Edition: BP 2025 (Ph. Eur. 11.6 update)
Action and use
Proton pump inhibitor; treatment of peptic ulcer disease.
DEFINITION
Esomeprazole for Injection is a sterile material consisting of Esomeprazole Sodium with or without excipients. It is supplied in a sealed container.
The contents of the sealed container comply with the requirements for Powders for Injections or Infusions stated under
Parenteral Preparations and with the following requirements.
Content of esomeprazole, C17H19N3O3S
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
IDENTIFICATION
A. The powder for injection complies with the test for Esomeprazole Impurity B.
B. In the test for Esomeprazole Impurity B, the UV spectrum, in the range 210 nm to 400 nm, of the principal peak obtained with solution (1) is similar to that of the peak to esomeprazole in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3).
TESTS
Alkalinity
pH of a solution containing the equivalent of 0.8% w/v of esomeprazole in 0.9% w/v of sodium chloride in water for injections, 9.0 to 11.0, Appendix V L.
Esomeprazole impurity B (enantiomeric purity)
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
Solution A Dilute a mixture of 11 volumes of 0.25M trisodium orthophosphate and 22 volumes of 0.5M disodium hydrogen orthophosphate to 100 volumes with water. Adjust to pH 11.0 with orthophosphoric acid or 10M sodium hydroxide.
(1) Disperse a quantity of the powder containing the equivalent of 40 mg of esomeprazole in 5 mL of methanol, dilute to 50 mL with solution A and filter (a 0.45-μm nylon filter is suitable). Further dilute 1 volume to 200 volumes with solution A.
(2) 0.0004% w/v of omeprazole BPCRS in solution A.
(3) 0.0008% w/v of omeprazole BPCRS in solution A.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.0 mm) packed with α1 -acid-glycoprotein silica gel for chiral separation (5 μm) (Chiralpak AGP is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 0.6 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 302 nm.
(f) Use a diode array detector (for identification A).
(g) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
13 volumes of acetonitrile and 87 volumes of a solution containing 0.0025M disodium hydrogen orthophosphate and 0.005 M sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the relative retention with reference to esomeprazole (retention time about 5 minutes) is: (R)-omeprazole (impurity B), about 0.7.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2), the resolution between the peaks due to (R)- omeprazole and esomeprazole is at least 3.0.
LIMITS
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the peak of any area due to impurity B is not greater than 0.2% by normalisation.
disregard any peak with an area less than 0.1% of that of the area of the peak due to esomeprazole.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions prepared in solution B. Solutions (1) and (4) should be freshly prepared and injected within 15 minutes.
Solution B 0.068% w/v of trisodium orthophosphate and 0.062% w/v disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate in water.
(1) Disperse a quantity of the powder containing the equivalent of 0.2 g of esomeprazole in 100 mL and dilute to 1 volume to 20 volumes.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 200 volumes.
(3) 0.0005% w/v each of omeprazole BPCRS and omeprazole impurity D EPCRS.
(4) 0.01% w/v of omeprazole impurity standard BPCRS.
(5) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 5 volumes.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (3 μm) (MicroSpher C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 280 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Solution C 0.017% w/v of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate monohydrate and 0.053% w/v of disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate, adjusted to pH 7.4.
50 volumes of 0.02M tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate, 260 volumes of acetonitrile and 690 volumes of solution C.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between omeprazole and impurity D and is at least 3.0.
CALCULATION OF IMPURITIES
For each impurity, use the concentration of omeprazole in solution (2).
For the reporting threshold, use the concentration of omeprazole in solution (5).
For peak identification, use solutions (3) and (4).
Omeprazole retention time: about 7 minutes.
Relative retention: impurity 5, about 0.25; impurity 3, about 0.3; impurity A, about 0.35; impurity E, about 0.45; impurity D; about 1.25; impurity 2, about 1.45.
LIMITS
— impurity 5: not more than 1.3%;
— impurity 2: not more than 0.9%;
— impurity D: not more than 0.5%;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.2%;
— total impurities: not more than 2.6%;
— reporting threshold: 0.1%.
ASSAY
Determine the weight of the contents of 10 containers as described in the test for uniformity of weight, Appendix XII C1, Powders for Parenteral Administration.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
Solution A Dilute a mixture of 11 volumes of 0.25M trisodium orthophosphate and 22 volumes of 0.5M disodium hydrogen orthophosphate to 100 volumes with water. Adjust to pH 11.0 with orthophosphoric acid or 10M sodium hydroxide.
(1) Disperse a quantity of the mixed contents of 10 containers containing the equivalent of 20 mg of esomeprazole with 20 mL of ethanol, dilute to 100 mL with solution A and filter (a 0.45-μm glass fibre filter is suitable). Dilute 1 volume to 5 volumes with water.
(2) 0.02% w/v of omeprazole BPCRS in a mixture of 1 volume of ethanol and 4 volumes of solution A. Dilute 1 volume to 5 volumes with water.
(3) 0.1% w/v of omeprazole BPCRS and 0.0005% w/v omeprazole impurity D EPCRS, each prepared by dissolving the reference material in 1 volume of ethanol and diluting to 5 volumes with solution A. Mix 1 volume of each solution and dilute to 10 volumes with water.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC CONDITIONS
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped extra-dense bonded octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 μm) (Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 302 nm.
(f) Inject 20 μL of each solution.
MOBILE PHASE
Solution D Dilute a mixture of 10.5 volumes of 1M sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate monohydrate and 60 volumes of 0.5M disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate to 100 volumes with water. Adjust to pH 7.3 with orthophosphoric acid or 10M sodium hydroxide.
35 volumes of acetonitrile, 50 volumes of solution D and dilute to 100 volumes with water.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the retention time of esomeprazole is about 5 minutes.
SYSTEM SUITABILITY
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity D and omeprazole is greater than 5.0.
DETERMINATION OF CONTENT
Calculate the content of C17H19N3O3S in a container of average content weight from the chromatograms obtained and from the declared content of C17H19N3O3S in omeprazole BPCRS.
LABELLING
The label of the sealed container states the quantity of Esomeprazole Sodium contained in it in terms of the equivalent amount of esomeprazole.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include impurities A and C to G listed under Esomeprazole Sodium and:
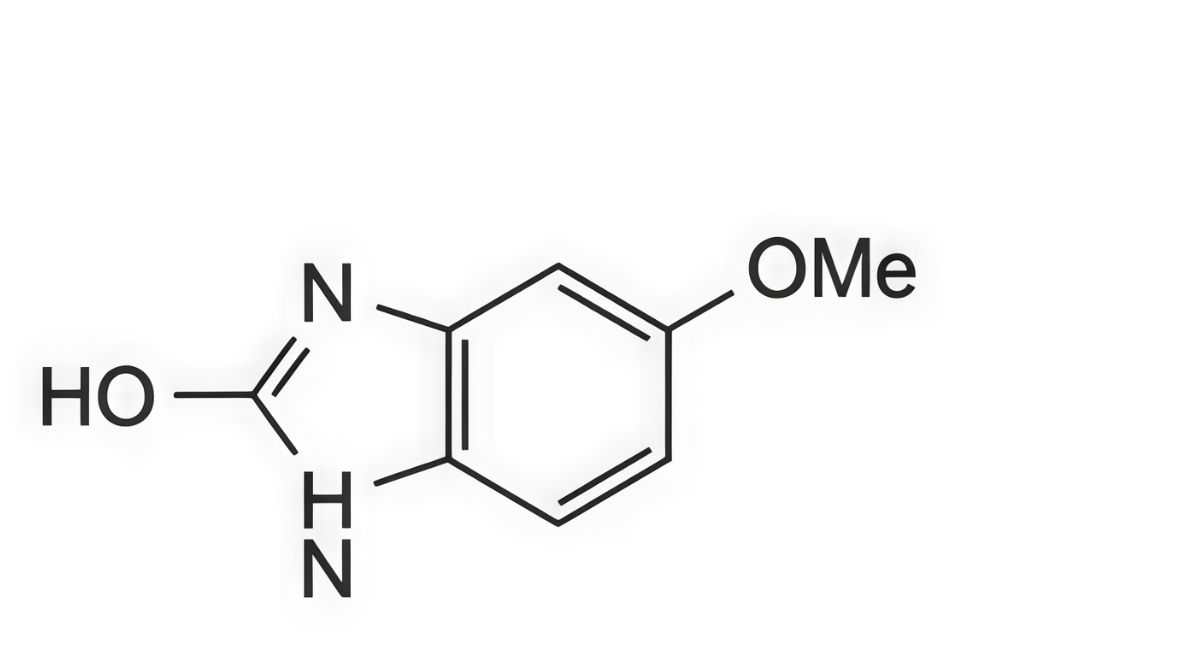
1. 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzimidazole (5-methoxy-2-benzimidazolinone),
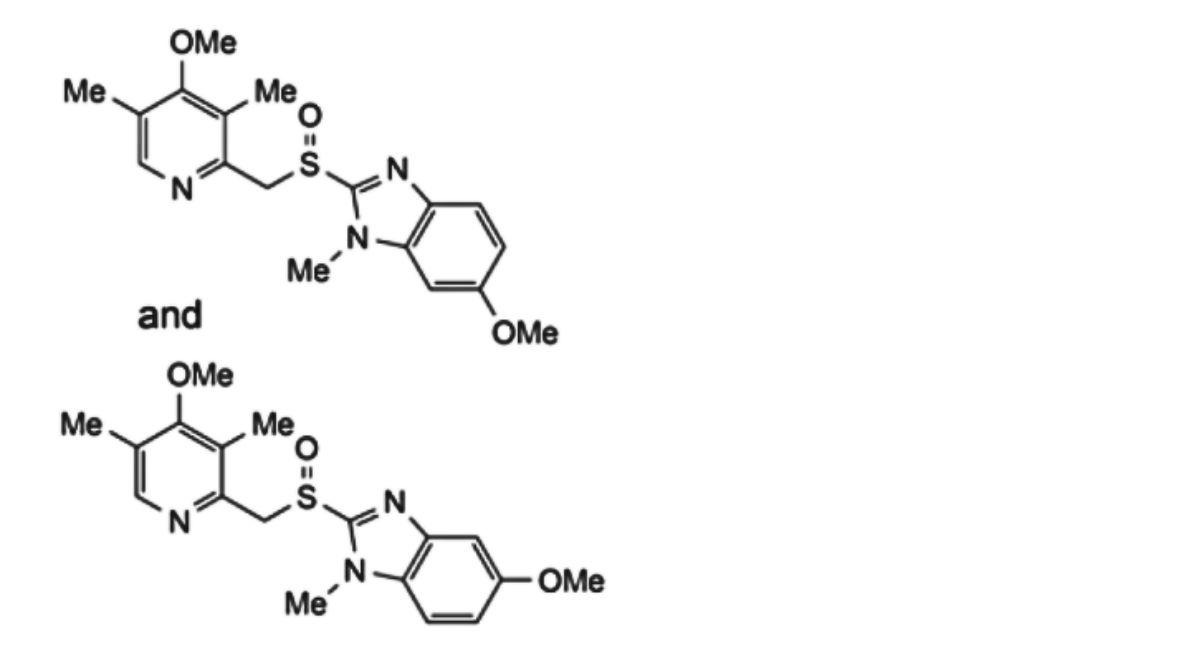
2. 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)-methyl]sulfinyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole and 6-methoxy-2-[[(4- methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)-methyl]sulfinyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole, regioisomers
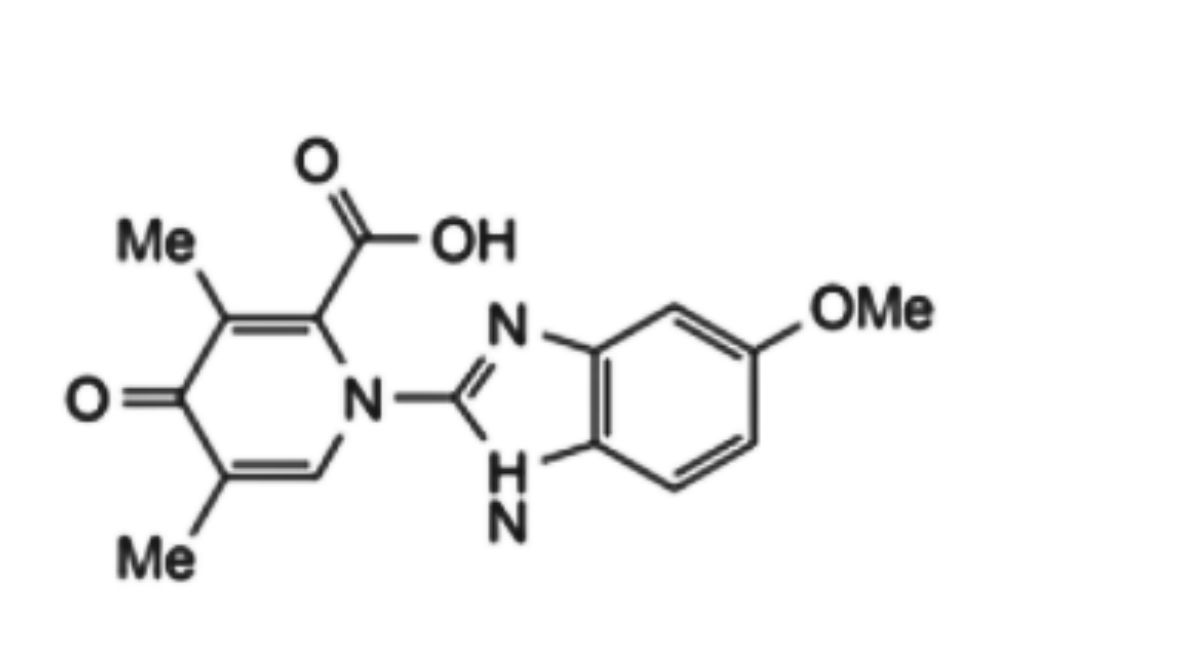
3. 1,4-dihydro-1-(5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid
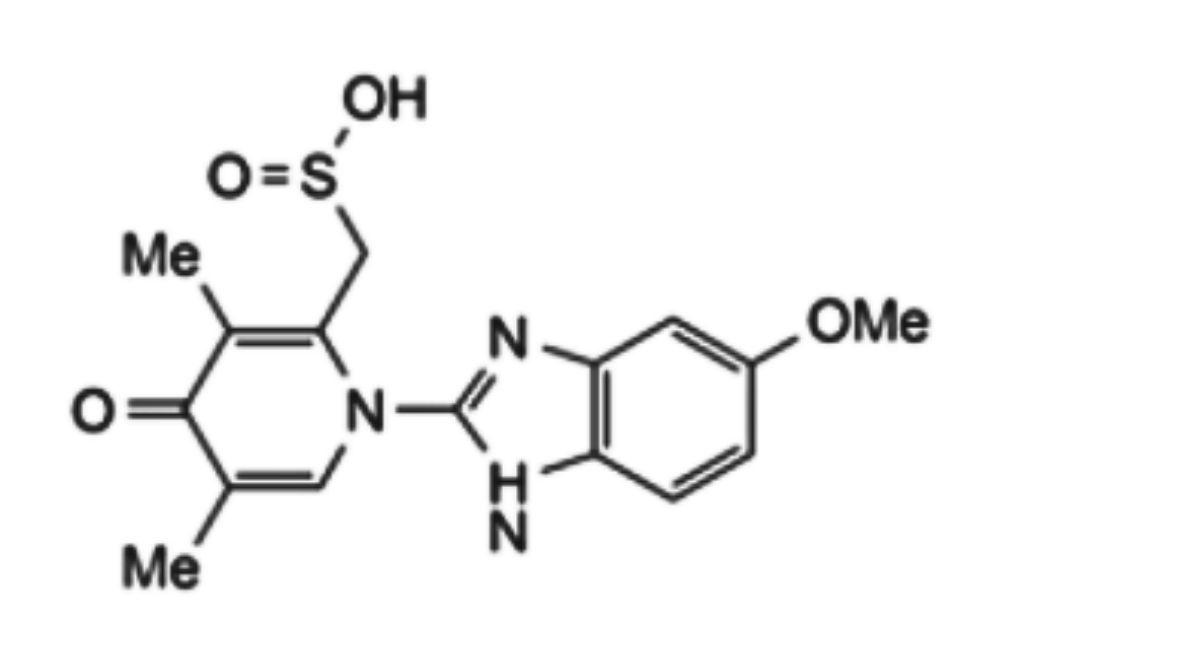
4. [1-(5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridin-2-yl] methanesulfinic acid
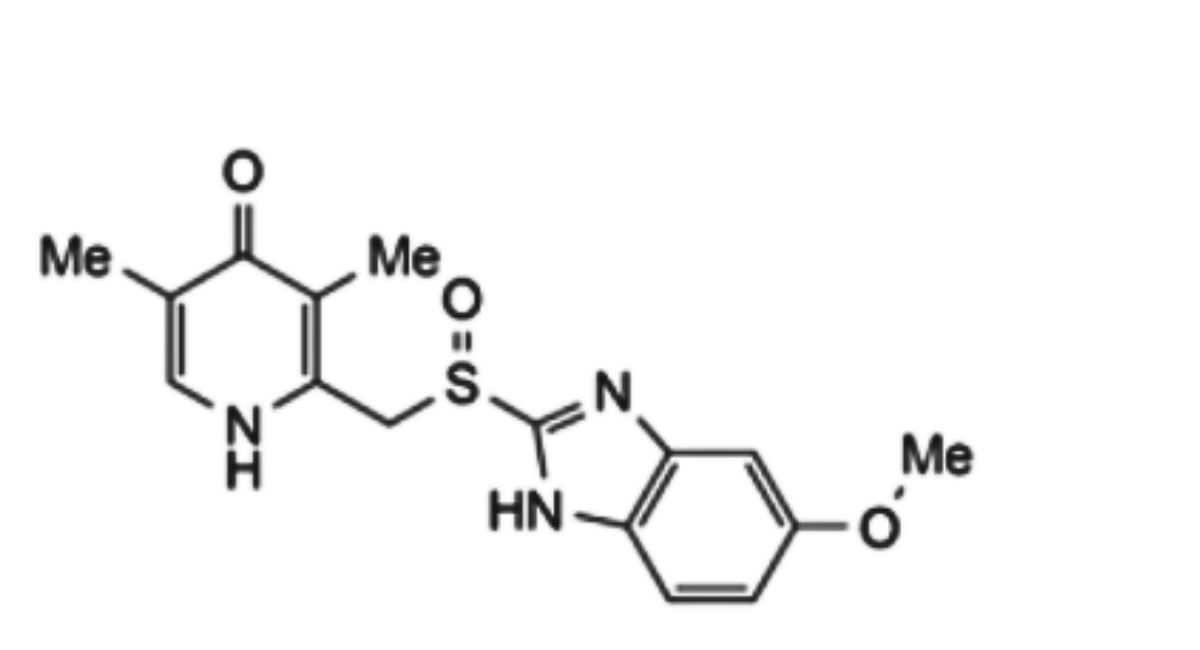
5. 2{[(5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfinyl]methyl}-3,5-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone






