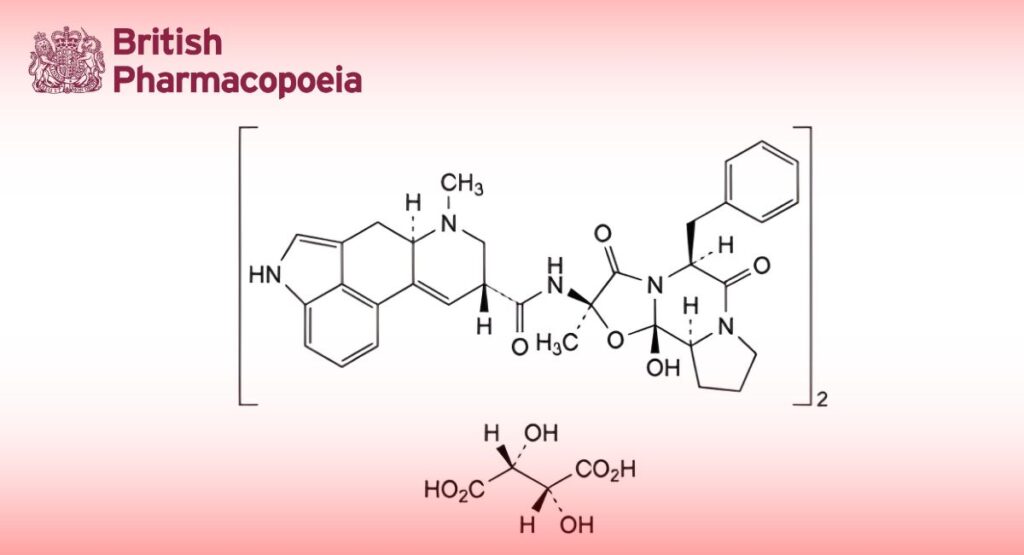
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0224)
C70H76N10O16 1313 379-79-3
Action and use
Oxytocic.
DEFINITION
Bis[(6aR,9R)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide] (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate.
Content
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
It may contain two molecules of methanol of crystallisation.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, slightly hygroscopic.
Solubility
Slightly soluble in ethanol 96 per cent. Aqueous solutions slowly become cloudy owing to hydrolysis; this may be prevented by the addition of tartaric acid.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: A.
Second identification: B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison: ergotamine tartrate CRS.
Preparation: As discs, triturate the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately with 0.2 mL of methanol R and then with potassium bromide R as prescribed in the general method.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution: Dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined in a mixture of 1 volume of methanol R and 9 volumes of methylene chloride R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution: Dissolve 5 mg of ergotamine tartrate CRS in a mixture of 1 volume of methanol R and 9 volumes of methylene chloride R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Plate: TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase: anhydrous ethanol R, methylene chloride R, dimethylformamide R, ether R (5:10:15:70 V/V/V/V).
Application: 5 μL; immediately expose the points of application to ammonia vapour for exactly 20 s by moving the line of application from side to side above a beaker 55 mm high and 45 mm in diameter containing about 20 mL of concentrated ammonia R; dry the line of application in a current of cold air for exactly 20 s.
Development: Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying: In a current of cold air for about 2 min.
Detection A: Examine for not more than 1 min in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results A: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and fluorescence to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
Detection B: Spray the plate abundantly with dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution R7 and dry in a current of warm air for about 2 min; examine in daylight.
Results B: The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
C. To 0.1 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 1 mL of glacial acetic acid R, 0.05 mL of ferric chloride solution R1 and 1 mL of phosphoric acid R and heat in a water-bath at 80 °C. After about 10 min, a blue or violet colour develops which becomes more intense on standing.
D. Dissolve about 10 mg in 1.0 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Transfer to a separating funnel and shake with 5 mL of methylene chloride R. Discard the organic layer. Neutralise the aqueous layer with a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid R. 0.1 mL of this solution gives reaction (b) of tartrates (2.3.1). Pour the reaction mixture into 1 mL of water R to observe the colour change to red or brownish-red.
TESTS
Carry out all operations as rapidly as possible, protected from light.
Solution S
Triturate 50 mg finely with about 25 mg of tartaric acid R and dissolve with shaking in 10 mL of water R.
pH (2.2.3)
4.0 to 5.5 for the suspension.
Shake 25 mg, finely powdered, with 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R.
Related substances
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29): use the normalisation procedure. Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture: water R, acetonitrile R (10:90 V/V).
Solution A: Dissolve 1.0 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 2.0 g of sodium 1-propanesulfonate R in 900 mL of water R, adjust to pH 4.3 with dilute phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water for chromatography R.
Test solution: Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solution: Dissolve 3 mg of ergotamine for system suitability CRS (containing impurities A and C) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 5 mL with the solvent mixture. In order to prepare impurity B in situ, maintain the solution at room temperature for 1 h.
Column:
— size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
— stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (1.8 μm);
— temperature: 15 °C.
Mobile phase:
— mobile phase A: acetonitrile for chromatography R, solution A (10:90 V/V);
— mobile phase B: solution A, acetonitrile for chromatography R (20:80 V/V);
| Time (min) |
Mobile phase A (per cent V/V) |
Mobile phase B (per cent V/V) |
| 0 – 7 | 80 → 50 | 20 → 50 |
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min.
Detection: Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Autosampler: Set at 4 °C.
Injection: 1 μL.
Identification of impurities: Use the chromatogram supplied with ergotamine for system suitability CRS and the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention: With reference to ergotamine (retention time = about 3 min): impurity A = about 0.9; impurity B = about 1.1; impurity C = about 1.2.
System suitability: Reference solution:
— resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity A and ergotamine.
Limits:
— correction factor: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak area of impurity C by 1.3;
— impurity C: maximum 0.4 per cent;
— impurities A, B: for each impurity, maximum 0.2 per cent;
— unspecified impurities: for each impurity, maximum 0.10 per cent;
— total: maximum 0.6 per cent;
— reporting threshold: 0.05 per cent.
Loss on drying (2.2.32)
Maximum 6.0 per cent, determined on 0.100 g by drying in vacuo at 95 °C for 6 h.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.200 g in 40 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.05 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.05 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 32.84 mg of C70H76N10O16.
STORAGE
In an airtight container, protected from light, at a temperature of 2 °C to 8 °C.
IMPURITIES
Specified impurities A, B, C.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use) D.
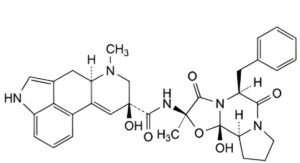
A. (6aR,9S)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-9-hydroxy-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (8-
hydroxyergotamine),
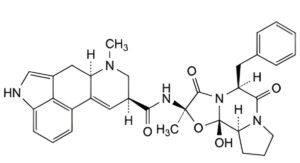
B. (6aR,9S)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (ergotaminine),
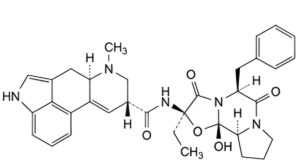
C. (6aR,9R)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-2-ethyl-10b-hydroxy-3,6-dioxooctahydro-8H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrrolo[2,1- c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (ergostine),
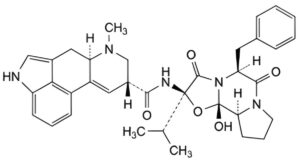
D. (6aR,9R)-N-[(2R,5S,10aS,10bS)-5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-3,6-dioxo-2-(propan-2-yl)octahydro-8H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2- a]pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl]-7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (ergocristine).