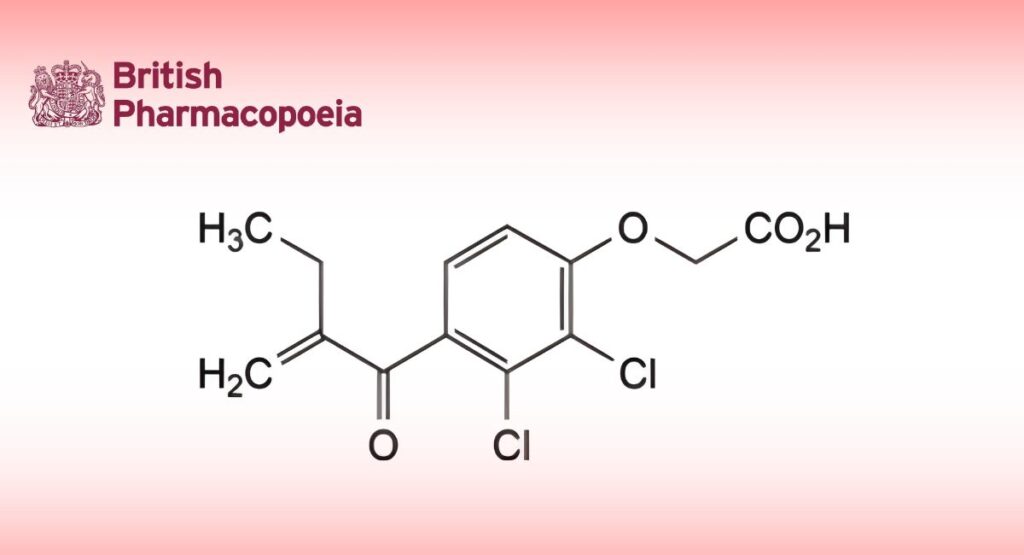
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0457)
C13H12Cl2O4 303.1 58-54-8
Action and use
Loop diuretic.
DEFINITION
[2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic acid.Content
98.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility
Very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in ammonia and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: C.
Second identification: A, B, D, E.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 121 °C to 124 °C.
B. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Solvent mixture 103 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R, methanol R (1:99 V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 50.0 mg in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Spectral range 230-350 nm.
Absorption maximum 270 nm.
Shoulder About 285 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum 110 to 120.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison etacrynic acid CRS.
D. Dissolve about 30 mg in 2 mL of aldehyde-free alcohol R. Dissolve 70 mg of hydroxylamine hydrochloride R in 0.1 mL of water R, add 7 mL of alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 10 mL with aldehyde-free alcohol R. Allow to stand and add 1 mL of the supernatant to the solution of the substance to be examined. Heat the mixture on a water-bath for 3 min. After cooling, add 3 mL of water R and 0.15 mL of hydrochloric acid R. Examined in ultraviolet light at 254 nm, the mixture shows an intense blue fluorescence.
E. Dissolve about 25 mg in 2 mL of a 42 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and heat in a water-bath for 5 min. Cool and add 0.25 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of sulfuric acid R and water R. Add 0.5 mL of a 100 g/L solution of chromotropic acid, sodium salt R and, carefully, 2 mL of sulfuric acid R. An intense violet colour is produced.
TESTS
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture acetonitrile R, water R (40:60 V/V).
Test solution: Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 25.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (a): Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution (b): Dissolve 5 mg of etacrynic acid for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A, B and C) in 5 mL of the solvent mixture.
Column:
— size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
— stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm);
— temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: 1 per cent V/V solution of triethylamine R adjusted to pH 6.8 with phosphoric acid R;
— mobile phase B: acetonitrile R;
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 2.5 | 70 | 30 |
| 2.5 – 3 | 70 → 65 | 30 → 35 |
| 3 – 6 | 65 | 35 |
| 6 – 7 | 65 → 45 | 35 → 55 |
| 7 – 22 | 45 | 55 |
Flow rate 0.8 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection 10 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with etacrynic acid for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to etacrynic acid (retention time = about 9 min): impurity A = about 0.8;
impurity B = about 1.3; impurity C = about 1.7.
System suitability: Reference solution (b):
— resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to impurity A and etacrynic acid.
Limits:
— correction factors: for the calculation of contents, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.6; impurity B = 0.6; impurity C = 1.3;
— impurity C: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
— impurities A, B: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
— total: not more than 8 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.8 per cent);
— disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 2.000 g by drying in vacuo at 60 °C.
Sulfated ash (2.4.14)
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.250 g in 100 mL of methanol R and add 5 mL of water R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 30.31 mg of C13H12Cl2O4.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
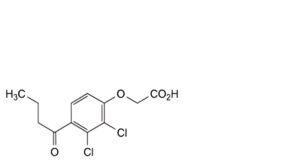
A. (4-butanoyl-2,3-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid,
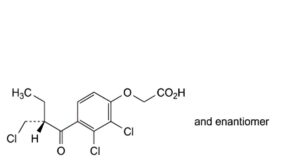
B. [2,3-dichloro-4-[2-(chloromethyl)butanoyl]phenoxy]acetic acid,
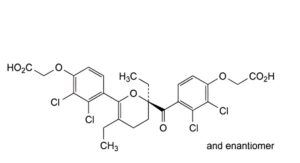
C. [4-[2-[4-(carboxymethoxy)-2,3-dichlorobenzoyl]-2,5-diethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-6-yl]-2,3-dichlorophenoxy]acetic acid.