater than A325,corr /0.970, where A325,corr is the corrected absorbance at 325 nm and is given by the following equation:
A325, corr = 6.815A325 − 2.555A310 − 4.260A334
A designates the absorbance at the wavelength indicated by the subscript.
If A325 has a value greater than A325, corr /0.970, calculate the content of vitamin A using the following expression:

The assay is not valid unless:
— the wavelength of maximum absorption lies between 323 nm and 327 nm;
— the absorbance at 300 nm relative to that at 325 nm is at most 0.73.
METHOD B
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution: Prepare duplicates. To 2.00 g in a round-bottomed flask, add 5 mL of a freshly prepared 100 g/L solution of ascorbic acid R, 10 mL of a freshly prepared 800 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R and 100 mL of anhydrous ethanol R. Boil under a reflux condenser on a water-bath for 15 min. Add 100 mL of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R and cool. Transfer the solution to a 500 mL separating funnel, rinsing the round-bottomed flask with about 75 mL of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R and then with 150 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of ether R and light petroleum R1. Shake for 1 min. When the layers have separated completely, discard the lower layer and wash the upper
layer, first with 50 mL of a 30 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R in a 10 per cent V/V solution of anhydrous ethanol R and then with 3 quantities, each of 50 mL, of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R. Filter the upper layer through 5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R on a fast filter paper into a 250 mL flask suitable for a rotary evaporator. Wash the funnel with 10 mL of fresh extraction mixture, filter and combine the upper layers. Distil them at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C under reduced pressure (water ejector) and fill with nitrogen R when evaporation is completed. Alternatively, evaporate the solvent under a gentle current of nitrogen R at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. Dissolve the residue in 2-propanol R, transfer to a 25 mL volumetric flask and dilute to 25 mL with 2-propanol R. Gentle heating in an ultrasonic bath may be required. A large fraction of the white residue is cholesterol, constituting approximately 50 per cent m/m of the unsaponifiable matter of cod-liver oil.
Reference solution (a): Prepare a solution of retinol acetate CRS in 2-propanol R1 so that 1 mL contains about 1000 IU of all-trans-retinol.
The exact concentration of reference solution (a) is assessed by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25). Dilute reference solution (a) with 2-propanol R1 to a presumed concentration of 10-15 IU/mL and measure the absorbance at 326 nm in matched 1 cm cells using 2-propanol R1 as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of vitamin A in International Units per millilitre of reference solution (a) using the following expression, taking into account the assigned content of retinol acetate CRS:
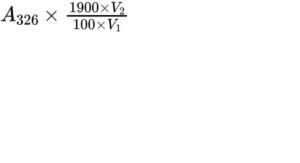
A326 = absorbance at 326 nm;
V1 = volume of reference solution (a) used;
V2 = volume of the diluted solution;
1900 = conversion factor for the specific absorbance of retinol acetate CRS, in International Units.
Reference solution (b) Proceed as described for the test solution but using 2.00 mL of reference solution (a) in place of the substance to be examined.
The exact concentration of reference solution (b) is assessed by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25). Dilute reference solution (b) with 2-propanol R1 to a presumed all-trans-retinol concentration of 10-15 IU/mL and measure the absorbance at 325 nm in matched 1 cm cells using 2-propanol R1 as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of all-trans-retinol in International Units per millilitre of reference solution (b), using the following expression:
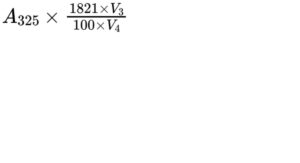
A325 = absorbance at 325 nm;
V3 = volume of the diluted solution;
V4 = volume of reference solution (b) used;
1821 = conversion factor for the specific absorbance of all-trans-retinol, in International Units.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5-10 μm).
Mobile phase: water R, methanol R (3:97 V/V).
Flow rate: 1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 325 nm.
Injection: 10 μL; inject in triplicate the test solution and reference solution (b).
Retention time: All-trans-retinol = 5 ± 1 min.
System suitability:
— the chromatogram obtained with the test solution shows a peak corresponding to the peak due to all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— the results obtained with the duplicate test solutions do not differ by more than 5 per cent;
— the recovery of all-trans-retinol in reference solution (b) as assessed by direct absorption spectrophotometry is greater than 95 per cent.
Calculate the content of vitamin A using the following expression:
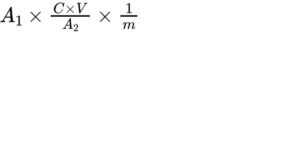
A1 = area of the peak due to all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution;
A2 = area of the peak due to all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
C = concentration of retinol acetate CRS in reference solution (a) as assessed prior to the saponification, in International Units per millilitre (= 1000 IU/mL);
V = volume of reference solution (a) treated (2.00 mL);
m = mass of the substance to be examined in the test solution (2.00 g).
Vitamin D3
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Carry out the assay as rapidly as possible, avoiding exposure to actinic light and air.
Internal standard solution: Dissolve 0.50 mg of ergocalciferol CRS in 100 mL of anhydrous ethanol R.
Test solution (a): To 4.00 g in a round-bottomed flask, add 5 mL of a freshly prepared 100 g/L solution of ascorbic acid R, 10 mL of a freshly prepared 800 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R and 100 mL of anhydrous ethanol R. Boil under a reflux condenser on a water-bath for 30 min. Add 100 mL of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R and cool the solution to room temperature. Transfer the solution to a 500 mL separating funnel, rinsing the round-bottomed flask with about 75 mL of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R and then with 150 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of ether R and light petroleum R1. Shake for 1 min. When the layers have separated completely, discard the lower layer and wash the upper layer, first with 50 mL of a 30 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R in a 10 per cent V/V solution of anhydrous ethanol R, and then with 3 quantities, each of 50 mL, of a 10 g/L solution of sodium chloride R. Filter the upper layer through 5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R on a fast filter paper into a 250 mL flask suitable for a rotary evaporator. Wash the funnel with 10 mL of fresh extraction mixture, filter and combine the upper layers. Distil them at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C under reduced pressure (water ejector) and fill with nitrogen R when evaporation is completed. Alternatively, evaporate the
solvent under a gentle current of nitrogen R at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. Dissolve the residue in 1.5 mL of the mobile phase described under Purification. Gentle heating in an ultrasonic bath may be required. A large fraction of the white residue is cholesterol, constituting approximately 50 per cent m/m of the unsaponifiable matter of cod-liver oil.
Test solution (b): Prepare duplicates. To 4.00 g add 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and proceed as described for test solution (a).
Reference solution (a): Dissolve 0.50 mg of cholecalciferol CRS in 100.0 mL of anhydrous ethanol R.
Reference solution (b): In a round-bottomed flask, add 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) and 2.0 mL of the internal standard solution and proceed as described for test solution (a).
PURIFICATION
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: nitrile silica gel for chromatography R (10 μm).
Mobile phase: isoamyl alcohol R, hexane R (1.6:98.4 V/V).
Flow rate: 1.1 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 265 nm.
Injection: 350 μL of reference solution (b) and test solutions (a) and (b). Collect each eluate from 2 min before until 2 min after the retention time of cholecalciferol, in a ground-glass-stoppered tube containing 1 mL of a 1 g/L solution of butylhydroxytoluene R in hexane R.
Evaporate separately to dryness at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C under a gentle
current of nitrogen R. Dissolve each residue in 1.5 mL of acetonitrile R.
DETERMINATION
Column:
— size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
Mobile phase: phosphoric acid R, 96 per cent V/V solution of acetonitrile R (0.2:99.8 V/V).
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 265 nm.
Injection: 2 quantities not exceeding 200 μL of each of the 3 solutions obtained under
Purification.
System suitability:
— resolution: minimum 1.4 between the peaks due to ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
— the results obtained with the test solution (b) duplicates do not differ by more than 5 per cent.
Calculate the content of vitamin D3 in International Units per gram using the following expression, taking into account the assigned content of cholecalciferol CRS:
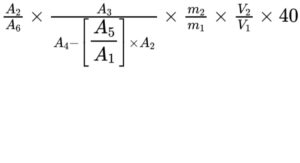
m1 = mass of the sample in test solution (b), in grams;
m2 = total mass of cholecalciferol CRS used for the preparation of reference solution (a), in micrograms (500 μg);
A1 = area (or height) of the peak due to cholecalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a);
A2 = area (or height) of the peak due to cholecalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b);
A3 = area (or height) of the peak due to ergocalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
A4 = area (or height) of the peak due to ergocalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b);
A5 = area (or height) of a possible peak in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a) with the same retention time as the peak co-eluting with ergocalciferol in test solution (b);
A6 = area (or height) of the peak due to cholecalciferol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
V1 = total volume of reference solution (a) (100 mL);
V2 = volume of reference solution (a) used for preparing reference solution (b) (2.0 mL).
STORAGE
In an airtight and well-filled container, protected from light. If no antioxidant is added, store under an inert gas.
Once the container has been opened, its contents are used as soon as possible and any part of the contents not used at once is protected by an atmosphere of inert gas.
LABELLING
The label states:
— the concentration of EPA and DHA, expressed as triglycerides;
— the number of International Units of vitamin A per gram;
— the number of International Units of vitamin D3 per gram.






